- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
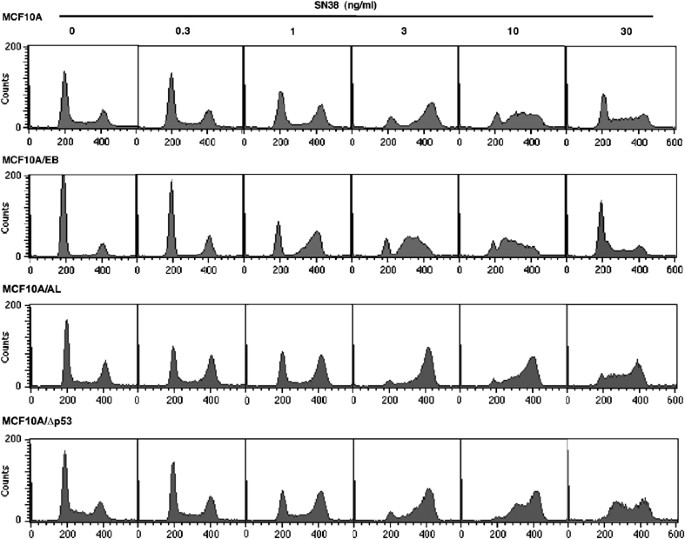
ABSTRACT The topoisomerase I inhibitor SN38 arrests cell cycle progression primarily in S or G2 phases of the cell cycle in a p53-independent manner. The Chk1 inhibitor,
7-hydroxystaurosporine (UCN-01), overcomes both S and G2 arrest preferentially in cells mutated for p53, driving cells through a lethal mitosis and thereby enhancing cytotoxicity. The
mechanism by which p53 maintains S and G2 arrest was investigated here. The p53 wild-type MCF10A cells were arrested in S phase by incubation with SN38 for 24 h. Subsequent incubation with
UCN-01 failed to abrogate arrest. To examine the impact of p53, MCF10A cells were developed, which express the tetramerization domain of p53 to inhibit endogenous p53 function. These cells
were attenuated in SN38-mediated induction of p21WAF1 and UCN-01 induced S, but not G2 progression. In contrast, MCF10A cells expressing short hairpin RNA to ablate p53 expression underwent
both S and G2 phase progression with UCN-01. The difference in G2 progression was attributed to p53-mediated gene repression; the MCF10A cells expressing the tetramerization domain retained
p53 protein and repressed both cyclin B and Chk1, while cells ablated for p53 did not repress these proteins. Hence, inhibition of p53 activator function permits S phase abrogation, while
additional inhibition of p53 repressor function is required for abrogation of G2 arrest. These studies provide a mechanistic explanation for how this therapeutic strategy can selectively
target tumor cells. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution
Subscribe to this journal Receive 50 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $5.18 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full
article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs *
Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS THE ANTI-TUMOR EFFECT OF TRIFLURIDINE VIA INDUCTION OF ABERRANT MITOSIS IS UNAFFECTED BY MUTATIONS MODULATING P53 ACTIVITY
Article Open access 02 July 2024 DUAL ROLE OF P21 IN REGULATING APOPTOSIS AND MITOTIC INTEGRITY IN RESPONSE TO DOXORUBICIN IN COLON CANCER CELLS Article Open access 02 April 2025
PHARMACOLOGICAL INHIBITION OF CRYPTOCHROME AND REV-ERB PROMOTES DNA REPAIR AND CELL CYCLE ARREST IN CISPLATIN-TREATED HUMAN CELLS Article Open access 09 September 2021 REFERENCES * Banin S,
Moyal L, Shieh S, Taya Y, Anderson CW, Chessa L, Smorodinsky NI, Prives C, Reiss Y, Shiloh Y and Ziv Y . (1998). Science, 281, 1674–1677. * Bunch RT and Eastman A . (1996). Clin. Cancer
Res., 2, 791–797. * Canman CE, Lim D-S, Cimprich KA, Taya Y, Tamai K, Sakaguchi K, Appella E, Kastan MB and Siliciano JD . (1998). Science, 281, 1677–1679. * Curtin JC, Dragnev KH, Sekula D,
Christie AJ, Dmitrovsky E and Spinella MJ . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 2559–2569. * Damia G, Sanchez Y, Erba E and Broggini M . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 10641–10645. * Demarcq C, Bunch RT,
Creswell D and Eastman A . (1994). Cell Growth Differ., 5, 983–993. * Falck J, Mailand N, Syljuasen RG, Bartek J and Lukas J . (2001). Nature, 410, 842–847. * Fan S, Smith ML, Rivet DJ, Duba
D, Zhan Q, Kohn KW, Fornace AJ and O'Connor PM . (1995). Cancer Res., 55, 1649–1654. * Flatt PM, Tang LJ, Scatena CD, Szak ST and Pietenpol JA . (2000). Mol. Cell. Biol., 20,
4210–4223. * Gorczyca W, Sarode V, Juan G, Melamed MR and Darzynkiewicz Z . (1997). Mod. Pathol., 10, 457–462. * Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A and Oren M . (1997). Nature, 387, 296–299. *
Hengstschlager M, Braun K, Soucek T, Miloloza A and Hengstschlager-Ottnad E . (1999). Mutat. Res., 436, 1–9. * Hirao A, Kong Y-Y, Matsuoka S, Wakeham A, Ruland J, Yoshida H, Liu D, Elledge
SJ and Mak TW . (2000). Science, 287, 1824–1827. * Hirose Y, Berger MS and Pieper RO . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 5843–5849. * Ho J and Benchimol S . (2003). Cell Death Differ., 10, 404–408. *
Husain A, Yan X-J, Rosales N, Aghajanian C, Schwartz GK and Spriggs DR . (1997). Clin. Cancer Res., 3, 2089–2097. * Johnson RA, Ince TA and Scotto KW . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276,
27716–27720. * Kitaura H, Shinshi M, Uchikoshi Y, Ono T, Tsurimoto T, Yoshikawa H, Iguchi-ariga SMM and Ariga H . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 10477–10483. * Kohn EA, Ruth ND, Brown MK,
Livingstone M and Eastman A . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 26553–26564. * Kohn EA, Yoo CJ and Eastman A . (2003). Cancer Res., 63, 31–35. * Kubbutat MH, Jones SN and Vousden KH . (1997).
Nature, 387, 299–303. * Lau CC and Pardee AB . (1982). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 79, 2942–2946. * Mailand N, Falck J, Lukas C, Syljuasen RG, Welcher M, Bartek J and Lukas J . (2000).
Science, 288, 1425–1429. * Manni I, Mazzaro G, Gurtner A, Mantovani R, Haugwitz U, Krause K, Engeland K, Sacchi A, Soddu S and Piaggio G . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 5570–5576. * Matsuoka
S, Huang M and Elledge SJ . (1998). Science, 282, 1893–1897. * Matsuoka S, Rotman G, Ogawa A, Shiloh Y, Tamai K and Elledge SJ . (2000). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 97, 10389–10394. *
Ossovskaya VS, Mazo IA, Chernov MV, Strezoska Z, Kondratov R, Stark GR, Chumakov PM and Gudkov AV . (1996). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 93, 10309–10314. * Park M, Chae H-D, Yun J, Jung M,
Kim Y-S, Kim S-H, Han MH and Shin DY . (2000). Cancer Res., 60, 542–545. * Powell SN, DeFrank JS, Connell P, Eogan M, Preffer F, Dombkowski D, Tang W and Friend S . (1995). Cancer Res., 55,
1643–1648. * Russell KJ, Wiens LW, Demers GW, Galloway DA, Plon SE and Groudine M . (1995). Cancer Res., 55, 1639–1642. * Sagata N . (2002). Science, 298, 1905–1907. * Santoni-rugiu E, Falck
J, Mailand N, Bartek J and Lukas J . (2000). Mol. Cell. Biol., 20, 3497–3509. * Schlegel R and Pardee AB . (1986). Science, 232, 1264–1266. * Schwarz JK, Lovly CM and Piwnica-Worms H .
(2003). Mol. Cancer Res., 1, 598–609. * Shao R-G, Cao C-X, Shimizu T, O'Connor PM, Kohn KW and Pommier Y . (1997). Cancer Res., 57, 4029–4035. * Shieh S-Y, Ahn J, Tamai K, Taya Y and
Prives C . (2000). Genes Dev., 14, 289–300. * Vigo E, Muller H, Prosperini E, Hateboer G, Cartwright P, Moroni MC and Helin K . (1999). Mol. Cell. Biol., 19, 6379–6395. * Wang Q, Fan S,
Eastman A, Worland PJ, Sausville EA and O'Connor PM . (1996). J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 88, 956–965. * Xiong Y, Hannon GJ, Zhang H, Casso D, Kobayashi R and Beach D . (1993). Nature, 366,
701–704. * Zeng Y, Forbes KC, Wu Z, Moreno S, Piwnica-Worms H and Enoch T . (1998). Nature, 395, 507–510. * Zhao H and Piwnica-Worms H . (2001). Mol. Cell. Biol., 21, 4129–4139. * Zhao H,
Watkins JL and Piwnica-Worms H . (2002). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 99, 14795–14800. Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank Mark Livingstone, Cell Signaling, for consultation and
early access to many of the phospho-specific antibodies used. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grant CA82220 and a Cancer Center Support Grant CA23108 to the Norris
Cotton Cancer Center. AAL was supported by a National Institutes of Health training Grant T3209658. EAK was supported by a fellowship from the Susan G Komen Breast Cancer Foundation. AUTHOR
INFORMATION Author notes * 3 These two authors contributed equally to this work AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Dartmouth Medical School, Lebanon, NH,
03756, USA Aime A Levesque, Ethan A Kohn, Edward Bresnick & Alan Eastman * Norris Cotton Cancer Center, One Medical Center Drive, Rubin Building Level 6, Lebanon, NH, 03756, USA Aime A
Levesque, Ethan A Kohn, Edward Bresnick & Alan Eastman Authors * Aime A Levesque View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Ethan A Kohn View
author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Edward Bresnick View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Alan
Eastman View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Levesque,
A., Kohn, E., Bresnick, E. _et al._ Distinct roles for p53 transactivation and repression in preventing UCN-01-mediated abrogation of DNA damage-induced arrest at S and G2 cell cycle
checkpoints. _Oncogene_ 24, 3786–3796 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208451 Download citation * Received: 09 January 2004 * Revised: 10 December 2004 * Accepted: 10 December 2004 *
Published: 14 March 2005 * Issue Date: 26 May 2005 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208451 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this
content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
KEYWORDS * p53 tumor suppressor * topoisomerase I inhibitors * cell cycle checkpoints * UCN-01 * cyclin B