- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
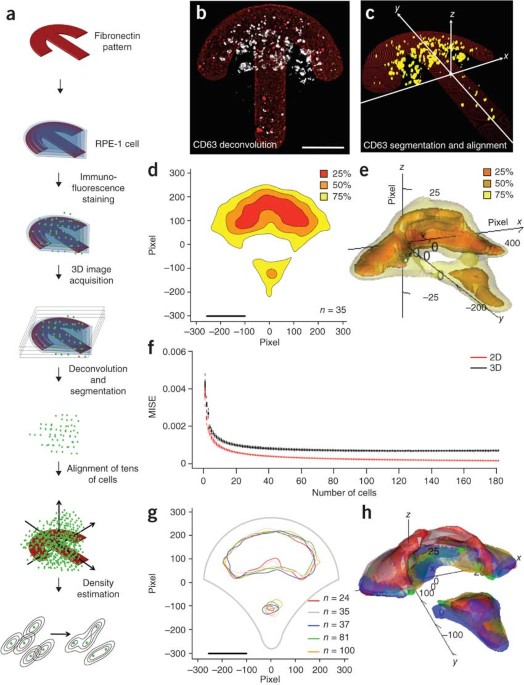
ABSTRACT We developed a computational imaging approach that describes the three-dimensional spatial organization of endomembranes from micromanipulation-normalized mammalian cells with
probabilistic density maps. Applied to several well-known marker proteins, this approach revealed the average steady-state organization of early endosomes, multivesicular bodies or
lysosomes, endoplasmic reticulum exit sites, the Golgi apparatus and Golgi-derived transport carriers in crossbow-shaped cells. The steady-state organization of each tested endomembranous
population was well-defined, unique and in some cases depended on the cellular adhesion geometry. Density maps of all endomembrane populations became stable when pooling several tens of
cells only and were reproducible in independent experiments, allowing construction of a standardized cell model. We detected subtle changes in steady-state organization induced by disruption
of the cellular cytoskeleton, with statistical significance observed for just 20 cells. Thus, combining micropatterning with construction of endomembrane density maps allows the systematic
study of intracellular trafficking determinants. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access
through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink *
Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional
subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS MEMBRANE TOPOGRAPHY AND THE OVERESTIMATION OF PROTEIN CLUSTERING IN SINGLE MOLECULE
LOCALISATION MICROSCOPY – IDENTIFICATION AND CORRECTION Article Open access 29 June 2024 NELLIE: AUTOMATED ORGANELLE SEGMENTATION, TRACKING AND HIERARCHICAL FEATURE EXTRACTION IN 2D/3D
LIVE-CELL MICROSCOPY Article Open access 27 February 2025 MAXIMUM-LIKELIHOOD MODEL FITTING FOR QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF SMLM DATA Article Open access 15 December 2022 REFERENCES * Bornens,
M. Organelle positioning and cell polarity. _Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol._ 9, 874–886 (2008). Article CAS Google Scholar * Caviston, J.P. & Holzbaur, E.L. Microtubule motors at the
intersection of trafficking and transport. _Trends Cell Biol._ 16, 530–537 (2006). Article CAS Google Scholar * Lanzetti, L. Actin in membrane trafficking. _Curr. Opin. Cell Biol._ 19,
453–458 (2007). Article CAS Google Scholar * Ross, J.L., Ali, M.Y. & Warshaw, D.M. Cargo transport: molecular motors navigate a complex cytoskeleton. _Curr. Opin. Cell Biol._ 20,
41–47 (2008). Article CAS Google Scholar * Insall, R.H. & Machesky, L.M. Actin dynamics at the leading edge: from simple machinery to complex networks. _Dev. Cell_ 17, 310–322 (2009).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Schmoranzer, J. et al. Par3 and dynein associate to regulate local microtubule dynamics and centrosome orientation during migration. _Curr. Biol._ 19,
1065–1074 (2009). Article CAS Google Scholar * Egea, G., Lazaro-Dieguez, F. & Vilella, M. Actin dynamics at the Golgi complex in mammalian cells. _Curr. Opin. Cell Biol._ 18, 168–178
(2006). Article CAS Google Scholar * Rivero, S., Cardenas, J., Bornens, M. & Rios, R.M. Microtubule nucleation at the cis-side of the Golgi apparatus requires AKAP450 and GM130. _EMBO
J._ 28, 1016–1028 (2009). Article CAS Google Scholar * Semenova, I. et al. Actin dynamics is essential for myosin-based transport of membrane organelles. _Curr. Biol._ 18, 1581–1586
(2008). Article CAS Google Scholar * Taunton, J. Actin filament nucleation by endosomes, lysosomes and secretory vesicles. _Curr. Opin. Cell Biol._ 13, 85–91 (2001). Article CAS Google
Scholar * Sachs, K., Perez, O., Pe'er, D., Lauffenburger, D.A. & Nolan, G.P. Causal protein-signaling networks derived from multiparameter single-cell data. _Science_ 308, 523–529
(2005). Article CAS Google Scholar * Sigal, A. et al. Variability and memory of protein levels in human cells. _Nature_ 444, 643–646 (2006). Article CAS Google Scholar * Snijder, B. et
al. Population context determines cell-to-cell variability in endocytosis and virus infection. _Nature_ 461, 520–523 (2009). Article CAS Google Scholar * Liu, W.F. & Chen, C.S.
Cellular and multicellular form and function. _Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev._ 59, 1319–1328 (2007). Article CAS Google Scholar * Thery, M., Pepin, A., Dressaire, E., Chen, Y. & Bornens, M.
Cell distribution of stress fibres in response to the geometry of the adhesive environment. _Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton_ 63, 341–355 (2006). Article CAS Google Scholar * Thery, M. et al.
Anisotropy of cell adhesive microenvironment governs cell internal organization and orientation of polarity. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 103, 19771–19776 (2006). Article CAS Google
Scholar * Racine, V. et al. Visualization and quantification of vesicle trafficking on a three-dimensional cytoskeleton network in living cells. _J. Microsc._ 225, 214–228 (2007). Article
Google Scholar * Bowman, A.W. & Foster, P. Density based exploration of bivariate data. _Stat. Comput._ 3, 171–177 (1993). Article Google Scholar * Hyndman, R. Computing and graphing
highest density regions. _Am. Stat._ 50, 120–126 (1996). Google Scholar * Pols, M.S. & Klumperman, J. Trafficking and function of the tetraspanin CD63. _Exp. Cell Res._ 315, 1584–1592
(2009). Article CAS Google Scholar * Chavrier, P., Parton, R.G., Hauri, H.P., Simons, K. & Zerial, M. Localization of low molecular weight GTP binding proteins to exocytic and
endocytic compartments. _Cell_ 62, 317–329 (1990). Article CAS Google Scholar * Tang, B.L. et al. The mammalian homolog of yeast Sec13p is enriched in the intermediate compartment and is
essential for protein transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus. _Mol. Cell. Biol._ 17, 256–266 (1997). Article CAS Google Scholar * Antony, C. et al. The small
GTP-binding protein rab6p is distributed from medial Golgi to the _trans_-Golgi network as determined by a confocal microscopic approach. _J. Cell Sci._ 103, 785–796 (1992). CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Grigoriev, I. et al. Rab6 regulates transport and targeting of exocytotic carriers. _Dev. Cell_ 13, 305–314 (2007). Article CAS Google Scholar * White, J. et al. Rab6
coordinates a novel Golgi to ER retrograde transport pathway in live cells. _J. Cell Biol._ 147, 743–760 (1999). Article CAS Google Scholar * Gretton, A., Borgwardt, K.M., Rasch, M.J.,
Schoelkopf, B. & Smola, A. A kernel method for the two-sample problem. _Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 19: Proceedings of the 2006 Conference_ 513–520 (MIT Press,
Cambridge, Masssachusetts, USA, 2007). * Wodarz, A. & Näthke, I. Cell polarity in development and cancer. _Nat. Cell Biol._ 9, 1016–1024 (2007). Article CAS Google Scholar * Rodriguez
Boulan, E. & Sabatini, D.D. Asymmetric budding of viruses in epithelial monlayers: a model system for study of epithelial polarity. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 75, 5071–5075 (1978).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Snider, J. et al. Intracellular actin-based transport: how far you go depends on how often you switch. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 101, 13204–13209 (2004).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Azioune, A., Storch, M., Bornens, M., Théry, M. & Piel, M. Simple and rapid process for single cell micro-patterning. _Lab Chip_ 9, 1640–1642 (2009).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Sibarita, J.B. Deconvolution microscopy. _Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol._ 95, 201–243 (2005). PubMed Google Scholar * Simonoff, J.S. _Smoothing Methods for
Statistics_. (Springer, New York, 1996). Book Google Scholar * Duong, T. & Hazelton, M.L. Plug-in bandwidth matrices for bivariate kernel density estimations. _J. Nonparametr. Stat._
17, 17–30 (2003). Article Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We acknowledge L. Sengmanivong of the Nikon Imaging Centre at Institut Curie–Centre National de la Recherche
Scientifique and V. Fraisier of the Plate-forme Imagerie Cellulaire et Tissulaire–Infrastructures en Biologie Santé et Agronomie Imaging Facility for their extensive help with microscopes
and in particular their help using the deconvolution service of the facility. We thank J.-B. Sibarita for advice on image analysis including use of the multidimensional image analysis
program and fruitful discussion during early phases of the project; I. Brito for statistical advice; W. Hong (Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology, Singapore) for providing the Sec13
antibody; M. Piel, A. Azioune and J. Fink for help with microprinting; and G. Egea, S. Miserey, A. Echard and J. Enninga for critical reading of the manuscript. K.S. received funding from
the Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale en France and Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer. This project was supported by grants from the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique
and Institut Curie. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Unité Mixte de Recherche 144, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, Institut Curie, Laboratory Molecular Mechanisms
of Intracellular Transport, Paris, France Kristine Schauer, Tarn Duong, Sabine Bardin, Michel Bornens & Bruno Goud * Institut Pasteur, Groupe Imagerie et Modélisation, Unité de
Recherche Associée 2582, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, Paris, France Tarn Duong * Mines ParisTech, Centre for Computational Biology, Institut Curie, Institut National de la
Santé Et de la Recherche Médicale U900, Paris, France Kevin Bleakley Authors * Kristine Schauer View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Tarn
Duong View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Kevin Bleakley View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google
Scholar * Sabine Bardin View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Michel Bornens View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * Bruno Goud View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS K.S. and B.G. designed the research, K.S. performed
the experiments and analysis and wrote the manuscript, T.D. developed the density calculation, K.B. developed the statistical analysis and edited the manuscript, S.B. adjusted patterning
techniques and M.B. contributed to the conception of the work. CORRESPONDING AUTHORS Correspondence to Kristine Schauer or Bruno Goud. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors
declare no competing financial interests. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY TEXT AND FIGURES Supplementary Figures 1–6, Supplementary Table 1 and Supplementary Notes 1–2 (PDF 2412 kb)
SUPPLEMENTARY VIDEO 1 Maximum intensity projection of the deconvolved fluorescence of GFP-Rab6-positive cells (_n_ = 82) under control conditions. (AVI 2507 kb) SUPPLEMENTARY VIDEO 2 Maximum
intensity projection of the deconvolved fluorescence of GFP-Rab6-positive cells (_n_ = 47) after nocodazole treatment. (AVI 1383 kb) SUPPLEMENTARY VIDEO 3 Maximum intensity projection of
the deconvolved fluorescence of GFP-Rab6-positive cells (_n_ = 50) after cytochalasin D treatment. (AVI 1667 kb) RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS
ARTICLE Schauer, K., Duong, T., Bleakley, K. _et al._ Probabilistic density maps to study global endomembrane organization. _Nat Methods_ 7, 560–566 (2010).
https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1462 Download citation * Received: 08 February 2010 * Accepted: 26 March 2010 * Published: 30 May 2010 * Issue Date: July 2010 * DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1462 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently
available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative