- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
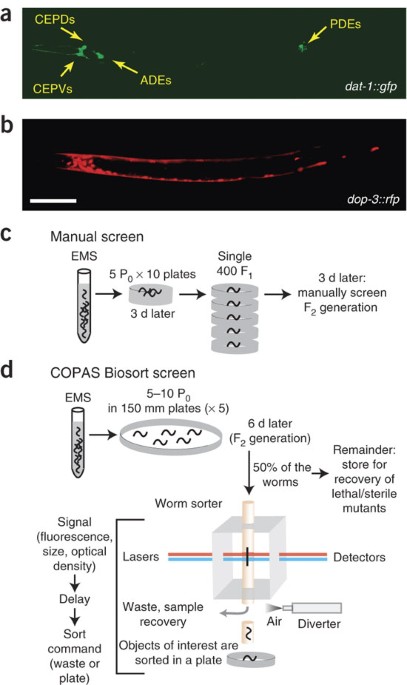
ABSTRACT We describe an automated method to isolate mutant _Caenorhabditis elegans_ that do not appropriately execute cellular differentiation programs. We used a fluorescence-activated
sorting mechanism implemented in the COPAS Biosort machine to isolate mutants with subtle alterations in the cellular specificity of GFP expression. This methodology is considerably more
efficient than comparable manual screens and enabled us to isolate mutants in which dopamine neurons do not differentiate appropriately. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This
is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $259.00
per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated
during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS SEX-SPECIFIC
DEVELOPMENTAL GENE EXPRESSION ATLAS UNVEILS DIMORPHIC GENE NETWORKS IN _C. ELEGANS_ Article Open access 20 May 2024 A FULL-BODY TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR EXPRESSION ATLAS WITH COMPLETELY RESOLVED
CELL IDENTITIES IN _C. ELEGANS_ Article Open access 09 January 2024 DISSECTING THE GENETIC LANDSCAPE OF GPCR SIGNALING THROUGH PHENOTYPIC PROFILING IN _C. ELEGANS_ Article Open access 18
December 2023 REFERENCES * Brenner, S. _Genetics_ 77, 71–94 (1974). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Jorgensen, E.M. & Mango, S.E. _Nat. Rev. Genet._ 3, 356–369 (2002).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Chalfie, M., Tu, Y., Euskirchen, G., Ward, W.W. & Prasher, D.C. _Science_ 263, 802–805 (1994). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Pulak, R.
_Methods Mol. Biol._ 351, 275–286 (2006). PubMed Google Scholar * Abeliovich, A. & Hammond, R. _Dev. Biol._ 304, 447–454 (2007). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Nass, R. et al.
_J. Neurochem._ 94, 774–785 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Nass, R., Hall, D.H., Miller, D.M., III & Blakely, R.D. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 99, 3264–3269 (2002).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Chase, D.L., Pepper, J.S. & Koelle, M.R. _Nat. Neurosci._ 7, 1096–1103 (2004). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Davis, M.W.
et al. _BMC Genomics_ 6, 118 (2005). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Zhao, C. & Emmons, S.W. _Nature_ 373, 74–78 (1995). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hack,
M.A. et al. _Nat. Neurosci._ 8, 865–872 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Guenther, C. & Garriga, G. _Development_ 122, 3509–3518 (1996). CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Chung, K., Crane, M.M. & Lu, H. _Nat. Methods_ 5, 637–643 (2008). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Boulin, T. & Bessereau, J.L. _Nat. Protoc._ 2, 1276–1287 (2007). Article
CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Sarin, S., Prabhu, S., O'Meara, M.M., Pe'er, I. & Hobert, O. _Nat. Methods_ advance online publication 1 August 2008 (doi:10.1038/nmeth.1249).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank A. Kruyer, A. Pretorian, J. Recio and Q. Chen for technical assistance, S. Sarin for
calculating the degree of saturation, V. Bertrand and F. Zhang for communicating unpublished results, and S. Mitani (Tokyo Women's Medical University School of Medicine) for providing
_lin-32_ deletion alleles. This work was funded by the US National Institutes of Health (R01NS039996-05; R01NS050266-03), the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, an European Molecular Biology
Organization long-term fellowship to M.D. and N.F., and a Marie Curie Outgoing International fellowship to N.F. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Biochemistry and
Molecular Biophysics, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Columbia University Medical Center, 701 W. 168th Street, New York, 10032, New York, USA Maria Doitsidou, Nuria Flames, Albert C Lee,
Alexander Boyanov & Oliver Hobert Authors * Maria Doitsidou View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Nuria Flames View author publications
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Albert C Lee View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Alexander Boyanov View
author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Oliver Hobert View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
CONTRIBUTIONS M.D. conducted the genetic screens (manual and sorter), implemented the sorter strategy, mapped and characterized mutants, and co-wrote the paper; N.F. implemented the sorter
strategy and conducted sorter screens; A.C.L. conducted manual screens; A.B. assisted in mapping mutants; and O.H. initiated and supervised the project, and co-wrote the paper. CORRESPONDING
AUTHORS Correspondence to Maria Doitsidou or Oliver Hobert. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY TEXT AND FIGURES Supplementary Figures 1–2, Supplementary Tables 1–6, Supplementary
Methods (PDF 3378 kb) RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Doitsidou, M., Flames, N., Lee, A. _et al._ Automated screening for mutants
affecting dopaminergic-neuron specification in _C. elegans_. _Nat Methods_ 5, 869–872 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1250 Download citation * Received: 28 April 2008 * Accepted: 29
July 2008 * Published: 31 August 2008 * Issue Date: October 2008 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1250 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read
this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative