- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
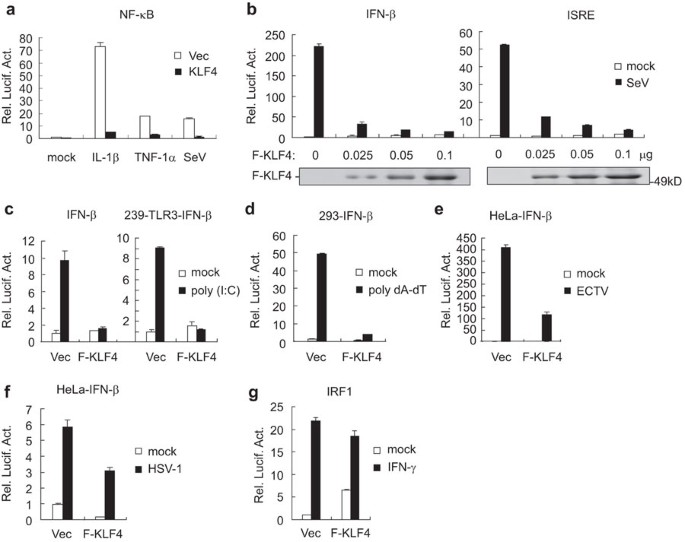
ABSTRACT Viral infection triggers activation of the transcription factors NF-κB and IRF3, which collaborate to induce the expression of type I interferons (IFNs) and elicit innate antiviral
response. In this report, we identified Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) as a negative regulator of virus-triggered signaling. Overexpression of KLF4 inhibited virus-induced activation of ISRE
and IFN-β promoter in various types of cells, while knockdown of KLF4 potentiated viral infection-triggered induction of _IFNB1_ and downstream genes and attenuated viral replication. In
addition, KLF4 was found to be localized in the cytosol and nucleus, and viral infection promoted the translocation of KLF4 from cytosol to nucleus. Upon virus infection, KLF4 was bound to
the promoter of _IFNB_ gene and inhibited the recruitment of IRF3 to the _IFNB_ promoter. Our study thus suggests that KLF4 negatively regulates cellular antiviral response. Access through
your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12
digital issues and online access to articles $119.00 per year only $9.92 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices
may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support
SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS TOB1 ATTENUATES IRF3-DIRECTED ANTIVIRAL RESPONSES BY RECRUITING HDAC8 TO SPECIFICALLY SUPPRESS IFN-Β EXPRESSION Article Open access 09 September 2022
THE INFLUENZA VIRUS PB2 PROTEIN EVADES ANTIVIRAL INNATE IMMUNITY BY INHIBITING JAK1/STAT SIGNALLING Article Open access 21 October 2022 PIM1 PROMOTES IFN-Β PRODUCTION BY INTERACTING WITH
IRF3 Article Open access 29 November 2022 REFERENCES * Hiscott J . Convergence of the NF-kappaB and IRF pathways in the regulation of the innate antiviral response. _Cytokine Growth Factor
Rev_ 2007; 18: 483–490. Article CAS Google Scholar * Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O . Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. _Cell_ 2006; 124: 783–801. CAS Google Scholar * Honda K,
Takaoka A, Taniguchi T . Type I interferon [corrected] gene induction by the interferon regulatory factor family of transcription factors. _Immunity_ 2006; 25: 349–360. Article CAS Google
Scholar * Baccala R, Gonzalez-Quintial R, Lawson BR, Stern ME, Kono DH, Beutler B _et al_. Sensors of the innate immune system: their mode of action. _Nat Rev Rheumatol_ 2009; 5: 448–456.
Article CAS Google Scholar * Beutler B, Eidenschenk C, Crozat K, Imler JL, Takeuchi O, Hoffmann JA _et al_. Genetic analysis of resistance to viral infection. _Nat Rev Immunol_ 2007; 7:
753–766. Article CAS Google Scholar * Andrejeva J, Childs KS, Young DF, Carlos TS, Stock N, Goodbourn S _et al_. The V proteins of paramyxoviruses bind the IFN-inducible RNA helicase,
mda-5, and inhibit its activation of the IFN-beta promoter. _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 2004; 101: 17264–17269. Article CAS Google Scholar * Yoneyama M, Kikuchi M, Natsukawa T, Shinobu N,
Imaizumi T, Miyagishi M _et al_. The RNA helicase RIG-I has an essential function in double-stranded RNA-induced innate antiviral responses. _Nat Immunol_ 2004; 5: 730–737. Article CAS
Google Scholar * O'Neill LA, Bowie AG . Sensing and signaling in antiviral innate immunity. _Curr Biol_ 2010; 20: R328–R333. Article CAS Google Scholar * Xu LG, Wang YY, Han KJ, Li
LY, Zhai Z, Shu HB . VISA is an adapter protein required for virus-triggered IFN-beta signaling. _Mol Cell_ 2005; 19: 727–740. Article CAS Google Scholar * Seth RB, Sun L, Ea CK, Chen ZJ
. Identification and characterization of MAVS, a mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein that activates NF-kappaB and IRF 3. _Cell_ 2005; 122: 669–682. Article CAS Google Scholar *
Meylan E,. Curran J, Hofmann K, Moradpour D, Binder M, Bartenschlager R _et al_. Cardif is an adaptor protein in the RIG-I antiviral pathway and is targeted by hepatitis C virus. _Nature_
2005; 437: 1167–1172. Article CAS Google Scholar * Kawai T, Takahashi K, Sato S, Coban C, Kumar H, Kato H _et al_. IPS-1, an adaptor triggering RIG-I- and Mda5-mediated type I interferon
induction. _Nat Immunol_ 2005; 6: 981–988. Article CAS Google Scholar * Lei CQ, Zhang Y, Li M, Jiang LQ, Zhong B, Kim YH _et al_. ECSIT bridges RIG-I-like receptors to VISA in signaling
events of innate antiviral responses. _J Innate Immun_ 2014; doi:10.1159/000365971. Article Google Scholar * Ermolaeva MA, Michallet MC, Papadopoulou N, Utermöhlen O, Kranidioti K, Kollias
G _et al_. Function of TRADD in tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 signaling and in TRIF-dependent inflammatory responses. _Nat Immunol_ 2008; 9: 1037–1046. Article CAS Google Scholar *
Zhong B, Yang Y, Li S, Wang YY, Li Y, Diao F _et al_. The adaptor protein MITA links virus-sensing receptors to IRF3 transcription factor activation. _Immunity_ 2008; 29: 538–550. Article
CAS Google Scholar * Ishikawa H, Barber GN . STING is an endoplasmic reticulum adaptor that facilitates innate immune signalling. _Nature_ 2008; 455: 674–678. Article CAS Google Scholar
* Xu LG, Jin L, Zhang BC, Akerlund LJ, Shu HB, Cambier JC . VISA is required for B cell expression of TLR7. _J Immunol_ 2012; 188: 248–258. Article CAS Google Scholar * Zhang L, Mo J,
Swanson KV, Wen H, Petrucelli A, Gregory SM _et al_. NLRC3, a member of the NLR family of proteins, is a negative regulator of innate immune signaling induced by the DNA sensor STING.
_Immunity_ 2014; 40: 329–341. Article CAS Google Scholar * Fitzgerald KA, McWhirter SM, Faia KL, Rowe DC, Latz E, Golenbock DT _et al_. IKKepsilon and TBK1 are essential components of the
IRF3 signaling pathway. _Nat Immunol_ 2003; 4: 491–496. Article CAS Google Scholar * Lei CQ, Zhong B, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Wang S, Shu HB . Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta regulates IRF3
transcription factor-mediated antiviral response via activation of the kinase TBK1. _Immunity_ 2010; 33: 878–889. Article CAS Google Scholar * Zhong B, Zhang L, Lei C, Li Y, Mao AP, Yang
Y _et al_. The ubiquitin ligase RNF5 regulates antiviral responses by mediating degradation of the adaptor protein MITA. _Immunity_ 2009; 30: 397–407. Article CAS Google Scholar * Li S,
Zheng H, Mao AP, Zhong B, Li Y, Liu Y _et al_. Regulation of virus-triggered signaling by OTUB1- and OTUB2-mediated deubiquitination of TRAF3 and TRAF6. _J Biol Chem_ 2010; 285: 4291–4297.
Article CAS Google Scholar * Zhong B, Zhang Y, Tan B, Liu TT, Wang YY, Shu HB . The E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF5 targets virus-induced signaling adaptor for ubiquitination and degradation. _J
Immunol_ 2010; 184: 6249–6255. Article CAS Google Scholar * McConnell BB, Yang VW . Mammalian Kruppel-like factors in health and diseases. _Physiol Rev_ 2010; 90: 1337–1381. Article CAS
Google Scholar * Zhang Y, Lei CQ, Hu YH, Xia T, Li M, Zhong B _et al_. Kruppel-like factor 6 is a co-activator of NF-kappaB that mediates p65-dependent transcription of selected
downstream genes. _J Biol Chem_ 2014; 289: 12876–12885. Article CAS Google Scholar * Zhang J, Hu MM, Shu HB, Li S . Death-associated protein kinase 1 is an IRF3/7-interacting protein that
is involved in the cellular antiviral immune response. _Cell Mol Immunol_ 2014; 11: 245–252. Article CAS Google Scholar * Qin Y, Zhou MT, Hu MM, Hu YH, Zhang J, Guo L _et al_. RNF26
temporally regulates virus-triggered type I interferon induction by two distinct mechanisms. _PLoS Pathog_ 2014; 10: e1004358. Article Google Scholar * Diao F, Li S, Tian Y, Zhang M, Xu
LG, Zhang Y _et al_. Negative regulation of MDA5- but not RIG-I-mediated innate antiviral signaling by the dihydroxyacetone kinase. _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 2007; 104: 11706–11711. Article
CAS Google Scholar * Wang S, Li Y, Hu YH, Song R, Gao Y, Liu HY _et al_. STUB1 is essential for T-cell activation by ubiquitinating CARMA1. _Eur J Immunol_ 2013; 43: 1034–1041. Article
CAS Google Scholar * Qin S, Zou Y, Zhang CL . Cross-talk between KLF4 and STAT3 regulates axon regeneration. _Nat Commun_ 2013; 4: 2633. Article Google Scholar Download references
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank members of our laboratory for technical help and stimulating discussions. This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China
(2012CB910201) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31130020, 31371427, 31101019 and 31221061). AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * College of Life Sciences,
Medical Research Institute, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China Wei-Wei Luo, Huan Lian, Bo Zhong, Hong-Bing Shu & Shu Li Authors * Wei-Wei Luo View author publications You can also search for
this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Huan Lian View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Bo Zhong View author publications You can also search
for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Hong-Bing Shu View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Shu Li View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Shu Li. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Luo, WW.,
Lian, H., Zhong, B. _et al._ Krüppel-like factor 4 negatively regulates cellular antiviral immune response. _Cell Mol Immunol_ 13, 65–72 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2014.125 Download
citation * Received: 31 July 2014 * Revised: 20 November 2014 * Accepted: 20 November 2014 * Published: 22 December 2014 * Issue Date: January 2016 * DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2014.125 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not
currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS * innate antiviral response * KLF4 * promoter *
translocation * type I interferons