- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
Access through your institution Buy or subscribe In 1976, the French-American-British (FAB) Cooperative Group published a morphologic classification of acute myeloid leukemia (AML).1 A
revision of this classification published in 1985 was widely used and recognized as the standard for AML classification for over 15 years.2 Included in the FAB classification were two groups
of AML that exhibited monocytic differentiation, acute myelomonocytic leukemia (AMML; M4), and acute monoblastic/monocytic leukemia (AMoL; M5). A subset of M4 with abnormal and increased
eosinophils (M4EO) was found to be associated with chromosome 16 abnormalities, either inv(16)(p13q22) or t(16;16)(p13;q22). Recognition of the biologic diversity within FAB AML subtypes led
to the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of AML, published in 2001, in which morphologic, immunophenotypic, genetic, and clinical features of AML were included in defining
disease entities.3 By WHO criteria, cases previously diagnosed as FAB M4 or M5 may be classified as AML with recurrent cytogenetic abnormalities
(inv(16)(p13q22)/t(16;16)(p13;q22)(CBF_β_/MYH11), 11q23(MLL), or t(8;21)(q22;q22)(AML1/ETO)), AML with multilineage dysplasia, therapy related AML, and AMML or AMoL subtypes of AML not
otherwise categorized (NOC). Appropriate classification of AML is important for clinical management and allows for future studies to expand and refine our understanding of these diseases.
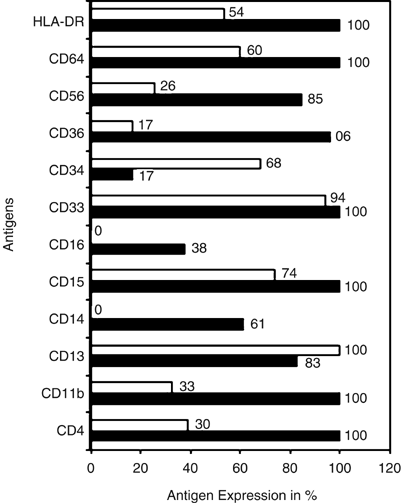
While immunophenotypic features are included in the WHO classification of AML, immunophenotypic criteria for monocytic AML have not been clearly defined. A high level of expression of CD14
is a specific feature of mature monocytes, but this antigen is frequently absent or underexpressed on immature monocytic cells. Furthermore, other antigens that are generally considered to
be monocyte-associated may be expressed in other types of AML. The goals of the present study were to identify immunophenotypic patterns that reliably characterize monocytic AMLs and to
explore their immunophenotypic heterogeneity in relationship to morphologic and cytogenetic subgroups. This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS
Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on
SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about
institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support REFERENCES * Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR _et al_. Proposals for the
classification of the acute leukaemias. French-American-British (FAB) co-operative group. _Br J Haematol_ 1976; 33: 451–458. Article CAS Google Scholar * Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel
MT, Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR _et al_. Proposed revised criteria for the classification of acute myeloid leukemia. A report of the French-American-British Cooperative Group. _Ann
Intern Med_ 1985; 103: 620–625. Article CAS Google Scholar * Brunning RD, Matutes E, Flandrin G, Vardiman J . Acute myeloid leukemia. In: Jaffe ES _et al._ (eds). _Pathology and Genetics
of Tumors of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues_. IARC press: Lyon, France, 2001, pp. 75–108. Google Scholar * Xu Y, McKenna RW, Karandikar NJ, Pildain AJ, Kroft SH . Flow cytometric
analysis of monocytes as a tool for distinguishing chronic myelomonocytic leukemia from reactive monocytosis. _Am J Clin Pathol_ 2005; 124: 799–806. Article Google Scholar * Adriaansen HJ,
te Boekhorst PA, Hagemeijer AM, van der Schoot CE, Delwel HR, van Dongen JJ . Acute myeloid leukemia M4 with bone marrow eosinophilia (M4Eo) and inv(16)(p13q22) exhibits a specific
immunophenotype with CD2 expression. _Blood_ 1993; 81: 3043–3051. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Claxton DF, Reading CL, Nagarajan L, Tsujimoto Y, Andersson BS, Estey E _et al_. Correlation
of CD2 expression with PML gene breakpoints in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia. _Blood_ 1992; 80: 582–586. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Baer MR, Stewart CC, Lawrence D, Arthur
DC, Mrozek K, Strout MP _et al_. Acute myeloid leukemia with 11q23 translocations: myelomonocytic immunophenotype by multiparameter flow cytometry. _Leukemia_ 1998; 12: 317–325. Article CAS
Google Scholar Download references AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Pathology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, USA Y Xu, R W
McKenna, K S Wilson, N J Karandikar, R A Schultz & S H Kroft Authors * Y Xu View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * R W McKenna View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * K S Wilson View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * N J Karandikar
View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * R A Schultz View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * S H
Kroft View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Y Xu. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT
THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Xu, Y., McKenna, R., Wilson, K. _et al._ Immunophenotypic identification of acute myeloid leukemia with monocytic differentiation. _Leukemia_ 20, 1321–1324
(2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404242 Download citation * Published: 27 April 2006 * Issue Date: 01 July 2006 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404242 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone
you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by
the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative