- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
The aim of the study was to examine an association between the Pro12Ala polymorphism of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-γ2 gene and blood pressure values assessed by
24-h ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) in obese patients with long-lasting type II diabetes. Two hundred and fourteen obese patients (95 men and 119 women) with above 10-year
history of type II diabetes were recruited for the study. In all the patients, ABPM was performed and other parameters, including age, body mass index (BMI), waist/hip ratio (WHR),
haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), serum lipids and creatinine were also evaluated. The Pro12Ala polymorphism was analysed by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism. Two
subgroups of patients were compared: (a) Pro/Pro: homozygotic Pro/Pro (n=154) and (b) Ala: Ala allele carriers (Ala/Ala+Ala/Pro) (n=60). The studied groups were not different when age, BMI,
WHR, HbA1c, lipids, creatinine and frequency of hypertension were compared. A similar ratio of patients from both groups were treated with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, calcium
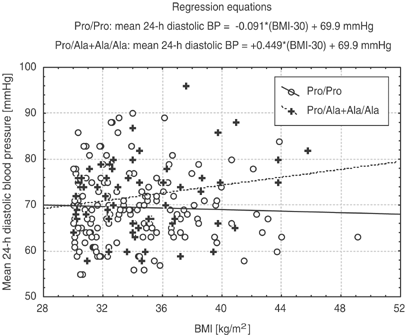
channel blockers, diuretics, β-blockers and α-blockers. A difference was observed in a mean 24-h (Ala: 71.9±8.1 vs Pro/Pro: 69.4±7.8 mm Hg, P=0.034) and a mean night time (Ala: 67.1±7.8 vs
Pro/Pro: 64.5±8.4 mm Hg, P=0.025) diastolic blood pressure, which was significantly higher in patients with Ala variant. There was also a trend towards a higher mean daytime diastolic blood
pressure in this group. It seems that the Pro12Ala variant is associated with an increased mean 24-h diastolic blood pressure in obese diabetic patients. Different reaction for
antihypertensive medication depending on a variant of the PPAR-γ2 gene should also be considered as a possible cause of the presented results.
The study was supported by Polish Scientific Research Committee – Grant no. 6P05B05020.
Department of Endocrinology, Hypertension and Metabolic Diseases, Pomeranian Medical University, Szczecin, Poland
Department of Clinical Biochemistry and Laboratory Diagnostics, Pomeranian Medical University, Szczecin, Poland
Department of Biochemistry, Pomeranian Medical University, Szczecin, Poland
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:







