- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
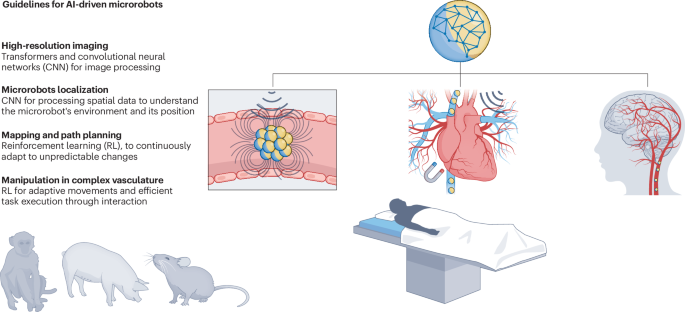
Navigating medical microrobots through intricate vascular pathways is challenging. AI-driven microrobots that leverage reinforcement learning and generative algorithms could navigate the
body’s complex vascular network to deliver precise dosages of medication directly to targeted lesions. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription
content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles $119.00 per year only
$9.92 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support REFERENCES * Yan, X. et al. Multifunctional biohybrid magnetite
microrobots for imaging-guided therapy. _Sci. Robot._ 2, eaaq1155 (2017). Article Google Scholar * Gwisai, T. et al. Magnetic torque–driven living microrobots for increased tumor
infiltration. _Sci. Robot._ 7, eabo0665 (2022). Article Google Scholar * Wrede, P. et al. Real-time 3D optoacoustic tracking of cell-sized magnetic microrobots circulating in the mouse
brain vasculature. _Sci. Adv_. 8, eabm9132 (2022). * Del Campo Fonseca, A. et al. Ultrasound trapping and navigation of microrobots in the mouse brain vasculature. _Nat. Commun._ 14, 5889
(2023). Article Google Scholar * Silver, D. et al. A general reinforcement learning algorithm that masters chess, shogi, and Go through self-play. _Science_ 362, 1140–1144 (2018). Article
MathSciNet Google Scholar * Mnih, V. et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. _Nature_ 518, 529–533 (2015). Article Google Scholar * Abbasi, S. A. et al.
Autonomous 3D positional control of a magnetic microrobot using reinforcement learning. _Nat. Mach. Intell._ 6, 92–105 (2024). Article Google Scholar * Schrage, M., Medany, M. & Ahmed,
D. Ultrasound microrobots with reinforcement learning. _Adv. Mater. Technol_. 8, 2201702. * Yang, L. et al. Autonomous environment-adaptive microrobot swarm navigation enabled by deep
learning-based real-time distribution planning. _Nat. Mach. Intell._ 4, 480–493 (2022). Article Google Scholar * Nagabandi, A., Kahn, G., Fearing, R. S. & Levine, S. Neural network
dynamics for model-based deep reinforcement learning with model-free fine-tuning. In _2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA)_ 7559–7566 (2018). * Boster, K. A.
S. et al. Artificial intelligence velocimetry reveals in vivo flow rates, pressure gradients, and shear stresses in murine perivascular flows. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci._ 120, e2217744120
(2023). Article Google Scholar * Errico, C. et al. Ultrafast ultrasound localization microscopy for deep super-resolution vascular imaging. _Nature_ 527, 499–502 (2015). Article Google
Scholar * Wang, Q. et al. Ultrasound Doppler-guided real-time navigation of a magnetic microswarm for active endovascular delivery. _Sci. Adv._ 7, eabe5914 (2021). Article Google Scholar
* Go, G. et al. Multifunctional microrobot with real-time visualization and magnetic resonance imaging for chemoembolization therapy of liver cancer. _Sci. Adv._ 8, eabq8545 (2022). Article
Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This project has received funding from the European Research Council under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation
Programme (grant agreement no. 853309, SONOBOTS); the Swiss National Science Foundation under project funding MINT 2022 (grant agreement no. 213058) and Spark 2023 (grant agreement no.
221285); and an ETH research grant (agreement no. ETH-08 20-1). AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Acoustic Robotics Systems Lab, ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland Mahmoud Medany
& Daniel Ahmed * Accelerated Discovery and AI, IBM Research Europe, Zurich, Switzerland S. Karthik Mukkavilli Authors * Mahmoud Medany View author publications You can also search for
this author inPubMed Google Scholar * S. Karthik Mukkavilli View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Daniel Ahmed View author publications You
can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Daniel Ahmed. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing
interests. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Medany, M., Mukkavilli, S.K. & Ahmed, D. AI-driven autonomous microrobots for targeted
medicine. _Nat Rev Bioeng_ 2, 914–915 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44222-024-00232-y Download citation * Published: 13 August 2024 * Issue Date: November 2024 * DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1038/s44222-024-00232-y SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not
currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative