- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
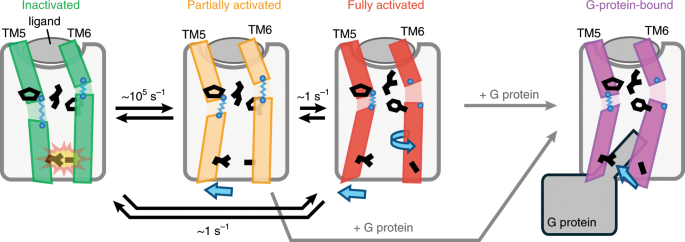
ABSTRACT G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are seven-transmembrane proteins mediating cellular signals in response to extracellular stimuli. Although three-dimensional structures showcase
snapshots that can be sampled in the process and nuclear magnetic resonance detects conformational equilibria, the mechanism by which agonist-activated GPCRs interact with various effectors
remains elusive. Here, we used paramagnetic nuclear magnetic resonance for leucine amide resonances to visualize the structure of β2-adrenoreceptor in the full agonist-bound state, without
thermostabilizing mutations abolishing its activity. The structure exhibited a unique orientation of the intracellular half of the transmembrane helix 6, forming a cluster of
G-protein-interacting residues. Furthermore, analyses of efficacy-dependent chemical shifts of the residues near the pivotal PIF microswitch identified an equilibrium among three
conformations, including one responsible for the varied signal level in each ligand-bound state. Together, these results provide a structural basis for the dynamic activation of GPCRs and
shed light on GPCR-mediated signal transduction. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access
through your institution Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription $32.99 / 30 days cancel any time Learn more Subscribe to
this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy
now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact
customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS STRUCTURES OF Β1-ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR IN COMPLEX WITH GS AND LIGANDS OF DIFFERENT EFFICACIES Article Open access 14 July 2022 BINDING
KINETICS DRIVE G PROTEIN SUBTYPE SELECTIVITY AT THE Β1-ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR Article Open access 13 February 2024 MECHANISTIC INSIGHTS INTO G-PROTEIN COUPLING WITH AN AGONIST-BOUND
G-PROTEIN-COUPLED RECEPTOR Article 12 June 2024 DATA AVAILABILITY Atomic coordinates for β2AR-Δ in the fully activated state have been deposited in the PDB under accession code 6KR8. The NMR
data and restraints used in the structure calculations have been deposited in the Biological Magnetic Resonance Data Bank under accession number 36284. The other data that support the
findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. CODE AVAILABILITY All code used in this study is available from the corresponding author upon
reasonable request. REFERENCES * Rosenbaum, D. M., Rasmussen, S. G. F. & Kobilka, B. K. The structure and function of G-protein-coupled receptors. _Nature_ 459, 356–363 (2009). CAS
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Erlandson, S. C., McMahon, C. & Kruse, A. C. Structural basis for G-protein-coupled receptor signaling. _Annu. Rev. Biophys._ 47, 1–18 (2018).
CAS Google Scholar * Flock, T. et al. Selectivity determinants of GPCR: G-protein binding. _Nature_ 545, 317–322 (2017). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Deupi, X. &
Kobilka, B. K. Energy landscapes as a tool to integrate GPCR structure, dynamics, and function. _Physiol. (Bethesda)_ 25, 293–303 (2010). CAS Google Scholar * Shimada, I., Ueda, T.,
Kofuku, Y., Eddy, M. T. & Wüthrich, K. GPCR drug discovery: integrating solution NMR data with crystal and cryo-EM structures. _Nat. Rev. Drug Discov._ 18, 59–82 (2018). PubMed PubMed
Central Google Scholar * Xiang, J. et al. Successful strategies to determine high-resolution structures of GPCRs. _Trends Pharmacol. Sci._ 37, 1055–1069 (2016). CAS PubMed Google Scholar
* Trzaskowski, B. et al. Action of molecular switches in GPCRs: theoretical and experimental studies. _Curr. Med. Chem._ 19, 1090–1109 (2012). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
* Edward Zhou, X., Melcher, K. & Eric Xu, H. Structural biology of G-protein‐coupled receptor signaling complexes. _Protein Sci._ 28, 487–501 (2019). CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Warne, T. et al. The structural basis for agonist and partial agonist action on a β(1)-adrenergic receptor. _Nature_ 469, 241–244 (2011). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar *
Lebon, G. et al. Agonist-bound adenosine A2A receptor structures reveal common features of GPCR activation. _Nature_ 474, 521–525 (2011). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar *
Egloff, P. et al. Structure of signaling-competent neurotensin receptor 1 obtained by directed evolution in Escherichia coli. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 111, E655–E662 (2014). CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Peng, Y. et al. 5-HT2C receptor structures reveal the structural basis of GPCR polypharmacology. _Cell_ 172, 719–730 (2018). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar *
Wacker, D. et al. Structural features for functional selectivity at serotonin receptors. _Science_ 340, 615–619 (2013). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * White, J. F. et al.
Structure of the agonist-bound neurotensin receptor. _Nature_ 490, 508–513 (2012). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Rasmussen, S. G. F. et al. Structure of a
nanobody-stabilized active state of the β(2) adrenoceptor. _Nature_ 469, 175–180 (2011). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Ring, A. M. et al. Adrenaline-activated structure of
β2-adrenoceptor stabilized by an engineered nanobody. _Nature_ 502, 575–579 (2013). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Rasmussen, S. G. et al. Crystal structure of the β2
adrenergic receptor-Gs protein complex. _Nature_ 477, 549–555 (2011). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Heydenreich, F. M., Vuckovic, Z., Matkovic, M. & Veprintsev, D. B.
Stabilization of G protein-coupled receptors by point mutations. _Front. Pharm._ 6, 82 (2015). Google Scholar * Kofuku, Y. et al. Efficacy of the β2-adrenergic receptor is determined by
conformational equilibrium in the transmembrane region. _Nat. Commun._ 3, 1045 (2012). PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Liu, J. J., Horst, R., Katritch, V., Stevens, R. C. &
Wüthrich, K. Biased signaling pathways in β2-adrenergic receptor characterized by 19F-NMR. _Science_ 1106, 1106–1111 (2012). Google Scholar * Solt, A. S. et al. Insight into partial agonism
by observing multiple equilibria for ligand-bound and Gs-mimetic nanobody-bound β1-adrenergic receptor. _Nat. Commun._ 8, 1795 (2017). PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Kruse, A. C.
et al. Activation and allosteric modulation of a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. _Nature_ 504, 101–106 (2013). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Manglik, A. et al.
Structural Insights into the dynamic process of β2-adrenergic receptor signaling. _Cell_ 161, 1101–1111 (2015). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Gregorio, G. G. et al.
Single-molecule analysis of ligand efficacy in β2AR-G-protein activation. _Nature_ 547, 68–73 (2017). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Wingler, L. M. et al. Angiotensin analogs
with divergent bias stabilize distinct receptor conformations. _Cell_ 176, 468–478 (2019). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Eddy, M. T. et al. Allosteric coupling of drug
binding and intracellular signaling in the A2A adenosine receptor. _Cell_ 172, 68–80 (2018). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Roth, C. B., Hanson, M. A. & Stevens, R. C. Stabilization of
the human β2-adrenergic receptor TM4–TM3–TM5 helix interface by mutagenesis of Glu1223.41, a critical residue in GPCR structure. _J. Mol. Biol._ 376, 1305–1319 (2008). CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Gossert, A. D. et al. A simple protocol for amino acid type selective isotope labeling in insect cells with improved yields and high reproducibility. _J. Biomol. NMR_ 51, 449–456
(2011). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Battiste, J. L. & Wagner, G. Utilization of site-directed spin labeling and high-resolution heteronuclear nuclear magnetic resonance for global
fold determination of large proteins with limited nuclear Overhauser effect data. _Biochemistry_ 39, 5355–5365 (2000). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Anthis, N. J. & Clore, G. M.
Visualizing transient dark states by NMR spectroscopy. _Q. Rev. Biophys._ 48, 35–116 (2015). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * King, G. J. et al. The Arabidopsis B3 domain
protein VERNALIZATION1 (VRN1) is involved in processes essential for development, with structural and mutational studies revealing its DNA-binding surface. _J. Biol. Chem._ 288, 3198–3207
(2013). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Reibarkh, M., Malia, T. J. & Wagner, G. NMR distinction of single- and multiple-mode binding of small-molecule protein ligands. _J. Am. Chem. Soc._
128, 2160–2161 (2006). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Hobbs, C. A., Bobay, B. G., Thompson, R. J., Perego, M. & Cavanagh, J. NMR solution structure and DNA-binding model
of the DNA-binding domain of competence protein A. _J. Mol. Biol._ 398, 248–263 (2010). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Takeuchi, K., Imai, M. & Shimada, I. Dynamic
equilibrium on DNA defines transcriptional regulation of a multidrug binding transcriptional repressor, LmrR. _Sci. Rep._ 7, 267 (2017). PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Minato, Y.,
Ueda, T., Machiyama, A., Iwaï, H. & Shimada, I. Dynamic domain arrangement of CheA–CheY complex regulates bacterial thermotaxis, as revealed by NMR. _Sci. Rep._ 7, 16462 (2017). PubMed
PubMed Central Google Scholar * Bain, A. D. Chemical exchange in NMR. _Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc._ 43, 63–103 (2003). CAS Google Scholar * Waudby, C. A., Ramos, A., Cabrita,
L. D. & Christodoulou, J. Two-dimensional NMR lineshape analysis. _Sci. Rep._ 6, 24826 (2016). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Hukushima, K. & Nemoto, K. Exchange
Monte Carlo method and application to spin glass simulations. _J. Phys. Soc. Jpn._ 65, 1604–1608 (1996). CAS Google Scholar * Nagata, K., Sugita, S. & Okada, M. Bayesian spectral
deconvolution with the exchange Monte Carlo method. _Neural Netw._ 28, 82–89 (2012). PubMed Google Scholar * Fernández, C. & Wider, G. TROSY in NMR studies of the structure and
function of large biological macromolecules. _Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol._ 13, 570–580 (2003). PubMed Google Scholar * Lapinaite, A. et al. The structure of the box C/D enzyme reveals
regulation of RNA methylation. _Nature_ 502, 519–523 (2013). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Gottstein, D., Reckel, S., Dötsch, V. & Güntert, P. Requirements on paramagnetic relaxation
enhancement data for membrane protein structure determination by NMR. _Structure_ 20, 1019–1027 (2012). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Isogai, S. et al. Backbone NMR reveals allosteric
signal transduction networks in the β1-adrenergic receptor. _Nature_ 314, 1–17 (2016). Google Scholar * Grzesiek, S., Cordier, F., Jaravine, V. & Barfield, M. Insights into biomolecular
hydrogen bonds from hydrogen bond scalar couplings. _Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc._ 45, 275–300 (2004). CAS Google Scholar * Zou, Y., Weis, W. I. & Kobilka, B. K. N-terminal T4
lysozyme fusion facilitates crystallization of a G protein coupled receptor. _PLoS One_ 7, e46039 (2012). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Rosenbaum, D. M. et al. GPCR
engineering yields high-resolution structural insights into 2-adrenergic receptor function. _Science_ 318, 1266–1273 (2007). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Fung, J. J. et al.
Ligand-regulated oligomerization of β(2)-adrenoceptors in a model lipid bilayer. _EMBO J._ 28, 3315–3328 (2009). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Nietlispach, D. Suppression of
anti-TROSY lines in a sensitivity enhanced gradient selection TROSY scheme. _J. Biomol. NMR_ 31, 161–166 (2005). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Helmus, J. J. & Jaroniec, C. P. NMRglue:
an open source Python package for the analysis of multidimensional NMR data. _J. Biomol. NMR_ 55, 355–367 (2013). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Sali, A. & Blundell, T.
L. Comparative protein modelling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. _J. Mol. Biol._ 234, 779–815 (1993). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Schwieters, C. D., Bermejo, G. A. & Clore, G.
M. Xplor-NIH for molecular structure determination from NMR and other data sources. _Protein Sci._ 27, 26–40 (2018). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Iwahara, J., Schwieters, C. D. &
Clore, G. M. Ensemble approach for NMR structure refinement against 1H paramagnetic relaxation enhancement data arising from a flexible paramagnetic group attached to a macromolecule. _J.
Am. Chem. Soc._ 126, 5879–5896 (2004). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * McConnell, H. M. Reaction rates by nuclear magnetic resonance. _J. Chem. Phys._ 28, 430–431 (1958). CAS Google Scholar
Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This work is supported by The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology and the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science KAKENHI
grant number JP17H06097 and by the development of innovative drug discovery technologies for middle-sized molecules from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (to I.S.).
AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan Shunsuke Imai, Tomoki Yokomizo, Yutaka Kofuku, Yutaro
Shiraishi, Takumi Ueda & Ichio Shimada Authors * Shunsuke Imai View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Tomoki Yokomizo View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Yutaka Kofuku View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Yutaro
Shiraishi View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Takumi Ueda View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google
Scholar * Ichio Shimada View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS S.I. designed the study, constructed β2AR-Δ and its variants,
purified proteins, conducted GTP turnover assays with T.Y., acquired NMR spectra, analyzed the PRE data and calculated the PRE structure and wrote the manuscript. Y.K. established the
purification protocol of β2AR at the early stage of the project and constructed the plasmid for the expression of cystathionine-γ-synthase. Y.S. prepared the virus stock for the coexpression
of the Gs heterotrimer and cultured the cells by using the virus stock. T.U. performed the exchange Monte Carlo calculation. I.S. designed the study, analyzed the data and wrote the
manuscript. CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Ichio Shimada. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing interests. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION PUBLISHER’S NOTE
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figs.
1–13 and Supplementary Table 1 REPORTING SUMMARY RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Imai, S., Yokomizo, T., Kofuku, Y. _et al._ Structural
equilibrium underlying ligand-dependent activation of β2-adrenoreceptor. _Nat Chem Biol_ 16, 430–439 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-019-0457-5 Download citation * Received: 13 July
2019 * Revised: 01 December 2019 * Accepted: 17 December 2019 * Published: 20 January 2020 * Issue Date: April 2020 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-019-0457-5 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone
you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by
the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative