- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
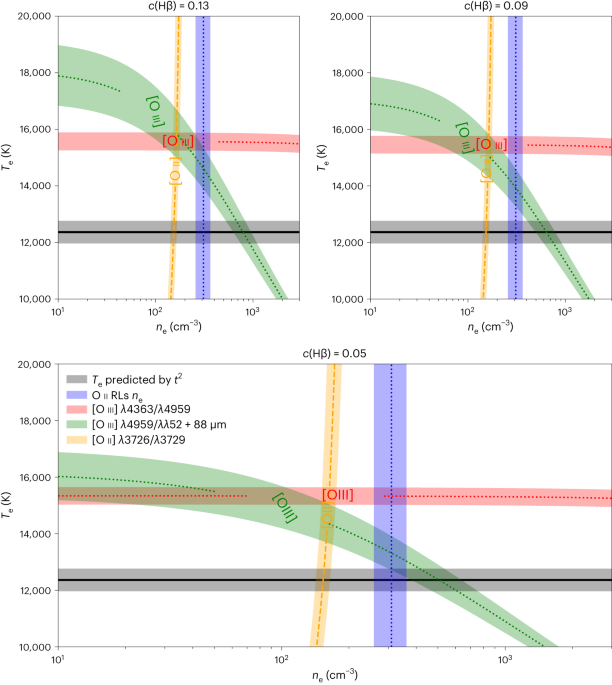
Access through your institution Buy or subscribe arising from Y. Chen et al. _Nature Astronomy_ https://doi.org/10.1038/s41550-023-01953-7 (2023) Historically, two indicators of heavy
element abundances in ionized nebulae—optical collisionally excited lines (CELs) with an exponential temperature (_T_e) dependence and recombination lines (RLs) with less _T_e
sensitivity—have produced inconsistent results. By using the less _T_e-dependent infrared (IR) [O iii] CELs, Chen et al.1 argue that the temperature inhomogeneities scenario proposed by
Peimbert2 cannot explain the abundance discrepancy in the star-forming galaxy Mrk 71. We show that this conclusion depends on several assumptions, mainly the absence of biases in electron
density (_n_e) determinations, a parameter on which IR CELs depend more than optical CELs. Since multiple _n_e indicators in previous and the discussed work on Mrk 71 show important
differences, we conclude that the existence of temperature inhomogeneities cannot be ruled out. This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access
through your institution Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription $29.99 / 30 days cancel any time Learn more Subscribe to
this journal Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles $119.00 per year only $9.92 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full
article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs *
Contact customer support DATA AVAILABILITY All the data discussed here were presented by ref. 1. CODE AVAILABILITY Our results use the PyNeb code, publicly available on GitHub:
https://github.com/Morisset/PyNeb_devel. REFERENCES * Chen, Y. et al. Accurate oxygen abundance of interstellar gas in Mrk 71 from optical and infrared spectra. _Nat. Astron._ 7, 771–778
(2023). Article ADS Google Scholar * Peimbert, M. Temperature determinations of H ii regions. _Astrophys. J._ 150, 825–834 (1967). Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Cardelli, J. A.,
Clayton, G. C. & Mathis, J. S. The relationship between infrared, optical, and ultraviolet extinction. _Astrophys. J._ 345, 245 (1989). Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Sutter, J.
& Fadda, D. [C ii] map of the molecular ring and arms of the spiral galaxy NGC 7331. _Astrophys. J._ 926, 82 (2022). Article ADS Google Scholar * Fadda, D., Jacobson, J. D. &
Appleton, P. N. Transient effects in Herschel/PACS spectroscopy. _Astron. Astrophys._ 594, A90 (2016). Article ADS Google Scholar * Luridiana, V., Morisset, C. & Shaw, R. A. PyNeb: a
new tool for analyzing emission lines. I. Code description and validation of results. _Astron. Astrophys._ 573, A42 (2015). Article ADS Google Scholar * Gonzalez-Delgado, R. M. et al.
Violent star formation in NGC 2363. _Astrophys. J._ 437, 239 (1994). Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Esteban, C., Peimbert, M., Torres-Peimbert, S. & Rodríguez, M. Optical
recombination lines of heavy elements in giant extragalactic H ii regions. _Astrophys. J._ 581, 241–257 (2002). Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Esteban, C. et al. Keck HIRES
spectroscopy of extragalactic H ii regions: C and O abundances from recombination lines. _Astrophys. J._ 700, 654–678 (2009). Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Mingozzi, M. et al. CLASSY
IV. Exploring UV diagnostics of the interstellar medium in local high-_z_ analogs at the dawn of the JWST era. _Astrophys. J._ 939, 110 (2022). Article ADS Google Scholar * García-Rojas,
J. & Esteban, C. On the abundance discrepancy problem in H ii regions. _Astrophys. J._ 670, 457–470 (2007). Article ADS Google Scholar * Peimbert, A., Peña-Guerrero, M. A. &
Peimbert, M. A classification of H ii regions based on oxygen and helium lines: the cases of TOL 2146-391 and TOL 0357-3915. _Astrophys. J._ 753, 39 (2012). Article ADS Google Scholar *
Rubin, R. H. The effect of density variations on elemental abundance ratios in gaseous nebulae. _Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser._ 69, 897 (1989). Article ADS CAS Google Scholar *
Méndez-Delgado, J. E., Esteban, C., García-Rojas, J., Kreckel, K. & Peimbert, M. Temperature inhomogeneities cause the abundance discrepancy in H ii regions. _Nature_ 618, 249–251
(2023). Article ADS PubMed Google Scholar * Méndez-Delgado, J. E. et al. Density biases and temperature relations for DESIRED H ii regions. _Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc._ 523, 2952–2973
(2023). Article ADS Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS J.E.M.-D. and K.K. gratefully acknowledge funding from the German Research Foundation in the form of an Emmy
Noether Research Group (grant no. KR4598/2-1, PI Kreckel). K.K. additionally gratefully acknowledges funding from the European Research Council’s starting grant (grant no. ERC StG-101077573,
ISM-METALS). C.E. and J.G.-R. acknowledge support from the Spanish Research Agency of the Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities (MCIU) under grant Espectroscopía de campo
integral de regiones H ii locales. Modelos para el estudio de regiones H ii extragalácticas (grant ref. 10.13039/501100011033) and support (grant no. P/308614), which is financed by the MCIU
and charged to the General State Budgets and by the General Budgets of the Autonomous Community of the Canary Islands by the MCIU. J.G.-R. acknowledges support from an advanced fellowship
under the Severo Ochoa excellence programme (ref. CEX2019-000920-S) and financial support from the Canarian Agency for Research, Innovation and Information Society of the Canary Islands
Government and from the European Regional Development Fund (grant ref. ProID2021010074). AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Astronomisches Rechen-Institut, Zentrum für Astronomie
der Universität Heidelberg, Heidelberg, Germany J. Eduardo Méndez-Delgado & Kathryn Kreckel * Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), Santa Cruz de Tenerife, Spain César Esteban
& Jorge García-Rojas * Departamento de Astrofísica, Universidad de La Laguna, Santa Cruz de Tenerife, Spain César Esteban & Jorge García-Rojas * Instituto de Astronomía, Universidad
Nacional Autónoma de México, Mexico City, Mexico Manuel Peimbert Authors * J. Eduardo Méndez-Delgado View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar *
César Esteban View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Jorge García-Rojas View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed
Google Scholar * Kathryn Kreckel View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Manuel Peimbert View author publications You can also search for this
author inPubMed Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS J.E.M.-D. led the analysis and writing of the manuscript. C.E., J.G.-R., K.K. and M.P. provided critical feedback and modified the text.
CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to J. Eduardo Méndez-Delgado. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing interests. PEER REVIEW PEER REVIEW INFORMATION
_Nature Astronomy_ thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION PUBLISHER’S NOTE Springer Nature remains neutral with regard
to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Méndez-Delgado, J.E., Esteban,
C., García-Rojas, J. _et al._ Effects of density and temperature variations on the metallicity of Mrk 71. _Nat Astron_ 8, 275–277 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41550-024-02198-8 Download
citation * Received: 19 June 2023 * Accepted: 08 January 2024 * Published: 05 February 2024 * Issue Date: March 2024 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41550-024-02198-8 SHARE THIS ARTICLE
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided
by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative