- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
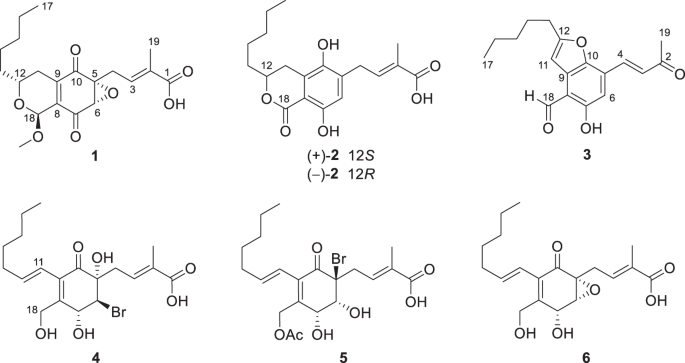
ABSTRACT New ambuic acid derivatives, pestallic acids R–V (1−5), together with ambuic acid (6), were isolated from the endophytic fungus _Pestalotiopsis trachicarpicola_ SC-J551 derived from
the fern _Blechnum orientale_ L., of which compound 2, being racemic, was separated to two optically pure enantiomers (+)-2 and (−)-2. The structures including absolute configurations of
these new compounds were elucidated by extensive spectroscopic analysis and theoretical simulations of their ECD spectra and 13C NMR chemical shifts. Compounds 1 and 3 exhibited cytotoxicity
against human carcinoma A549, HeLa, HepG2, and MCF-7 cells (IC50: 3.6–12.5 μM) and compound 3 was also active against _Staphylococcus aureus_ and MRSA (MIC = 20 μg ml−1). Compound (±)-2
showed inhibitory activity against LPS-induced NO release (IC50 = 21.1 μM) and _t_-BHP-induced ROS production (IC50 = 8.5 μM) in RAW264.7 macrophages. Access through your institution Buy or
subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online
access $259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which
are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS
ANTIBACTERIAL ANGUCYCLINONE AND Α-PYRONE DERIVATIVES FROM DESERT-DERIVED _NOCARDIOPSIS DASSONVILLEI_ HDN 154151 Article 25 April 2022 ANTIMICROBIAL POLYKETIDES FROM MAGELLAN
SEAMOUNT-DERIVED FUNGUS _TALAROMYCES SCORTEUS_ AS-242 Article 17 October 2023 DISCOVERY, TOTAL SYNTHESES AND POTENT ANTI-INFLAMMATORY ACTIVITY OF PYRROLINONE-FUSED BENZOAZEPINE ALKALOIDS
ASPERAZEPANONES A AND B FROM _ASPERGILLUS CANDIDUS_ Article Open access 06 July 2022 REFERENCES * Tan R-X, Zou W-X. Endophytes: a rich source of functional metabolites. Nat Prod Rep.
2001;18:448–59. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Gupta S, Chaturvedi P, Kulkarni MG, Van Staden J. A critical review on exploiting the pharmaceutical potential of plant endophytic
fungi. Biotechnol Adv. 2020;39:107462. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Gao H, Li G, Lou H-X. Structural diversity and biological activities of novel secondary metabolites from
endophytes. Molecules. 2018;23:646. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Deshmukh SK, Prakash V, Ranjan N. Recent advances in the discovery of bioactive metabolites from
_Pestalotiopsis_. Phytochem Rev. 2017;16:883–920. Article CAS Google Scholar * Wu C, Wang Y, Yang Y. _Pestalotiopsis_ diversity: species, dispositions, secondary metabolites, and
bioactivities. Molecules. 2022;27:8088. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Ding G, Li Y, Fu S, Liu S, Wei J, Che Y. Ambuic acid and torreyanic acid derivatives from the
endolichenic fungus _Pestalotiopsis_ sp. J Nat Prod. 2009;72:182–6. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Li J, Xie J, Yu F-X, Chen Y-H, Zhao P-J. Pestalotic acids A-I, antibacterial
ambuic acid analogues, from a mycoparasite (_Pestalotipsis_ sp. cr014) of _Cronartium ribicola_. Arch Pharm Res. 2016; https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-016-0837-2. * Li JY, Harper JK, Grant
DM, Tombe BO, Bashyal B, Hess WM, et al. Ambuic acid, a highly functionalized cyclohexenone with antifungal activity from _Pestalotiopsis_ spp. and _Monochaetia_ sp. Phytochemistry.
2001;56:463–8. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Yuan C, Ding G, Wang H-Y, Guo Y-H, Shang H, Ma X-J, et al. Polyketide-terpene hybrid metabolites from an endolichenic fungus
_Pestalotiopsis_ sp. BioMed Res Int. 2017;2017:6961928. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Zhang Q, Luan R, Li H, Liu Y, Liu P, Wang L, et al. Anti-inflammatory action of
ambuic acid, a natural product isolated from the solid culture of _Pestalotiopsis neglecta_, through blocking ERK/JNK mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med.
2018;16:1538–46. PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Li C-S, Yang B-J, Turkson J, Cao S. Anti-proliferative ambuic acid derivatives from hawaiian endophytic fungus _Pestalotiopsis_ sp.
FT172. Phytochemistry. 2017;140:77–82. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Yu X, Gao Y, Frank M, Mándi A, Kurtán T, Müller WEG, et al. Induction of ambuic acid
derivatives by the endophytic fungus _Pestalotiopsis lespedezae_ through an OSMAC approach. Tetrahedron. 2021;79:131876. Article CAS Google Scholar * Jiang Z, Wu P, Li H, Xue J, Wei X.
Pestalotinones A-D, new benzophenone antibiotics from endophytic fungus _Pestalotiopsis trachicarpicola_ SC-J551. J Antibiot. 2022;75:207–12. Article CAS Google Scholar * Friebolin H.
Basic One and Two-Dimensional NMR Spectroscopy. 5th ed. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co; 2010. Google Scholar * Cen-Pacheco F, Villa-Pulgarin JA, Mollinedo F, Norte M, Daranas AH,
Fernández JJ. Cytotoxic oxasqualenoids from the red alga _Laurencia viridis_. Eur J Med Chem. 2011;46:3302–08. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Wiberg KB, Pratt WE. Effect of halogen
substituents on NMR chemical shifts. 13C spectra of bicyclic halides. Tetrahedron Lett. 1978;49:4865–68. Article Google Scholar * Fu Y, Wu P, Xue J, Wei X. Cytotoxic and antibacterial
quinone sesquiterpenes from a _Myrothecium_ fungus. J Nat Prod. 2014;77:1791–9. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and
survival-application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983;65:55–63. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Shi J-F, Wu P, Jiang Z-H, Wei X-Y. Synthesis and
tumor cell growth inhibitory activity of biotinylated annonaceous acetogenins. Eur J Med Chem. 2014;71:219–28. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Cheng X-L, Li H-X, Chen J, Wu P, Xue
J-H, Zhou Z-Y, et al. Bioactive diarylheptanoids from _Alpinia coriandriodora_. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2021;11:63–72. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Duan F-F, Gao Y, Liu J-J, Liu L,
Peng X-G, Ruan H-L. Pseudeurglobosins A–F, six rearranged [11]-chaetoglobosins with immunosuppressive activities from _Pseudeurotium bakeri_ P1-1-1. Org Chem Front. 2021;8:7015–24. Article
CAS Google Scholar * Li X, Wu P, Li H, Xue J, Xu H, Wei X. Antibacterial and cytotoxic phenyltetracenoid polyketides from _Streptomyces morookaense_. J Nat Prod. 2021;84:1806–15. Article
CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Gao S, Wu P, Xue J, Li H, Wei X. Cytochalasans from the endophytic fungus _Diaporthe ueckerae_ associated with the fern _Pteris vittata_. Phytochemistry.
2022;202:113295. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank Mr. Yunfei Yuan, South China Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences, for NMR
spectroscopic measurements and Ms. Aijun Sun, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, for HRESIMS measurements. This work was supported by NSFC grants (Nos.
82073732 and 81872773). Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available on The Journal of Antibiotics website (http://www.nature.com/ja). Computational details, NMR spectra and HR-ESIMS
of 1‒5, and HPLC chromatograms of 1‒6 (PDF). AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Applied Botany, South China Botanical Garden, Chinese
Academy of Sciences, Xingke Road 723, Tianhe District, Guangzhou, 510650, People’s Republic of China Fanyu Dong, Zhiming Jiang, Ping Wu, Fangfang Duan, Jinghua Xue, Haibo Tan & Xiaoyi
Wei * School of Life Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Yuquanlu 19A, Beijing, 100049, People’s Republic of China Fanyu Dong & Zhiming Jiang Authors * Fanyu Dong View
author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Zhiming Jiang View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Ping Wu
View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Fangfang Duan View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar *
Jinghua Xue View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Haibo Tan View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google
Scholar * Xiaoyi Wei View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHORS Correspondence to Ping Wu or Xiaoyi Wei. ETHICS DECLARATIONS
CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors declare no competing interests. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION PUBLISHER’S NOTE Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published
maps and institutional affiliations. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds
exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely
governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law. Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Dong, F., Jiang, Z., Wu, P. _et al._ Bioactive ambuic
acid congeners from endophytic fungus _Pestalotiopsis trachicarpicola_ SC-J551. _J Antibiot_ 77, 21–29 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-023-00674-3 Download citation * Received: 02
July 2023 * Revised: 10 October 2023 * Accepted: 26 October 2023 * Published: 13 November 2023 * Issue Date: January 2024 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-023-00674-3 SHARE THIS ARTICLE
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative








