- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT Multiple myeloma (MM) represents approximately 15% of haematological malignancies and most of the patients present with bone involvement. Focal or diffuse spinal osteolysis may
result in significant morbidity by causing painful progressive vertebral compression fractures (VCFs) and deformities. Advances in the systemic treatment of myeloma have achieved high
response rates and prolonged the survival significantly. Early diagnosis and management of skeletal events contribute to improving the prognosis and quality of life of MM patients. The
management of patients with significant pain due to VCFs in the acute phase is not standardised. While some patients are successfully treated conservatively, and pain relief is achieved
within a few weeks, a large percentage has disabling pain and morbidity and hence they are considered for surgical intervention. Balloon kyphoplasty and percutaneous vertebroplasty are
minimally invasive procedures which have been shown to relieve pain and restore function. Despite increasing positive evidence for the use of these procedures, the indications, timing,
efficacy, safety and their role in the treatment algorithm of myeloma spinal disease are yet to be elucidated. This paper reports an update of the consensus statement from the International
Myeloma Working Group on the role of cement augmentation in myeloma patients with VCFs. SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS ROLE OF PERCUTANEOUS VERTEBROPLASTY WITH HIGH-VISCOSITY CEMENT
IN THE TREATMENT OF SEVERE OSTEOPOROTIC VERTEBRAL COMPRESSION FRACTURES Article Open access 25 February 2021 CEMENT AUGMENTATION FOR TREATMENT OF HIGH TO MID-THORACIC OSTEOPOROTIC
COMPRESSION FRACTURES, HIGH-VISCOSITY CEMENT PERCUTANEOUS VERTEBROPLASTY VERSUS BALLOON KYPHOPLASTY Article Open access 12 November 2022 INCIDENCE AND RISK FACTORS OF ADJACENT VERTEBRAL
FRACTURE AFTER PERCUTANEOUS VERTEBROPLASTY OR KYPHOPLASTY IN POSTMENOPAUSAL WOMEN: A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY Article Open access 03 August 2024 INTRODUCTION Multiple myeloma (MM) is a
haematologic malignancy characterised by infiltration of the bone marrow by plasma cells which can be associated with lytic bone disease causing severe bone pain, pathological fractures and
neurological compromise including cauda equina/spinal cord compression. Up to 90% of the myeloma patients develop osteolytic lesions during the course of their disease1,2,3 and 70% of
patients are affected at some stage by osteolytic/osteopenic disease of the spine4. Several skeletal events over a patient’s lifetime result in substantial morbidity, mortality5 and
increased healthcare costs. The introduction of new targeted therapeutic agents in combination with stem cell transplantation has led to a remarkable evolution in the management of myeloma
over the last 2 decades6,7. Patients with myeloma are living much longer because of improved treatment of the primary disease. Haematological medical management aims at improving the
survival of these patients and maintaining their quality of life (QoL). It is thus especially important to treat the osteolytic bone disease and vertebral compression fractures (VCFs) of the
spine in a timely manner. Historically, haematologists treated the pain associated with VCFs with radiotherapy and strong opioids. However, these treatments have their own side effects and
do not stabilise the fracture. In many cases, pain remains disabling and some patients develop progressive deformities. Some of the fractures also fail to heal and may result in significant
chronic pain. Treatment of the spine is directed towards keeping the patient pain free, ambulatory and continent. A secondary aim should be to minimise any progressive kyphotic deformity
which can lead to a poor QoL. Vertebrae that are severely compressed can lose more than 50% of their original height8. Following a spinal fracture, there is an exponential risk of a
subsequent one due to an abnormal sagittal balance that ensues and the additional compressive forces on the anterior aspect of the spine9,10,11. Moreover, the patients adopt a kyphotic
posture to minimise pain from their VCFs and to compensate for the weakness of the spinal musculature12,13,14. Patients with multiple fractures have reduced activities of daily living,
pulmonary and gastric problems and have increased morbidity and mortality11,13. The kyphotic posture significantly reduces lung function15 and pulmonary disease is the commonest cause of
death in women with VCFs11,16,17. Another major consequence of the spinal deformities is the psychological impact to these patients who often suffer from depression, anxiety and low
self-esteem, with accompanying loss of QoL18,19,20. The introduction of minimally invasive procedures such as balloon kyphoplasty (BKP) and percutaneous vertebroplasty (PV) has enabled the
vast majority of the treated patients to return to a near normal level of function within a very short period of time with excellent pain relief21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33. In
2008, a consensus statement was published by the International Myeloma Working Group (IMWG) on the role of vertebral augmentation with cement in MM34. The aim of this paper is to update the
previous recommendations by the IMWG considering new published data. OVERVIEW OF VERTEBRAL CEMENT AUGMENTATION PROCEDURES (VCPS), PV AND BKP VERSUS ALTERNATE OPTIONS AS THERAPY FOR VCFS The
PV and BKP have been extensively used in the treatment of painful osteoporotic and cancer-related VCFs. The value of these modalities in treating osteoporotic VCFs was questioned because of
the results from two prospective randomised trials that showed no benefit when compared with a sham procedure in relieving pain35,36,37,38,39,40. Kallmes et al. had a simulated surgical
procedure as control group without cement augmentation, and in the study by Buchbinder et al., the patients had a sham procedure which entailed injection of a local anaesthetic into the
periosteum over the lamina and pedicle. Some of the criticisms of these two studies, the patients most in need of cement augmentation and therefore potentially the ones with the maximum
amount of benefit, were possibly excluded from the studies on the basis that they would not allow themselves to be randomised into one of the two groups. The patients enrolled in the studies
may have had facet joint-related pain and not the severe pain that one would usually associate with an acute VCF. This may explain why the patients did not show improvement following VP. It
is recognised clinically that the severe pain due to an acute VCF subsides if the fracture starts to heal but patients can experience residual pain related to a resultant deformity. The
deformity alters the facet joint mechanics and facet-related pain can ensue. Wilson et al. reported that a third of the patients technically suitable for VP for an osteoporotic fracture,
responded beneficially to a facet joint injection alone. In this study, the percentage of the enrolled patients may had facet-related pain rather pain from the original fracture41,42.
Significant reduction in mortality and morbidity using cement augmentation with BKP or VP versus nonsurgical management was reported in retrospective analyses25,43. However, these studies
reported outcomes on osteoporotic and not on cancer patients. In the cancer population, prospective and retrospective analyses reported favourable results in the treatment of painful
metastatic cancer and myeloma-related VCF’s with PV and BKP24,29,44,45,46,47,48,49. The prospective randomised controlled trial Cancer Patient Fracture Evaluation (CAFE), provided evidence
for the superiority of BKP versus non-surgical management (NSM) of painful VCFs. 134 cancer patients were enrolled, of whom 49 had MM. Of these, 22 were randomly assigned to BKP and 27 to
NSM33. BKP was found to be significantly more favourable than NSM offering rapid and sustained pain relief at 1 year, as well as improved back function, QoL, activity, reduced use of
analgesics and bed rest days. Similarly, other studies have reported beneficial results of BKP and PV in rapid pain control, functional and QoL in MM patients with
VCFs24,29,30,31,45,48,50,51,52. Additional kyphoplasty was more effective than additional radiation or systemic therapy in terms of pain relief, reduction of pain associated disability and
of fracture incidence of the entire thoracolumbar spine44. It is very important that we do not deny treatment in MM patients that may be very effective in relieving the pain from their acute
VCF. They may require VCP (VP or BKP) to give them rapid relief of their pain and return them to function as soon as possible. The pain relief from cement augmentation has been sustained
over long post-operative periods in patients with MM21,30,50,53,54. Many patients with myeloma who get over the acute fracture pain may benefit from facet joint injections for facet-related
pain due to the kyphotic deformity. The evidence on bracing in the management of osteoporotic VCFs is conflicting and the role of the use of external supportive devices including rigid
thoracolumbar spinal orthosis (TLSO) or hyperextension braces is yet to be defined55. Splinting of fractures and thermoplastic bracing of spinal deformities has been used for many years to
treat disability and pain. Bracing for 8–12 weeks has also been used for the treatment of VCF’s related to myeloma52. This may be all that is needed to give the patients pain relief from
their acute fracture pain. The thermoplastic brace may also give temporary stability to a fractured spine and to patients with sternal fracture56 while chemotherapy is initiated. The most
important treatment modality is the systemic anti-myeloma therapy to get the myeloma under control. After one or two cycles of systemic anti-myeloma therapy, cement augmentation (PV and BKP)
can be performed if in fact the acute fracture pain is still present. Often these patients have had relief of their acute fracture pain with the thermoplastic brace alone or with the
addition of 4–6 weeks of medical/conservative treatment. This means that the patients may not need cement augmentation. Instead if they have chronic pain of a lower intensity over their
kyphotic deformity they may benefit from some facet joint injections. A small group of myeloma patients present with a soft tissue myelomatous mass within the spinal canal that can result in
spinal cord or cauda equine compression. These patients often present with neurological deficits and each case needs to be assessed individually. MRI scanning is clearly imperative but a CT
scan with soft tissue windows will help to delineate whether the neural compression is due to bone or soft tissue. If the compression is due to a soft tissue mass with associated
neurological impairment, then this may be amenable to steroids/chemotherapy and immediate radiotherapy. Patients with cord compression and no neurological deficit may not need radiotherapy
because chemotherapy and steroids have been shown to result in excellent resolution of the soft tissue myelomatous mass. Ideally, if patients can be treated with steroids, radiotherapy and
chemotherapy and have a very good resolution of their symptoms in 24 h, then they may not need surgical decompression and stabilisation. All decisions regarding patients with spinal cord
compression need to be taken into conjunction with an experienced spinal surgeon. Clearly, if a patient has spinal cord or cauda equina compression and has significant neurological sequelae
then they may require urgent surgical decompression and associated fixation. The aim however in patients with haematological malignancies should be to try and avoid placement of
screws/fixation of the spine. The metalwork has a higher than normal risk of failure because the bone is very weak due to MM causing secondary osteoporosis. In addition, there is a higher
risk of metalwork infection because the patients are immunosuppressed during their conventional chemotherapy, immunotherapy and stem cell transplantation. After resolution of the intraspinal
mass with chemotherapy, radiotherapy and steroids the fractured vertebra may need to be augmented with cement to treat the acute fracture pain but also to give mechanical support to the
anterior and middle columns of the spine57 thereby preventing further collapse of the vertebral body. Further collapse, particularly into kyphosis, may lead to spinal cord compromise because
of the deformity. Patients that present with no intraspinal soft tissue mass, but overt bony destruction and dubious spinal stability are another important group of patients. A posterior
vertebral wall defect or pedicle/facet fracture may lead one to question the spinal stability in this patient group. Often all that is needed is a spinal brace to keep them out of pain while
the spine confers itself stability by producing bridging bony osteophytes58,59. This appearance is similar to diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis60. It is a phenomenon that may be
accelerated by or the result of treatment with bisphosphonates. This is a very interesting finding and warrants further research to see whether patients with myeloma present a completely
different clinical problem than patients with osteolytic metastases due to solid tumours. The following is the consensus statement for recommendations for spinal support and cement
augmentation from the International Myeloma Working Group. MM patients with significant pain at a fracture site should be offered a BKP or PV procedure and the procedure should be performed
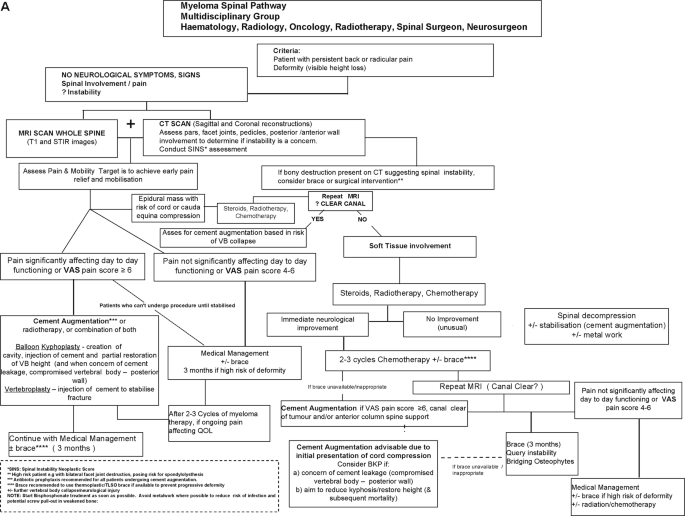
within 4–8 weeks unless there are medical contraindications (Tables 1 and 2, Fig. 1a, b). IDENTIFICATION OF PATIENTS SUITABLE FOR VERTEBRAL AUGMENTATION * Careful assessment to determine the
severity and site of the pain61. Patients with acute fracture pain should be considered and not the patient with facet joint-related pain. The clinical picture should be confirmed with MRI
scanning. The most useful MRI images to show an acute or on-going painful fracture are the sagittal STIR and T1 weighted sequences. The T1 weighted images may be more helpful in diagnosing a
VCF in a MM patient than the STIR images. In addition, T1 images may also show the fracture line. * MRI is crucial to document any radiological nerve root/cauda equina or spinal cord
compression. * CT scan with sagittal and coronal reconstructions may be needed to assess if there is spinal instability. A SINS classification can be helpful when determining the stability
of the spine. If there is a posterior wall defect or pedicle/facet joint involvement, then CT can determine the safety of cement placement within the vertebral body. If patients get a
recurrence of pain after a successful cement augmentation, then sagittal T1 and STIR images of the spine should be repeated to see if there is a new fracture that could develop following
myeloma treatment. * Assessment of myeloma disease status and therefore risk related to anaesthetic and any cement augmentation procedure. This includes potential anti-myeloma treatment
requirements and risk for infection and bleeding. Coordination of procedure with treating haematologist/oncologist to avoid anaemia, leukopaenia and/or thrombocytopaenia related to systemic
anti-myeloma therapy. TIMING OF VERTEBRAL CEMENT AUGMENTATION (PV OR BKP) The CAFÉ Trial investigated early intervention in cancer patients who had VCF’s treated with BKP. The functional
outcome (RDQ) was superior for the patients having BKP in the 1st month compared to the patients who received non-surgical treatment. The patients in the BKP group showed a marked reduction
in back pain and required less pain relief. This is important for myeloma patients since most of them have a degree of renal impairment. In addition, improvement of function and mobility can
reduce thrombotic and infection risk. Therefore, early intervention within 4–8 weeks62,63 of VCF’s with cement augmentation not only treats the pain associated with the fracture but in
addition improves clinical outcome and QoL52 (Table 2). NUMBER OF LEVELS TO BE CONSIDERED FOR TREATMENT For patients with multiple VCF’s and significant pain, the maximum number of levels
that should be augmented at a time should be determined by the operator. There is no upper limit for total number of vertebrae that should be treated in one intervention. The panel’s
recommendation is that it is appropriate to treat up to 3 levels at a time and any decision treating more levels than this should be taken with caution. The reason for this is that cement
embolus to the lungs may occur compromising respiratory function. Cement augmentation without cement leakage into the disc above or below should not increase the risk of adjacent vertebral
body fracture. Cement leakage rates with BKP are reported to be less than with VP28,31. This is also the consensus of the panel. THE HIGHEST LEVEL OF CEMENT AUGMENTATION Cement augmentation
of the spine is possible at all spinal levels. The C2 vertebral body can be augmented via a trans-oral or submandibular route. The C3–C7 vertebral bodies can be accessed and augmented
through a standard open anterior cervical approach64,65,66 or percutaneously if the experience is available. The thoracic and lumbar vertebral bodies can be augmented with cement in the
standard transpedicular or extrapedicular approach. Pain due to fractures from T1 to T4 rarely needs to be treated with cement augmentation because the pain usually settles with conservative
management. Sarcroplasty can be performed if there is evidence of sacral insufficiency fractures. THE METHOD OF VERTEBRAL CEMENT AUGMENTATION Published studies report contradicting results
for cement augmentation38,39,40,48,67,68,69,70,71. Although there has been a change in emphasis from VP to BKP, the evidence for one procedure over the other is debatable. A meta-analysis of
randomised and non-randomised trials of VP, BKP and NSM in patients with VCF due to osteoporosis31 has found that BKP was better than VP or NSM in reducing disability. Both BKP and VP were
better for reducing pain (mostly during the first 8 weeks) and subsequent fracture risk (by about 50%) when compared to NSM. There was no difference between BKP and VP for these parameters.
Cement leakage into the canal, lungs or other major organs was less for BKP than for VP. BKP was better in restoring mid-vertebral height and in changing kyphotic angle than VP and was also
associated with less incidence of refracture. BKP, which involves inflation of a balloon tamp to create a void in the vertebral body, controls the delivery of cement better than PV. Patients
with multiple VCF’s may become very kyphotic in the thoracic and lumbar regions of the spine. A hyperkyphosis results in a positive sagittal alignment also termed sagittal imbalance.
Patients with a positive sagittal balance find it more difficult to stand in the upright posture and in attempting to do so expend more energy. Poor sagittal alignment has been shown to be a
strong predictor of disability72. There has been debate as to the potential for BKP and PV to restore vertebral body height following a VCF. Some papers however report an improvement in the
Cobb angle (degree of kyphosis) following BKP50,54,73,74 for VCF’s related to MM. Similar outcomes of KIVA implant to BKP vertebral augmentation were reported in patients with VCFs
secondary to cancer and osteoporosis75,76,77,78,79. More research is needed to answer this question definitively. In addition, direct comparison of the complications of NSM, VP and BKP and
the optimal timing for VCF treatment in MM patients are questions that could be answered in a prospective randomised, controlled clinical trial. USE OF RADIOTHERAPY The use of radiotherapy
for local disease control and palliation should be used judiciously and sparingly depending on the patient’s presentation, need for urgent response, and prior treatment history and response.
MRI and CT scans are crucial to differentiate between a soft tissue myelomatous mass in the spinal canal from bony encroachment. The reason for this is that radiation therapy is very
effective in reducing the size of a soft tissue myelomatous mass but not effective if there is bony neural compression and does not stabilise the VCF. Radiotherapy should be limited as much
as possible to spare the patient’s marrow function. Current systemic combination therapies of steroids with novel agents work rapidly and should decrease the need for palliative
radiotherapy. Radiation therapy may be appropriate for: * (1) Patients with a soft tissue mass or plasmacytoma that has not resolved with systemic therapy * (2) Patients who cannot receive
systemic therapy * (3) Relapsed refractory patients * (4) Palliative approach for poor performance status patients * (5) When mass is associated with severe pain * (6) Location of
plasmacytoma precluding use of BKP or PV; e.g. tumour impacting posterior part of the vertebral body close to spinal cord and nerves. Receiving radiotherapy and the dose of previous
radiotherapy are not contraindications for cement augmentation (PV or BKP) if it is needed. The need and timing of a cement augmentation procedure for patients that have been irradiated
depends on the patient’s pain (Fig. 2). The cement augmentation procedures are performed through small stab incisions and therefore the usual concerns over wound healing do not exist.
Patients that have a posterior wall defect (associated with a soft tissue mass encroaching the spinal canal) or pedicle/facet joint involvement may need supplementary cement augmentation
despite having received radiotherapy to stabilise the anterior and middle columns of the spine. Planned vertebral augmentation 4–8 weeks later (or after the second cycle of chemotherapy) is
appropriate for patients with relative vertebral instability. The aim of the cement augmentation is to halt further collapse of the fractured vertebral body that could result in progressive
kyphosis and secondary neural compromise. Overall, the proposed algorithm for spinal support in myeloma presenting with VCFs or spinal cord compression is summarised in a flow diagram in
Fig. 1b. The first major decision point is the presence or absence of signs and/or symptoms of neurological deficit. Obviously, if there is, this is an urgent matter and recommendations
proceed accordingly. Once the situation has been assessed, stabilised and treated, then cement augmentation can be an option if there is persistent pain. For patients without neurologic
compromise, imaging and multi-disciplinary assessment are recommended as the basis for consideration of cement augmentation. Integration within the total treatment schema is the primary
plan. DISCUSSION The prognosis of patients with myeloma has improved considerably over the last 15 years because of the advances in Haematological Oncology. We therefore need to become more
proficient at treating the associated medical/surgical complications related to the disease. One such complication is one or more VCF’s of the spine. Patients may present with significant
spinal fracture pain or neurological compromise. These signs and symptoms may present at the time of the index procedure or when there is a relapse of the disease. Essentially, myeloma
patients that present with spinal symptoms and signs need to be assessed to establish the source and nature of their pain and presence/absence of neurological compromise and spinal
instability. Those that present with neurological compromise may have spinal cord, cauda equina or nerve root compression. It is imperative, in patients with neurological compromise, to get
not only an MRI scan with STIR and T1 weighted images but also a CT scan (with soft tissue windowing) to delineate whether it is bone or soft tissue compromising the neurological structures.
Soft tissue in the spinal canal due to a myelomatous deposit is usually very sensitive to treatment with chemotherapy/radiotherapy/steroids and therefore the neural compression can be
treated by these modalities without the need for surgical decompression. Ideally, one would like to avoid any instrumentation in myeloma patients if possible because of the risk of
subsequent metalwork/deep spinal infection during periods of immunocompromise. However, if there is significant spinal cord compromise/cauda equina compression then surgical decompression
may be needed as an emergency and an immediate spinal surgical consultation should be sought on all such patients. Once the spinal cord/cauda equine compression has been treated with
steroids/chemotherapy/radiotherapy, cement augmentation may be needed to alleviate the pain associated with the fracture or to restore spinal stability. It is uncommon for a myeloma patient
to present with neurological compromise because of bony encroachment but if it occurs, radiotherapy/chemotherapy/steroids will not be an effective treatment. Surgery may be needed in this
cohort of patients. Patients who present with spinal pain, but no neurological compromise should have an MRI scan performed with STIR and T1 weighted images to detect any spinal fractures.
The T1 weighted images may be better than the STIR images in highlighting the fracture line in vertebrae infiltrated with a myelomatous deposit. If one has concerns about the spinal
stability because of a posterior wall defect or pedicle/facet joint/pars involvement, then a CT scan with sagittal and coronal reconstructions can be very helpful. Patients can have quite
significant bony defects but still be structurally stable in an orthotic brace80. A brace may be all that is needed in patients with a spinal fracture if they can mobilise without
significant pain. The external orthosis will also keep the patients in the upright posture (and potentially prevent the development of a kyphotic deformity) while their fractures heal.
Patients who present with spinal pain and have a new diagnosis of myeloma may need, depending on systemic symptoms, to have their disease controlled with chemotherapy prior to any
consideration for cement augmentation. The chemotherapy immune-compromises the patients and therefore the correct timing of cement augmentation should be a multi-disciplinary decision.
Antibiotic prophylaxis in the peri-operative period is strongly advised to avoid infection. The orthotic brace can be a very useful tool to control the pain to an acceptable level while the
disease is being treated with the first couple of cycles of chemotherapy. Another important aspect of the treatment in myeloma patients involves bisphosphonate therapy. This drug treatment
clearly helps to stabilise the bone density in patients with myeloma but, in addition may have a positive effect in producing an external scaffold of bone around the vertebral bodies to
confer them extra stability. This external scaffold, which has been described as DISH in prior publications81 in patients with myeloma, may decrease the need for spinal fixation in patients
otherwise thought to be at risk of spinal instability because of involvement of all three bony spinal columns57. CONCLUSION The prognosis of MM is continually improving due to medical
advances. The treatment of myeloma with chemo- immunotherapeutic agents and autologous stem cell transplantation renders the patient immunocompromised for periods of time, exposing them to
infection. Spinal fixation has been employed traditionally to treat myeloma patients when decompression and stabilisation were deemed to be essential. However, it is well established that in
situ instrumentation is at risk of getting infected when the patients are in an immunocompromised state. If the metalwork gets infected, then the consequences can be catastrophic. Cement
augmentation is a very effective way of stabilising the anterior and middle spinal columns without the need for metalwork fixation. It is an excellent way to relieve the pain from a VCF. The
myeloma spine treated with bisphosphonates appears to produce an external scaffold of bone that stabilises even the most moth-eaten spinal elements once the disease process is under
control. An external orthosis can be very effective when trying to achieve pain relief from a fracture. It also helps to maintain the correct sagittal balance in patients with multiple
fractures while they heal or before they are treated with cement augmentation. The development of radiofrequency ablation in combination with cement augmentation procedures is currently
under investigation with encouraging results. REFERENCES * Terpos, E., Christoulas, D. & Gavriatopoulou, M. Biology and treatment of myeloma related bone disease. _Metabolism_ 80, 80–90
(2018). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Terpos, E., Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I., Gavriatopoulou, M. & Dimopoulos, M. A. Pathogenesis of bone disease in multiple myeloma: from bench to
bedside. _Blood Cancer J._ 8, 7 (2018). PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Terpos, E., Christoulas, D., Gavriatopoulou, M. & Dimopoulos, M. A. Mechanisms of bone destruction in
multiple myeloma. _Eur. J. Cancer Care_ 26, e12761–12771 (2017). Google Scholar * Callander, N. S. & Roodman, G. D. Myeloma bone disease. _Semin. Hematol._ 38, 276–285 (2001). CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Eda, H., Santo, L., Roodman, G. D. & Raje, N. Bone disease in multiple myeloma. _Cancer Treat. Res._ 169, 251–270 (2016). CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Landgren, O. & Rajkumar, S. V. New developments in diagnosis, prognosis, and assessment of response in multiple myeloma. _Clin. Cancer Res._ 22, 5428–5433 (2016). CAS PubMed PubMed
Central Google Scholar * Rajkumar, S. V. Myeloma today: disease definitions and treatment advances. _Am. J. Hematol._ 91, 90–100 (2016). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar *
Genant, H. K., Wu, C. Y., van Kuijk, C. & Nevitt, M. C. Vertebral fracture assessment using a semiquantitative technique. _J. Bone Miner. Res._ 8, 1137–1148 (1993). CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Lindsay, R. et al. Risk of new vertebral fracture in the year following a fracture. _JAMA_ 285, 320–323 (2001). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Heggeness, M. H. Spine fracture with
neurological deficit in osteoporosis. _Osteoporos. Int._ 3, 215–221 (1993). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kado, D. M. et al. Incident vertebral fractures and mortality in older women: a
prospective study. _Osteoporos. Int._ 14, 589–594 (2003). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Huang, M. H., Barrett-Connor, E., Greendale, G. A. & Kado, D. M. Hyperkyphotic posture and risk
of future osteoporotic fractures: the Rancho Bernardo study. _J. Bone Miner. Res._ 21, 419–423 (2006). PubMed Google Scholar * Kado, D. M. et al. Hyperkyphosis predicts mortality
independent of vertebral osteoporosis in older women. _Ann. Intern. Med._ 150, 681–687 (2009). PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Katzman, W. B., Vittinghoff, E. & Kado, D. M.
Age-related hyperkyphosis, independent of spinal osteoporosis, is associated with impaired mobility in older community-dwelling women. _Osteoporos. Int._ 22, 85–90 (2011). CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Schlaich, C. et al. Reduced pulmonary function in patients with spinal osteoporotic fractures. _Osteoporos. Int._ 8, 261–267 (1998). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Katzman,
W. B., Vittinghoff, E., Ensrud, K., Black, D. M. & Kado, D. M. Increasing kyphosis predicts worsening mobility in older community-dwelling women: a prospective cohort study. _J. Am.
Geriatr. Soc._ 59, 96–100 (2011). PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Kado, D. M., Lui, L. Y. & Cummings, S. R., Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group. Rapid resting heart
rate: a simple and powerful predictor of osteoporotic fractures and mortality in older women. _J. Am. Geriatr. Soc._ 50, 455–460 (2002). PubMed Google Scholar * Lyles, K. W. et al.
Association of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with impaired functional status. _Am. J. Med._ 94, 595–601 (1993). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Silverman, S. L. The clinical
consequences of vertebral compression fracture. _Bone_ 13, S27–S31 (1992). PubMed Google Scholar * Gold, D. T. The clinical impact of vertebral fractures: quality of life in women with
osteoporosis. _Bone_ 18, 185S–189S (1996). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Dudeney, S., Lieberman, I. H., Reinhardt, M. K. & Hussein, M. Kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteolytic
vertebral compression fractures as a result of multiple myeloma. _J. Clin. Oncol._ 20, 2382–2387 (2002). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Bouza, C., Lopez-Cuadrado, T., Cediel, P.,
Saz-Parkinson, Z. & Amate, J. M. Balloon kyphoplasty in malignant spinal fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. _BMC Palliat. Care_ 8, 12 (2009). PubMed PubMed Central
Google Scholar * Boonen, S. et al. Balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of acute vertebral compression fractures: 2-year results from a randomized trial. _J. Bone Miner. Res._ 26,
1627–1637 (2011). PubMed Google Scholar * Burton, A. W. et al. Vertebral compression fracture treatment with vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: experience in 407 patients with 1,156 fractures
in a tertiary cancer center. _Pain Med._ 12, 1750–1757 (2011). PubMed Google Scholar * Edidin, A. A., Ong, K. L., Lau, E. & Kurtz, S. M. Morbidity and mortality after vertebral
fractures: comparison of vertebral augmentation and nonoperative management in the medicare population. _Spine_ 40, 1228–1241 (2015). Google Scholar * Evans, A. J. et al. Randomized
controlled trial of vertebroplasty versus kyphoplasty in the treatment of vertebral compression fractures. _J. Neurointerv. Surg._ 8, 756–763 (2016). PubMed Google Scholar * Ha, K. Y. et
al. Bone cement augmentation procedures for spinal pathologic fractures by multiple myeloma. _J. Korean Med. Sci._ 30, 88–94 (2015). PubMed Google Scholar * Health Quality Ontario.
Vertebral augmentation involving vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty for cancer-related vertebral compression fractures: a systematic review. _Ont. Health Technol. Assess. Ser._ 16, 1–202 (2016).
PubMed Central Google Scholar * Julka, A., Tolhurst, S. R., Srinivasan, R. C. & Graziano, G. P. Functional outcomes and height restoration for patients with multiple myeloma-related
osteolytic vertebral compression fractures treated with kyphoplasty. _J. Spinal Disord. Tech._ 27, 342–346 (2014). PubMed Google Scholar * Khan, O. A., Brinjikji, W. & Kallmes, D. F.
Vertebral augmentation in patients with multiple myeloma: a pooled analysis of published case series. _Am. J. Neuroradiol._ 35, 207–210 (2014). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Papanastassiou,
I. D. et al. Comparing effects of kyphoplasty, vertebroplasty, and non-surgical management in a systematic review of randomized and non-randomized controlled studies. _Eur. Spine J._ 21,
1826–1843 (2012). PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Lieberman, I. H., Dudeney, S., Reinhardt, M. K. & Bell, G. Initial outcome and efficacy of “kyphoplasty” in the treatment of
painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. _Spine_ 26, 1631–1638 (2001). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Berenson, J. et al. Balloon kyphoplasty versus non-surgical fracture
management for treatment of painful vertebral body compression fractures in patients with cancer: a multicentre, randomised controlled trial. _Lancet Oncol._ 12, 225–235 (2011). PubMed
Google Scholar * Hussein, M. A. et al. The role of vertebral augmentation in multiple myeloma: International Myeloma Working Group Consensus Statement. _Leukemia_ 22, 1479–1484 (2008). CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Buchbinder R., et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. _Cochrane Database Syst. Rev._ 4, CD006349 (2015). * Comstock,
B. A. et al. Investigational vertebroplasty safety and efficacy trial (INVEST): patient-reported outcomes through 1 year. _Radiology_ 269, 224–231 (2013). PubMed PubMed Central Google
Scholar * Kallmes, D. F. & Comstock, B. A. Commentary: No comparison: conservative management of painful spontaneous osteoporotic compression fractures is the way to go. _Spine J._ 12,
1006–1007 (2012). PubMed Google Scholar * Staples, M. P. et al. Effectiveness of vertebroplasty using individual patient data from two randomised placebo controlled trials: meta-analysis.
_BMJ_ 343, d3952 (2011). PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Kallmes, D. F. et al. A randomized trial of vertebroplasty for osteoporotic spinal fractures. _N. Engl. J. Med._ 361,
569–579 (2009). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Buchbinder, R. & Kallmes, D. F. Vertebroplasty: when randomized placebo-controlled trial results clash with common belief.
_Spine J._ 10, 241–243 (2010). PubMed Google Scholar * Wilson, D. J., Owen, S. & Corkill, R. A. Coblation vertebroplasty for complex vertebral insufficiency fractures. _Eur. Radiol._
23, 1785–1790 (2013). PubMed Google Scholar * Wilson, D. R. et al. Effect of augmentation on the mechanics of vertebral wedge fractures. _Spine_ 25, 158–165 (2000). CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Edidin, A. A., Ong, K. L., Lau, E. & Kurtz, S. M. Mortality risk for operated and nonoperated vertebral fracture patients in the medicare population. _J. Bone Miner. Res._ 26,
1617–1626 (2011). PubMed Google Scholar * Kasperk, C. et al. Kyphoplasty in patients with multiple myeloma a retrospective comparative pilot study. _J. Surg. Oncol._ 105, 679–686 (2012).
PubMed Google Scholar * Mendoza, T. R. et al. Changes in pain and other symptoms in patients with painful multiple myeloma-related vertebral fracture treated with kyphoplasty or
vertebroplasty. _J. Pain_ 13, 564–570 (2012). PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * La Maida, G. A. et al. Cement leakage: safety of minimally invasive surgical techniques in the
treatment of multiple myeloma vertebral lesions. _Eur. Spine J._ 21, S61–S68 (2012). PubMed Google Scholar * Simony, A., Hansen, E. J., Gaurilcikas, M., Abildgaard, N. & Andersen, M.
O. Pain reduction after percutaneous vertebroplasty for myeloma-associated vertebral fractures. _Dan. Med. J._ 61, A4945 (2014). PubMed Google Scholar * Anselmetti, G. C. et al.
Percutaneous vertebroplasty in multiple myeloma: prospective long-term follow-up in 106 consecutive patients. _Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol._ 35, 139–145 (2012). PubMed Google Scholar *
Anselmetti, G. C. et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: multi-centric results from EVEREST experience in large cohort of patients. _Eur. J. Radiol._ 81, 4083–4086 (2012). PubMed Google
Scholar * Zou, J., Mei, X., Gan, M. & Yang, H. Kyphoplasty for spinal fractures from multiple myeloma. _J. Surg. Oncol._ 102, 43–47 (2010). PubMed Google Scholar * Astolfi, S.,
Scaramuzzo, L. & Logroscino, C. A. A minimally invasive surgical treatment possibility of osteolytic vertebral collapse in multiple myeloma. _Eur. Spine J._ 18, 115–121 (2009). PubMed
PubMed Central Google Scholar * Malhotra, K. et al. Spinal disease in myeloma: cohort analysis at a specialist spinal surgery centre indicates benefit of early surgical augmentation or
bracing. _BMC Cancer_ 16, 444 (2016). PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Pflugmacher, R. et al. [A prospective two-year follow-up of thoracic and lumbar osteolytic vertebral fractures
caused by multiple myeloma treated with balloon kyphoplasty]. _Z. Orthop. Ihre Grenzgeb._ 145, 39–47 (2007). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Pflugmacher, R. et al. [Comparative findings of
balloon kyphoplasty in patients with vertebral fractures due to osteoporosis, metastases and myeloma]. _Z. Orthop. Unf._ 150, 198–204 (2012). CAS Google Scholar * Goodwin, V. A., Hall, A.
J., Rogers, E. & Bethel, A. Orthotics and taping in the management of vertebral fractures in people with osteoporosis: a systematic review. _BMJ Open._ 6, e010657 (2016). PubMed PubMed
Central Google Scholar * Butler, J. S. et al. Pathologic sternal involvement is a potential risk factor for severe sagittal plane deformity in multiple myeloma with concomitant thoracic
fractures. _Spine J._ 15, 2503–2508 (2015). PubMed Google Scholar * Denis, F. The three column spine and its significance in the classification of acute thoracolumbar spinal injuries.
_Spine_ 8, 817–831 (1983). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Molloy, S. & Kyriakou, C. Expert’s comment concerning Grand Rounds case entitled “total spondylectomy for solitary bone
plasmacytoma of the lumbar spine in a young woman. A case report and review of the literature” (by N. von der Hoeh, S.K. Tschoeke, J. Gulow, A. Voelker, U. Siebolts and C.-E. Heyde). _Eur.
Spine J._ 23, 40–42 (2014). PubMed Google Scholar * Malhotra, K., Lui, D. F., Butler, J. S., Selvadurai, S. & Molloy, S. Successful nonsurgical treatment for highly unstable fracture
subluxation of the spine secondary to myeloma. _Spine J._ 16, e547–e551 (2016). PubMed Google Scholar * Mata, S. et al. A controlled study of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis.
Clinical features and functional status. _Medicine_ 76, 104–117 (1997). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Langdon, J., Way, A., Heaton, S., Bernard, J. & Molloy, S. Vertebral compression
fractures—new clinical signs to aid diagnosis. _Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl._ 92, 163–166 (2010). PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Papanastassiou, I. D. & Vrionis, F. D. Is early
vertebroplasty/kyphoplasty justified in multiple myeloma given the rapid vertebral fracture progression? _Spine J._ 16, 833–834 (2016). PubMed Google Scholar * Papanastassiou, I. D. et al.
Adverse prognostic factors and optimal intervention time for kyphoplasty/vertebroplasty in osteoporotic fractures. _Biomed. Res. Int._ 2014, 925683 (2014). PubMed PubMed Central Google
Scholar * Smith, G. R. & Hotchkiss, R. N. Radial head and neck fractures: anatomic guidelines for proper placement of internal fixation. _J. Shoulder Elbow Surg._ 5, 113–117 (1996). CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Guzik, G. Quality of life of patients after surgical treatment of cervical spine metastases. _BMC Musculoskelet. Disord._ 17, 315 (2016). PubMed PubMed Central
Google Scholar * Druschel, C., Schaser, K. D., Melcher, I., Haas, N. P. & Disch, A. C. Minimally invasive combined anterior kyphoplasty for osteolytic C2 and C5 metastases. _Arch.
Orthop. Trauma Surg._ 131, 977–981 (2011). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Buchbinder, R., Kallmes, D. & Glasziou, P. Vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment for vertebral fractures.
_Lancet_ 376, 2070 (2010). PubMed Google Scholar * Gray, L. A., Rad, A. E., Gaughen, J. R. Jr., Kaufmann, T. J. & Kallmes, D. F. Efficacy of percutaneous vertebroplasty for multiple
synchronous and metachronous vertebral compression fractures. _Am. J. Neuroradiol._ 30, 318–322 (2009). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Jarvik, J. G. & Kallmes, D. F. Point of view.
Efficacy of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. _Spine_ 34, 613–614 (2009). PubMed Google Scholar * Kallmes, D. F., Buchbinder, R. & Miller, F. G. Viewpoint: Randomised controlled trials
using invasive control interventions should be included in Cochrane Reviews. _Cochrane Database Syst. Rev._ 8, ED000030 (2011). * Anselmetti, G. C., Muto, M., Guglielmi, G. & Masala, S.
Percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty. _Radiol. Clin. North Am._ 48, 641–649 (2010). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Glassman, S. D. et al. The impact of positive sagittal balance in
adult spinal deformity. _Spine_ 30, 2024–2029 (2005). PubMed Google Scholar * Pflugmacher, R., Beth, P., Schroeder, R. J., Schaser, K. D. & Melcher, I. Balloon kyphoplasty for the
treatment of pathological fractures in the thoracic and lumbar spine caused by metastasis: one-year follow-up. _Acta Radiol._ 48, 89–95 (2007). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Pflugmacher, R.
et al. Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty in the treatment of pathological vertebral body fracture and deformity in multiple myeloma: a one-year follow-up. _Acta Radiol._ 47, 369–376 (2006).
CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Korovessis, P., Vardakastanis, K., Repantis, T. & Vitsas, V. Balloon kyphoplasty versus KIVA vertebral augmentation—comparison of 2 techniques for
osteoporotic vertebral body fractures: a prospective randomized study. _Spine_ 38, 292–299 (2013). PubMed Google Scholar * Korovessis, P., Repantis, T., Miller, L. E. & Block, J. E.
Initial clinical experience with a novel vertebral augmentation system for treatment of symptomatic vertebral compression fractures: a case series of 26 consecutive patients. _BMC
Musculoskelet. Disord._ 12, 206 (2011). PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Korovessis, P., Vardakastanis, K., Vitsas, V. & Syrimpeis, V. Is Kiva implant advantageous to balloon
kyphoplasty in treating osteolytic metastasis to the spine? Comparison of 2 percutaneous minimal invasive spine techniques: a prospective randomized controlled short-term study. _Spine_ 39,
E231–E239 (2014). PubMed Google Scholar * Anselmetti, G. C. et al. Percutaneous vertebral augmentation assisted by PEEK implant in painful osteolytic vertebral metastasis involving the
vertebral wall: experience on 40 patients. _Pain Physician_ 16, E397–E404 (2013). PubMed Google Scholar * Tutton, S. M. et al. KAST Study: the Kiva system as a vertebral augmentation
treatment—a safety and effectiveness trial: a randomized, noninferiority trial comparing the Kiva system with balloon kyphoplasty in treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression
fractures. _Spine_ 40, 865–875 (2015). PubMed Google Scholar * Molloy, S. et al. Is balloon kyphoplasty safe and effective for cancer-related vertebral compression fractures with posterior
vertebral body wall defects? _J. Surg. Oncol._ 113, 835–842 (2016). PubMed Google Scholar * Scutellari, P. N., Orzincolo, C., Spanedda, R. & Piva, N. Plasma cell dyscrasias and
diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. Is it a merely accidental association?. _Radiol. Med._ 81, 625–632 (1991). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Fourney, D. R. et al. Spinal instability
neoplastic score: an analysis of reliability and validity from the spine oncology study group. _J. Clin. Oncol._ 29, 3072–3077 (2011). PubMed Google Scholar * Fisher, C. G. et al. A novel
classification system for spinal instability in neoplastic disease: an evidence-based approach and expert consensus from the Spine Oncology Study Group. _Spine_ 35, E1221–E1229 (2010).
PubMed Google Scholar Download references AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * University College London and Northwick Park Hospitals, London, UK Charalampia Kyriakou * Royal
National Orthopedic Hospital, Stanmore, UK Charalampia Kyriakou & Sean Molloy * Moffitt Cancer Center, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL, USA Frank Vrionis * Roswell Park Cancer
Center, Buffalo, NY, USA Ronald Alberico * Klinikum Leverkusen, Leverkusen, Germany Leonard Bastian * Karmanos Cancer Institute, Detroit, MI, USA Jeffrey A. Zonder * Memorial Sloan-Kettering
Cancer Center, New York, NY, USA Sergio Giralt * Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, USA Noopur Raje * Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN,
USA Robert A. Kyle * Indiana University, Indianapolis, IN, USA David G. D. Roodman * University of Athens School of Medicine, Athens, Greece Meletios A. Dimopoulos & Evangelos Terpos *
Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, USA S. Vincent Rajkumar * Cedars-Sinai Samuel Oschin Cancer Center, Los Angeles, CA, USA Brian B. G. Durie Authors * Charalampia Kyriakou View author publications
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Sean Molloy View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Frank Vrionis View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Ronald Alberico View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Leonard
Bastian View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Jeffrey A. Zonder View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google
Scholar * Sergio Giralt View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Noopur Raje View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * Robert A. Kyle View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * David G. D. Roodman View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Meletios A. Dimopoulos View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * S. Vincent Rajkumar View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Brian B. G. Durie View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Evangelos
Terpos View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Charalampia Kyriakou. ETHICS DECLARATIONS CONFLICT OF
INTEREST The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION PUBLISHER’S NOTE: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in
published maps and institutional affiliations. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS OPEN ACCESS This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use,
sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative
Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated
otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds
the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. Reprints and
permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Kyriakou, C., Molloy, S., Vrionis, F. _et al._ The role of cement augmentation with percutaneous vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty for
the treatment of vertebral compression fractures in multiple myeloma: a consensus statement from the International Myeloma Working Group (IMWG). _Blood Cancer J._ 9, 27 (2019).
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41408-019-0187-7 Download citation * Received: 03 June 2018 * Revised: 09 September 2018 * Accepted: 31 October 2018 * Published: 26 February 2019 * DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41408-019-0187-7 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not
currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative





