- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT An concept of electromagnetic brain-computer-metasurface (EBCM), and remotely mindcontrolled metasurface (RMCM) via brainwaves is reported in _eLight_. Rather than DC voltage from
power supply or AC voltages from signal generators, such metasurfaces are controlled by brainwaves collected in real time and can transmit information wirelessly between human brains. Such
platforms can lead to a promising approach for the service of disabled people. Reconfigurable metasurfaces are highly desirable for applications including dynamical camouflaging and
intelligent electromagnetic (EM) skin due to their tunable EM features or functionalities1,2,3. Tuning are traditionally achieved by using electric voltage4, thermal free carriers5,
mechanical stretching6, or optical illumination7. In recent works published in eLight8,9, Ma et al.8 and Zhu et al.9 casted a roadmap fusing of the reprogrammable EM metasurfaces with
Brain-computer interface (BCI), which paved the way towards non-contact and real-time tuning of metasurfaces. With their findings, metasurfaces can be dynamically tuned by brain messages,
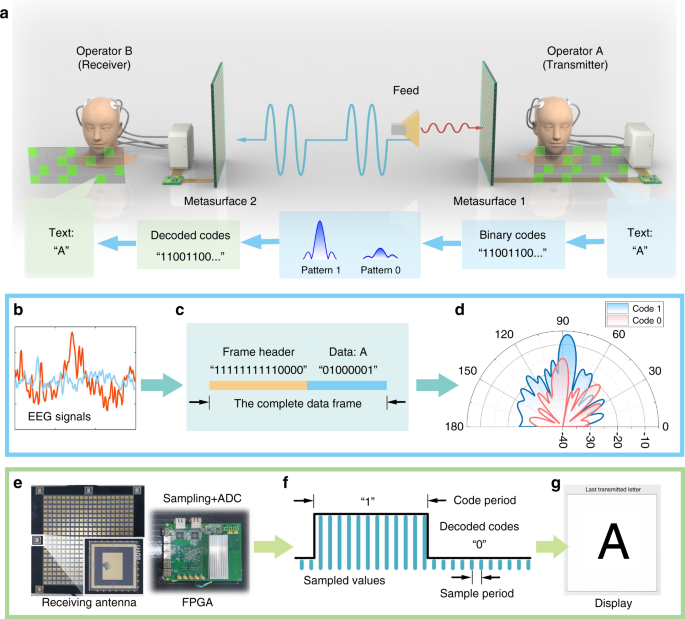
and wirelessly transmit brain messages between operators. As reported by8 and shown in Fig. 1, the text image in front of Operator A can generate EEG signals and be decoded in ASCII coding
sequences. When implemented on FPGA, it can switch time-varying patterns on the transmitter’s metasurface and be wireless transmitted to the receiver’s metasurface, and then translated back
into text information in front of Operator B. In the whole process, neither Operator A nor Operator B needs muscle actions. The authors named this platform as electromagnetic
brain-computer-metasurface (EBCM). With EBCM, the authors also demonstrated three typical schemes with distinct functions, including visual beam scanning, multiple EM function switching, and
metasurface pattern input, which contains more than 20 coding patterns for different single-beam scanning, multi-beam forming, OAM-beam generation, and RCS control. At the same time, Ref. 9
demonstrated a programmable metasurface with coding sequences that are reprogrammed by the human mind to perform different functionalities9. As shown in Fig. 29, the authors proposed a
framework for realizing remotely mind-controlled metasurface (RMCM) using a brainwave extraction module. This framework consists of three parts, i.e., sensor, controller, and actuator. The
sensor refers to the brainwave module that can record brainwaves and transmit them to the controller via Bluetooth. The controller consists of the microprogrammed control unit (MCU) and an
output terminal. Arduino is selected as the controller in this work. The controller receives brainwave signals from the sensor, converts them into attention signals, and then feeds the
attention signals into the actuator. According to the level of attention intensity, the attention signals fall within four separate intervals which are characterized by four thresholds. The
output pins of the controller are connected to the actuator, and the high/low level of output voltage corresponds to the coding 1/0 sequence. Under the switch on/off state of the PIN diodes,
a phase difference of 180° is produced to enable 1-bit coding. The output voltage level sequences from the controller denote different coding sequences on the metasurface, to control the
scattering pattern. Both the simulated and test results show that the EM response of metasurface can be directly controlled by the user’s brainwaves. Both EBCM and RMCM show good
performances in EM wave modulation, providing a new route to intelligent metasurfaces. In comparison with the state-of-the-art tuning methods, the presented new control manner - mind control
with brainwaves - is more direct and effective, leading to a promising approach for the service of disabled people. Customized designs for different users will further improve the accuracy
of equipment in the future. Combined with intelligent algorithms such as machine learning, the presented two works may further open up a new direction to advanced bio-intelligent metasurface
systems. REFERENCES * Huang, C. et al. Reconfigurable metasurface cloak for dynamical electromagnetic illusions. _ACS Photonics_ 5, 1718–1725 (2017). Article Google Scholar * Tsilipakos,
O. et al. Toward intelligent metasurfaces: the progress from globally tunable metasurfaces to software-defined metasurfaces with an embedded network of controllers. _Adv. Opt. Mater._ 8,
2000783 (2020). Article Google Scholar * Luo, X. Metasurface waves in digital optics. _J. Phys. Photonics_ 2, 041003 (2020). Article ADS Google Scholar * Cui, T., Bai, B. & Sun, H.
Tunable metasurfaces based on active materials. _Adv. Funct. Mater._ 29, 1806692 (2019). Article Google Scholar * Rahmani, M. et al. Reversible thermal tuning of all-dielectric
metasurfaces. _Adv. Funct. Mater._ 27, 1700580 (2017). Article Google Scholar * Ee, H. S. & Agarwal, R. Tunable metasurface and flat optical zoom lens on a stretchable substrate. _Nano
Lett._ 16, 2818–2823 (2016). Article ADS Google Scholar * Shcherbakov, M. R. et al. Ultrafast all-optical tuning of direct-gap semiconductor metasurfaces. _Nat. Commun._ 8, 17 (2017).
Article ADS Google Scholar * Ma, Q. et al. Directly wireless communication of human minds via non-invasive brain-computer-metasurface platform. _eLight_ 2, 11 (2022).
https://doi.org/10.1186/s43593-022-00019-x. * Zhu, R. et al. Remotely mind-controlled metasurface via brainwaves. _eLight_ 2, 10 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43593-022-00016-0. Download
references AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * State Key Laboratory of Optical Technologies on Nano-Fabrication and Micro-Engineering, Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese
Academy of Sciences, P.O. Box 350, Chengdu, 610209, China Xiangang Luo Authors * Xiangang Luo View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Xiangang Luo. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS OPEN ACCESS This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits
use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the
Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated
otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds
the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. Reprints and
permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Luo, X. Directly wireless communication of human minds via mind-controlled programming metasurface. _Light Sci Appl_ 11, 182 (2022).
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-022-00831-7 Download citation * Published: 16 June 2022 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-022-00831-7 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following
link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature
SharedIt content-sharing initiative