- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT Hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) plays critical roles in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Here, we were interested in knowing whether the oncogene Lin28A and its
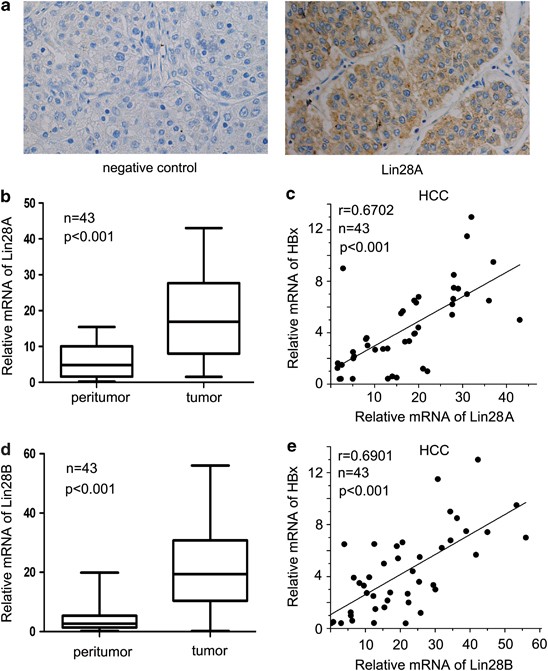
homolog Lin28B are involved in the hepatocarcinogenesis mediated by HBx. We showed that the expression levels of Lin28A and Lin28B were increased in clinical HCC tissues, HepG2.2.15 cell
line and liver tissues of p21-HBx transgenic mice. Interestingly, the expression levels of HBx were positively associated with those of Lin28A/Lin28B in clinical HCC tissues. Moreover, the
overexpression of HBx resulted in the upregulation of Lin28A/Lin28B in hepatoma HepG2/H7402 cell lines by transient transfection, suggesting that HBx was able to upregulate Lin28A and
Lin28B. Then, we examined the mechanism by which HBx upregulated Lin28A and Lin28B. We identified that the promoter region of Lin28A regulated by HBx was located at nt −235/−66 that
contained Sp-1 binding element. Co-immunoprecipitation showed that HBx was able to interact with Sp-1 in HepG2-X cells. Moreover, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) demonstrated that HBx
could bind to the promoter of Lin28A, which failed to work when Sp-1 was silenced. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) further identified that HBx was able to interact with Sp-1
element in Lin28A promoter via transcription factor Sp-1. In addition, we found that c-Myc was involved in the activation of Lin28B mediated by HBx. In function, Lin28A/Lin28B played
important roles in HBx-enhanced proliferation of hepatoma cells _in vitro_ and _in vivo_. In conclusion, HBx activates Lin28A/Lin28B through Sp-1/c-Myc in hepatoma cells. Lin28A/Lin28B
serves as key driver genes in HBx-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS
OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 50 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $5.18 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on
SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about
institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS LNCRNA MAPKAPK5_AS1 FACILITATES CELL PROLIFERATION IN HEPATITIS B VIRUS -RELATED
HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA Article 09 March 2022 ANTI-ONCOGENE PTPN13 INACTIVATION BY HEPATITIS B VIRUS X PROTEIN COUNTERACTS IGF2BP1 TO PROMOTE HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA PROGRESSION Article
Open access 13 October 2020 HBX INCREASES CHROMATIN ACCESSIBILITY AND ETV4 EXPRESSION TO REGULATE DISHEVELLED-2 AND PROMOTE HCC PROGRESSION Article Open access 04 February 2022 REFERENCES *
Michielsen P, Ho E . Viral hepatitis B and hepatocellular carcinoma. _Acta Gastroenterol Belg_ 2011; 74: 4–8. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Arbuthnot P, Kew M . Hepatitis B virus and
hepatocellular carcinoma. _Int J Exp Pathol_ 2001; 82: 77–100. Article CAS Google Scholar * Tang H, Da L, Mao Y, Li Y, Li D, Xu Z _et al_. Hepatitis B virus X protein sensitizes cells to
starvation-induced autophagy via up-regulation of beclin 1 expression. _Hepatology_ 2009; 49: 60–71. Article CAS Google Scholar * Ng SA, Lee C . Hepatitis B virus X gene and
hepatocarcinogenesis. _J Gastroenterol_ 2011; 46: 974–990. Article CAS Google Scholar * Du Y, Kong G, You X, Zhang S, Zhang T, Gao Y _et al_. Elevation of highly up-regulated in liver
cancer (Hulc) by hepatitis B virus X protein promotes hepatoma cell proliferation via down-regulating p18. _J Biol Chem_ 2012; 287: 26302–26311. Article CAS Google Scholar * Shan C, Xu F,
Zhang S, You J, You X, Qiu L _et al_. Hepatitis B virus X protein promotes liver cell proliferation via a positive cascade loop involving arachidonic acid metabolism and p-ERK1/2. _Cell
Res_ 2010; 20: 563–575. Article CAS Google Scholar * Wang Q, Zhang W, Liu Q, Zhang X, Lv N, Ye L . A mutant of hepatitis B virus X protein (HBxDelta127) promotes cell growth through a
positive feedback loop involving 5-lipoxygenase and fatty acid synthase. _Neoplasia_ 2010; 12: 103–115. Article Google Scholar * Zhang T, Zhang J, You X, Liu Q, Du Y, Gao Y _et al_.
Hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) modulates oncogene YAP via CREB to promote growth of hepatoma cells. _Hepatology_ 2012; 56: 2051–2059. Article CAS Google Scholar * Qiu C, Ma Y, Wang J,
Peng S, Huang Y . Lin28-mediated post-transcriptional regulation of Oct4 expression in human embryonic stem cells. _Nucleic Acids Res_ 2010; 38: 1240–1248. Article CAS Google Scholar * Xu
B, Huang Y . Histone H2a mRNA interacts with Lin28 and contains a Lin28-dependent posttranscriptional regulatory element. _Nucleic Acids Res_ 2009; 37: 4256–4263. Article CAS Google
Scholar * Peng S, Maihle NJ, Huang Y . Pluripotency factors Lin28 and Oct4 identify a sub-population of stem cell-like cells in ovarian cancer. _Oncogene_ 2010; 29: 2153–2159. Article CAS
Google Scholar * Xu B, Zhang K, Huang Y . Lin28 modulates cell growth and associates with a subset of cell cycle regulator mRNAs in mouse embryonic stem cells. _RNA_ 2009; 15: 357–361.
Article CAS Google Scholar * Polesskaya A, Cuvellier S, Naguibneva I, Duquet A, Moss EG, Harel-Bellan A . Lin-28 binds IGF-2 mRNA and participates in skeletal myogenesis by increasing
translation efficiency. _Genes Dev_ 2007; 21: 1125–1138. Article CAS Google Scholar * Newman MA, Thomson JM, Hammond SM . Lin-28 interaction with the Let-7 precursor loop mediates
regulated microRNA processing. _RNA_ 2008; 14: 1539–1549. Article CAS Google Scholar * Piskounova E, Viswanathan SR, Janas M, LaPierre RJ, Daley GQ, Sliz P _et al_. Determinants of
microRNA processing inhibition by the developmentally regulated RNA-binding protein Lin28. _J Biol Chem_ 2008; 283: 21310–21314. Article CAS Google Scholar * Yu J, Vodyanik MA, Smuga-Otto
K, Antosiewicz-Bourget J, Frane JL, Tian S _et al_. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. _Science_ 2007; 318: 1917–1920. Article CAS Google Scholar *
Viswanathan SR, Powers JT, Einhorn W, Hoshida Y, Ng TL, Toffanin S _et al_. Lin28 promotes transformation and is associated with advanced human malignancies. _Nat Genet_ 2009; 41: 843–848.
Article CAS Google Scholar * Iliopoulos D, Hirsch HA, Struhl K . An epigenetic switch involving NF-kappaB, Lin28, Let-7 MicroRNA, and IL6 links inflammation to cell transformation. _Cell_
2009; 139: 693–706. Article CAS Google Scholar * Sakurai M, Miki Y, Masuda M, Hata S, Shibahara Y, Hirakawa H _et al_. LIN28: a regulator of tumor-suppressing activity of let-7 microRNA
in human breast cancer. _J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol_ 2012; 131: 101–106. Article CAS Google Scholar * Cao D, Allan RW, Cheng L, Peng Y, Guo CC, Dahiya N _et al_. RNA-binding protein LIN28
is a marker for testicular germ cell tumors. _Hum Pathol_ 2011; 42: 710–718. Article CAS Google Scholar * Pan L, Gong Z, Zhong Z, Dong Z, Liu Q, Le Y _et al_. Lin-28 reactivation is
required for let-7 repression and proliferation in human small cell lung cancer cells. _Mol Cell Biochem_ 2011; 355: 257–263. Article CAS Google Scholar * Ali N, Allam H, May R, Sureban
SM, Bronze MS, Bader T _et al_. Hepatitis C virus-induced cancer stem cell-like signatures in cell culture and murine tumor xenografts. _J Virol_ 2011; 85: 12292–12303. Article CAS Google
Scholar * Guo Y, Chen Y, Ito H, Watanabe A, Ge X, Kodama T _et al_. Identification and characterization of lin-28 homolog B (LIN28B) in human hepatocellular carcinoma. _Gene_ 2006; 384:
51–61. Article CAS Google Scholar * Piskounova E, Polytarchou C, Thornton JE, LaPierre RJ, Pothoulakis C, Hagan JP _et al_. Lin28A and Lin28B inhibit let-7 microRNA biogenesis by distinct
mechanisms. _Cell_ 2011; 147: 1066–1079. Article CAS Google Scholar * King CE, Wang L, Winograd R, Madison BB, Mongroo PS, Johnstone CN _et al_. LIN28B fosters colon cancer migration,
invasion and transformation through let-7-dependent and -independent mechanisms. _Oncogene_ 2011; 30: 4185–4193. Article CAS Google Scholar * Wang Y, Cui F, Lv Y, Li C, Xu X, Deng C _et
al_. HBsAg and HBx knocked into the p21 locus causes hepatocellular carcinoma in mice. _Hepatology_ 2004; 39: 318–324. Article CAS Google Scholar * Wu HY, Chang CI, Lin BW, Yu FL, Lin PY,
Hsu JL _et al_. Suppression of hepatitis B virus x protein-mediated tumorigenic effects by ursolic Acid. _J Agric Food Chem_ 2011; 59: 1713–1722. Article CAS Google Scholar * Chang TC,
Zeitels LR, Hwang HW, Chivukula RR, Wentzel EA, Dews M _et al_. Lin-28B transactivation is necessary for Myc-mediated let-7 repression and proliferation. _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 2009; 106:
3384–3389. Article CAS Google Scholar * Li W, Miao X, Qi Z, Zeng W, Liang J, Liang Z . Hepatitis B virus X protein upregulates HSP90alpha expression via activation of c-Myc in human
hepatocarcinoma cell line, HepG2. _Virol J_ 2010; 7: 45. Article Google Scholar * Kong GY, Zhang JP, Zhang S, Shan CL, Ye LH, Zhang XD . Hepatitis B virus X protein promotes hepatoma cell
proliferation via upregulation of MEKK2. _Acta Pharmacol Sin_ 2011; 32: 1173–1180. Article CAS Google Scholar * Liang L, Wong CM, Ying Q, Fan DN, Huang S, Ding J _et al_. MicroRNA-125b
suppressesed human liver cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by directly targeting oncogene LIN28B2. _Hepatology_ 2010; 52: 1731–1740. Article CAS Google Scholar * Tang H, Oishi N,
Kaneko S, Murakami S . Molecular functions and biological roles of hepatitis B virus x protein. _Cancer Sci_ 2006; 97: 977–983. Article CAS Google Scholar * Helland A, Anglesio MS, George
J, Cowin PA, Johnstone CN, House CM _et al_. Deregulation of MYCN, LIN28B and LET7 in a molecular subtype of aggressive high-grade serous ovarian cancers. _PLoS One_ 2011; 6: e18064.
Article CAS Google Scholar * King CE, Cuatrecasas M, Castells A, Sepulveda AR, Lee JS, Rustgi AK . LIN28B promotes colon cancer progression and metastasis. _Cancer Res_ 2011; 71:
4260–4268. Article CAS Google Scholar * Hamano R, Miyata H, Yamasaki M, Sugimura K, Tanaka K, Kurokawa Y _et al_. High expression of Lin28 is associated with tumour aggressiveness and
poor prognosis of patients in oesophagus cancer. _Br J Cancer_ 2012; 106: 1415–1423. Article CAS Google Scholar * Wang YC, Chen YL, Yuan RH, Pan HW, Yang WC, Hsu HC _et al_. Lin-28B
expression promotes transformation and invasion in human hepatocellular carcinoma. _Carcinogenesis_ 2010; 31: 1516–1522. Article CAS Google Scholar * Safe S, Abdelrahim M . Sp
transcription factor family and its role in cancer. _Eur J Cancer_ 2005; 41: 2438–2448. Article CAS Google Scholar * Abdelrahim M, Smith R, Burghardt R, Safe S . Role of Sp proteins in
regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression and proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells. _Cancer Res_ 2004; 64: 6740–6749. Article CAS Google Scholar * Sze KM, Wong KL,
Chu GK, Lee JM, Yau TO, Ng IO . Loss of phosphatase and tensin homolog enhances cell invasion and migration through AKT/Sp-1 transcription factor/matrix metalloproteinase 2 activation in
hepatocellular carcinoma and has clinicopathologic significance. _Hepatology_ 2011; 53: 1558–1569. Article CAS Google Scholar * Qadri I, Maguire HF, Siddiqui A . Hepatitis B virus
transactivator protein X interacts with the TATA-binding protein. _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 1995; 92: 1003–1007. Article CAS Google Scholar * Shon JK, Shon BH, Park IY, Lee SU, Fa L, Chang
KY _et al_. Hepatitis B virus-X protein recruits histone deacetylase 1 to repress insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 transcription. _Virus Res_ 2009; 139: 14–21. Article CAS
Google Scholar * Li L, Jin R, Zhang X, Lv F, Liu L, Liu D _et al_. Oncogenic activation of GPC3 by c-Myc in human hepatocellular carcinoma. _Hepatology_ 2012; 56: 1380–1390. Article CAS
Google Scholar * Arzumanyan A, Friedman T, Ng IO, Clayton MM, Lian Z, Feitelson MA . Does the hepatitis B antigen HBx promote the appearance of liver cancer stem cells? _Cancer Res_ 2011;
71: 3701–3708. Article CAS Google Scholar * Kim HH, Kuwano Y, Srikantan S, Lee EK, Martindale JL, Gorospe M . HuR recruits let-7/RISC to repress c-Myc expression. _Genes Dev_ 2009; 23:
1743–1748. Article CAS Google Scholar * Zhang X, Dong N, Zhang H, You J, Wang H, Ye L . Effects of hepatitis B virus X protein on human telomerase reverse transcriptase expression and
activity in hepatoma cells. _J Lab Clin Med_ 2005; 145: 98–104. Article CAS Google Scholar * Zhang X, Dong N, Yin L, Cai N, Ma H, You J _et al_. Hepatitis B virus X protein upregulates
survivin expression in hepatoma tissues. _J Med Virol_ 2005; 77: 374–381. Article CAS Google Scholar * Carmona S, Ely A, Crowther C, Moolla N, Salazar FH, Marion PL _et al_. Effective
inhibition of HBV replication in vivo by anti-HBx short hairpin RNAs. _Mol Ther_ 2006; 13: 411–421. Article CAS Google Scholar * Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ . Analyzing real-time PCR data by
the comparative C(T) method. _Nat Protoc_ 2008; 3: 1101–1108. Article CAS Google Scholar * Kong G, Zhang J, Zhang S, Shan C, Ye L, Zhang X . Upregulated microRNA-29a by hepatitis B virus
X protein enhances hepatoma cell migration by targeting PTEN in cell culture model. _PLoS One_ 2011; 6: e19518. Article CAS Google Scholar * Fang H, Sodja C, Chartier J, Desbois A, Lei J,
Walker PR _et al_. Identification of a functional CRE in the promoter of Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy gene fukutin. _Brain Res Mol Brain Res_ 2005; 136: 1–11. Article CAS Google
Scholar * Shan C, Zhang S, Cui W, You X, Kong G, Du Y _et al_. Hepatitis B virus X protein activates CD59 involving DNA binding and let-7i in protection of hepatoma and hepatic cells from
complement attack. _Carcinogenesis_ 2011; 32: 1190–1197. Article CAS Google Scholar * Liu Q, Chen J, Liu L, Zhang J, Wang D, Ma L _et al_. The X protein of hepatitis B virus inhibits
apoptosis in hepatoma cells through enhancing the methionine adenosyltransferase 2A gene expression and reducing S-adenosylmethionine production. _J Biol Chem_ 2011; 286: 17168–17180.
Article CAS Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank Dr Xiao Yang (from the Genetic Laboratory of Development and Diseases, Institute of Biotechnology, Beijing,
People’s Republic of China) for kindly providing the HBx transgenic mice. This work was supported in part by National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, No. 2009CB521702) and
National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81071624, 81272218). AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Cancer Research, Key Laboratory of Molecular Microbiology
and Technology of Ministry of Education, College of Life Sciences, Nankai University, Tianjin, People’s Republic of China X You, T Zhang, N Lv, C Shan, Y Du, G Kong, T Wang & X Zhang *
Department of Biochemistry, College of Life Sciences, Nankai University, Tianjin, People’s Republic of China F Liu, Q Liu & L Ye Authors * X You View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * F Liu View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * T Zhang View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * N Lv View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Q Liu View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * C Shan View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Y Du View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * G Kong View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * T Wang View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * L Ye View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * X Zhang View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHORS Correspondence to L Ye or X Zhang. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no conflict of interest.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S1 (JPG 93 KB) SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S2 (JPG 163
KB) SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S3 (JPG 178 KB) SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S4 (JPG 139 KB) SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S5 (JPG 169 KB) SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S6 (JPG 1050 KB) SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S7 (JPG 451 KB)
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS (DOC 31 KB) SUPPLEMENTARY TABLE 1 (JPG 396 KB) RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE You, X., Liu, F., Zhang, T.
_et al._ Hepatitis B virus X protein upregulates Lin28A/Lin28B through Sp-1/c-Myc to enhance the proliferation of hepatoma cells. _Oncogene_ 33, 449–460 (2014).
https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.618 Download citation * Received: 22 May 2012 * Revised: 02 November 2012 * Accepted: 14 November 2012 * Published: 14 January 2013 * Issue Date: 23 January
2014 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.618 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is
not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS * hepatitis B virus X protein * Lin28A * Lin28B *
proliferation * hepatocellular carcinoma





