- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
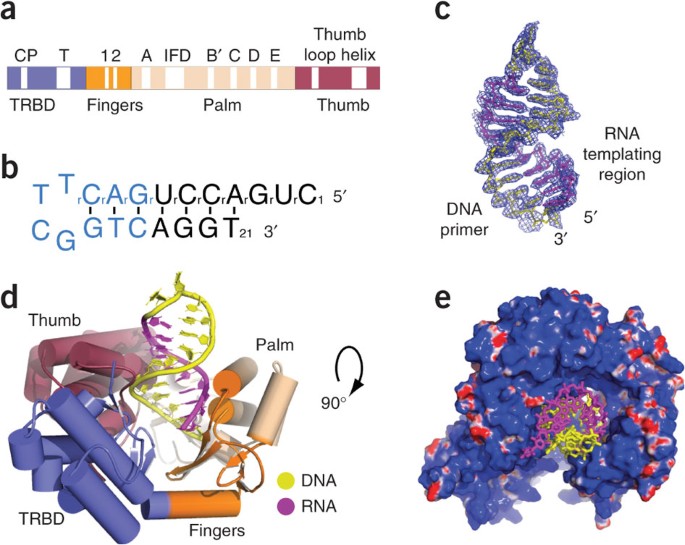
ABSTRACT Telomerase is a specialized DNA polymerase that extends the 3′ ends of eukaryotic linear chromosomes, a process required for genomic stability and cell viability. Here we present
the crystal structure of the active _Tribolium castaneum_ telomerase catalytic subunit, TERT, bound to an RNA-DNA hairpin designed to resemble the putative RNA-templating region and
telomeric DNA. The RNA-DNA hybrid adopts a helical structure, docked in the interior cavity of the TERT ring. Contacts between the RNA template and motifs 2 and B′ position the
solvent-accessible RNA bases close to the enzyme active site for nucleotide binding and selectivity. Nucleic acid binding induces rigid TERT conformational changes to form a tight catalytic
complex. Overall, TERT–RNA template and TERT–telomeric DNA associations are remarkably similar to those observed for retroviral reverse transcriptases, suggesting common mechanistic aspects
of DNA replication between the two families of enzymes. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS
Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $209.00 per year only $17.42 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on
SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about
institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS ZIPPER HEAD MECHANISM OF TELOMERE SYNTHESIS BY HUMAN TELOMERASE Article Open
access 15 November 2021 STRUCTURES OF TELOMERASE AT SEVERAL STEPS OF TELOMERE REPEAT SYNTHESIS Article 12 May 2021 STRUCTURE OF ACTIVE HUMAN TELOMERASE WITH TELOMERE SHELTERIN PROTEIN TPP1
Article 13 April 2022 ACCESSION CODES PRIMARY ACCESSIONS PROTEIN DATA BANK * 3KYL REFERENCES * Gillis, A.J., Schuller, A.P. & Skordalakes, E. Structure of the _Tribolium castaneum_
telomerase catalytic subunit TERT. _Nature_ 455, 633–637 (2008). Article CAS Google Scholar * Greider, C.W. & Blackburn, E.H. Identification of a specific telomere terminal
transferase activity in _Tetrahymena_ extracts. _Cell_ 43, 405–413 (1985). Article CAS Google Scholar * Harley, C.B., Futcher, A.B. & Greider, C.W. Telomeres shorten during ageing of
human fibroblasts. _Nature_ 345, 458–460 (1990). Article CAS Google Scholar * Kim, N.W. et al. Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal cells and cancer. _Science_
266, 2011–2015 (1994). Article CAS Google Scholar * Harley, C.B., Vaziri, H., Counter, C.M. & Allsopp, R.C. The telomere hypothesis of cellular aging. _Exp. Gerontol._ 27, 375–382
(1992). Article CAS Google Scholar * Harley, C.B. & Villeponteau, B. Telomeres and telomerase in aging and cancer. _Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev._ 5, 249–255 (1995). Article CAS Google
Scholar * Harley, C.B. Telomerase and cancer therapeutics. _Nat. Rev. Cancer_ 8, 167–179 (2008). Article CAS Google Scholar * Bosoy, D., Peng, Y., Mian, I.S. & Lue, N.F. Conserved
N-terminal motifs of telomerase reverse transcriptase required for ribonucleoprotein assembly _in vivo_. _J. Biol. Chem._ 278, 3882–3890 (2003). Article CAS Google Scholar * Bryan, T.M.,
Goodrich, K.J. & Cech, T.R. Telomerase RNA bound by protein motifs specific to telomerase reverse transcriptase. _Mol. Cell_ 6, 493–499 (2000). Article CAS Google Scholar * Lai, C.K.,
Mitchell, J.R. & Collins, K. RNA binding domain of telomerase reverse transcriptase. _Mol. Cell. Biol._ 21, 990–1000 (2001). Article CAS Google Scholar * Drosopoulos, W.C. &
Prasad, V.R. Telomerase-specific T motif is a restrictive determinant of repetitive reverse transcription by human telomerase. _Mol. Cell. Biol._ 30, 447–459 (2010). Article CAS Google
Scholar * Rouda, S. & Skordalakes, E. Structure of the RNA-binding domain of telomerase: implications for RNA recognition and binding. _Structure_ 15, 1403–1412 (2007). Article CAS
Google Scholar * Hammond, P.W., Lively, T.N. & Cech, T.R. The anchor site of telomerase from _Euplotes aediculatus_ revealed by photo-cross-linking to single- and double-stranded DNA
primers. _Mol. Cell. Biol._ 17, 296–308 (1997). Article CAS Google Scholar * Jacobs, S.A., Podell, E.R. & Cech, T.R. Crystal structure of the essential N-terminal domain of telomerase
reverse transcriptase. _Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol._ 13, 218–225 (2006). Article CAS Google Scholar * Wyatt, H.D., Lobb, D.A. & Beattie, T.L. Characterization of physical and functional
anchor site interactions in human telomerase. _Mol. Cell. Biol._ 27, 3226–3240 (2007). Article CAS Google Scholar * Moriarty, T.J., Marie-Egyptienne, D.T. & Autexier, C. Functional
organization of repeat addition processivity and DNA synthesis determinants in the human telomerase multimer. _Mol. Cell. Biol._ 24, 3720–3733 (2004). Article CAS Google Scholar * Wyatt,
H.D., Tsang, A.R., Lobb, D.A. & Beattie, T.L. Human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) Q169 is essential for telomerase function _in vitro_ and _in vivo_. _PLoS One_ 4, e7176
(2009). Article Google Scholar * Chen, J.L. & Greider, C.W. An emerging consensus for telomerase RNA structure. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 101, 14683–14684 (2004). Article CAS
Google Scholar * Lin, J. et al. A universal telomerase RNA core structure includes structured motifs required for binding the telomerase reverse transcriptase protein. _Proc. Natl. Acad.
Sci. USA_ 101, 14713–14718 (2004). Article CAS Google Scholar * Gilley, D., Lee, M.S. & Blackburn, E.H. Altering specific telomerase RNA template residues affects active site
function. _Genes Dev._ 9, 2214–2226 (1995). Article CAS Google Scholar * Greider, C.W. & Blackburn, E.H. A telomeric sequence in the RNA of _Tetrahymena_ telomerase required for
telomere repeat synthesis. _Nature_ 337, 331–337 (1989). Article CAS Google Scholar * Lee, M.S. & Blackburn, E.H. Sequence-specific DNA primer effects on telomerase polymerization
activity. _Mol. Cell. Biol._ 13, 6586–6599 (1993). Article CAS Google Scholar * Lingner, J., Hendrick, L.L. & Cech, T.R. Telomerase RNAs of different ciliates have a common secondary
structure and a permuted template. _Genes Dev._ 8, 1984–1998 (1994). Article CAS Google Scholar * Shippen-Lentz, D. & Blackburn, E.H. Functional evidence for an RNA template in
telomerase. _Science_ 247, 546–552 (1990). Article CAS Google Scholar * Autexier, C. & Greider, C.W. Boundary elements of the _Tetrahymena_ telomerase RNA template and alignment
domains. _Genes Dev._ 9, 2227–2239 (1995). Article CAS Google Scholar * Harrington, L.A. & Greider, C.W. Telomerase primer specificity and chromosome healing. _Nature_ 353, 451–454
(1991). Article CAS Google Scholar * Greider, C.W. Telomerase is processive. _Mol. Cell. Biol._ 11, 4572–4580 (1991). Article CAS Google Scholar * Wang, F. et al. The POT1–TPP1
telomere complex is a telomerase processivity factor. _Nature_ 445, 506–510 (2007). Article CAS Google Scholar * Zaug, A.J., Podell, E.R. & Cech, T.R. Mutation in TERT separates
processivity from anchor-site function. _Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol._ 15, 870–872 (2008). Article CAS Google Scholar * Finger, S.N. & Bryan, T.M. Multiple DNA-binding sites in
_Tetrahymena_ telomerase. _Nucleic Acids Res._ 36, 1260–1272 (2008). Article CAS Google Scholar * Osanai, M., Kojima, K.K., Futahashi, R., Yaguchi, S. & Fujiwara, H. Identification
and characterization of the telomerase reverse transcriptase of _Bombyx mori_ (silkworm) and _Tribolium castaneum_ (flour beetle). _Gene_ 376, 281–289 (2006). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Richards, S. et al. The genome of the model beetle and pest _Tribolium castaneum_. _Nature_ 452, 949–955 (2008). Article CAS Google Scholar * Bosoy, D. & Lue, N.F. Functional
analysis of conserved residues in the putative “finger” domain of telomerase reverse transcriptase. _J. Biol. Chem._ 276, 46305–46312 (2001). Article CAS Google Scholar * Hossain, S.,
Singh, S. & Lue, N.F. Functional analysis of the C-terminal extension of telomerase reverse transcriptase. A putative “thumb” domain. _J. Biol. Chem._ 277, 36174–36180 (2002). Article
CAS Google Scholar * Huang, H., Chopra, R., Verdine, G.L. & Harrison, S.C. Structure of a covalently trapped catalytic complex of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase: implications for drug
resistance. _Science_ 282, 1669–1675 (1998). Article CAS Google Scholar * Sarafianos, S.G. et al. Crystal structure of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase in complex with a polypurine tract
RNA:DNA. _EMBO J._ 20, 1449–1461 (2001). Article CAS Google Scholar * Lue, N.F., Lin, Y.C. & Mian, I.S. A conserved telomerase motif within the catalytic domain of telomerase reverse
transcriptase is specifically required for repeat addition processivity. _Mol. Cell. Biol._ 23, 8440–8449 (2003). Article CAS Google Scholar * Jacobo-Molina, A. et al. Crystal structure
of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase complexed with double-stranded DNA at 3.0 Å resolution shows bent DNA. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 90, 6320–6324 (1993). Article
CAS Google Scholar * Kohlstaedt, L.A., Wang, J., Friedman, J.M., Rice, P.A. & Steitz, T.A. Crystal structure at 3.5 Å resolution of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase complexed with an
inhibitor. _Science_ 256, 1783–1790 (1992). Article CAS Google Scholar * Drosopoulos, W.C. & Prasad, V.R. The active site residue Valine 867 in human telomerase reverse transcriptase
influences nucleotide incorporation and fidelity. _Nucleic Acids Res._ 35, 1155–1168 (2007). Article CAS Google Scholar * Rodgers, D.W. et al. The structure of unliganded reverse
transcriptase from the human immunodeficiency virus type 1. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 92, 1222–1226 (1995). Article CAS Google Scholar * Steitz, T.A. DNA and RNA polymerases:
structural diversity and common mechanisms. _Harvey Lect._ 93, 75–93 (1997). PubMed Google Scholar * Beese, L.S., Derbyshire, V. & Steitz, T.A. Structure of DNA polymerase I Klenow
fragment bound to duplex DNA. _Science_ 260, 352–355 (1993). Article CAS Google Scholar * Tantillo, C. et al. Locations of anti-AIDS drug binding sites and resistance mutations in the
three-dimensional structure of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Implications for mechanisms of drug inhibition and resistance. _J. Mol. Biol._ 243, 369–387 (1994). Article CAS Google Scholar
* Cases-Gonzalez, C.E., Gutierrez-Rivas, M. & Menendez-Arias, L. Coupling ribose selection to fidelity of DNA synthesis. The role of Tyr-115 of human immunodeficiency virus type 1
reverse transcriptase. _J. Biol. Chem._ 275, 19759–19767 (2000). Article CAS Google Scholar * Ding, J. et al. Structure and functional implications of the polymerase active site region in
a complex of HIV-1 RT with a double-stranded DNA template-primer and an antibody Fab fragment at 2.8 Å resolution. _J. Mol. Biol._ 284, 1095–1111 (1998). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Steitz, T.A. DNA polymerases: structural diversity and common mechanisms. _J. Biol. Chem._ 274, 17395–17398 (1999). Article CAS Google Scholar * Bressanelli, S., Tomei, L., Rey, F.A.
& De Francesco, R. Structural analysis of the hepatitis C virus RNA polymerase in complex with ribonucleotides. _J. Virol._ 76, 3482–3492 (2002). Article CAS Google Scholar * Ling,
H., Boudsocq, F., Woodgate, R. & Yang, W. Crystal structure of a Y-family DNA polymerase in action: a mechanism for error-prone and lesion-bypass replication. _Cell_ 107, 91–102 (2001).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Jeruzalmi, D., O'Donnell, M. & Kuriyan, J. Clamp loaders and sliding clamps. _Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol._ 12, 217–224 (2002). Article CAS Google
Scholar * Chen, J.L. & Greider, C.W. Template boundary definition in mammalian telomerase. _Genes Dev._ 17, 2747–2752 (2003). Article CAS Google Scholar * Lai, C.K., Miller, M.C.
& Collins, K. Template boundary definition in _Tetrahymena_ telomerase. _Genes Dev._ 16, 415–420 (2002). Article CAS Google Scholar * Tzfati, Y., Fulton, T.B., Roy, J. &
Blackburn, E.H. Template boundary in a yeast telomerase specified by RNA structure. _Science_ 288, 863–867 (2000). Article CAS Google Scholar * Sasaki, T. & Fujiwara, H. Detection and
distribution patterns of telomerase activity in insects. _Eur. J. Biochem._ 267, 3025–3031 (2000). Article CAS Google Scholar * Holton, J. & Alber, T. Automated protein crystal
structure determination using ELVES. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 101, 1537–1542 (2004). Article CAS Google Scholar * Potterton, E., Briggs, P., Turkenburg, M. & Dodson, E. A
graphical user interface to the CCP4 program suite. _Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr._ 59, 1131–1137 (2003). Article Google Scholar * Brunger, A.T. et al. Crystallography & NMR
system: A new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. _Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr._ 54, 905–921 (1998). Article CAS Google Scholar * Emsley, P. & Cowtan,
K. Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. _Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr._ 60, 2126–2132 (2004). Article Google Scholar * Murshudov, G.N., Vagin, A.A. & Dodson,
E.J. Refinement of macromolecular structures by the maximum-likelihood method. _Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr._ 53, 240–255 (1997). Article CAS Google Scholar Download references
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We would like to thank S.J. Gamblin and S. Pennell for helpful discussions. Funding for this project was generously provided by the Ellison Medical and the V Foundations as
well as the Pennsylvania Department of Health. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Gene Expression and Regulation Program, The Wistar Institute, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA
Meghan Mitchell, Andrew Gillis & Emmanuel Skordalakes * Department of Integrated Biosciences, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, University of Tokyo, Kashiwa, Japan Mizuko Futahashi
& Haruhiko Fujiwara Authors * Meghan Mitchell View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Andrew Gillis View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Mizuko Futahashi View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Haruhiko Fujiwara View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Emmanuel Skordalakes View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
CONTRIBUTIONS E.S. designed the experiment plan, analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript; A.G. prepared the recombinant telomerase and carried out the reverse transcriptase assays; M.M.
carried out the TRAP assays; H.F. and M.F. provided advice with the _T. castaneum_ TRAP assays. CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Emmanuel Skordalakes. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING
INTERESTS The authors declare no competing financial interests. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY TEXT AND FIGURES Supplementary Figures 1–4 (PDF 2115 kb) RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS
Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Mitchell, M., Gillis, A., Futahashi, M. _et al._ Structural basis for telomerase catalytic subunit TERT binding to RNA template
and telomeric DNA. _Nat Struct Mol Biol_ 17, 513–518 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1777 Download citation * Received: 17 October 2009 * Accepted: 20 January 2010 * Published: 28 March
2010 * Issue Date: April 2010 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1777 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative