- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
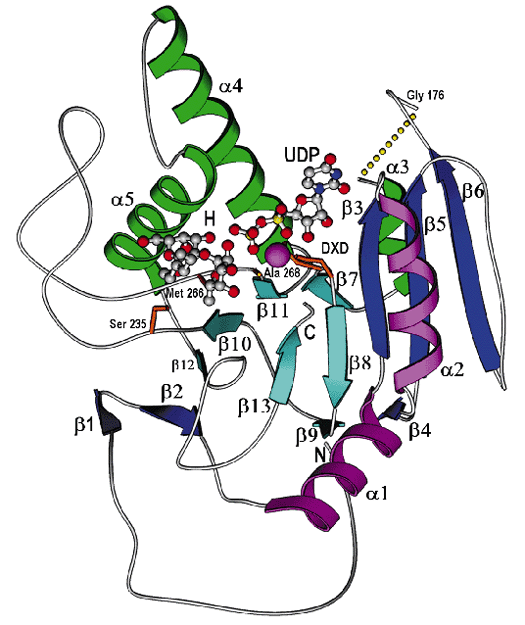
ABSTRACT The human ABO(H) blood group antigens are produced by specific glycosyltransferase enzymes. An N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase (GTA) uses a UDP-GalNAc donor to convert the
H-antigen acceptor to the A antigen, whereas a galactosyltransferase (GTB) uses a UDP-galactose donor to convert the H-antigen acceptor to the B antigen. GTA and GTB differ only in the
identity of four critical amino acid residues. Crystal structures at 1.8–1.32 Å resolution of the GTA and GTB enzymes both free and in complex with disaccharide H-antigen acceptor and UDP
reveal the basis for donor and acceptor specificity and show that only two of the critical amino acid residues are positioned to contact donor or acceptor substrates. Given the need for
stringent stereo- and regioselectivity in this biosynthesis, these structures further demonstrate that the ability of the two enzymes to distinguish between the A and B donors is largely
determined by a single amino acid residue. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access
through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $209.00 per year only $17.42 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink *
Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional
subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS TURNING UNIVERSAL O INTO RARE BOMBAY TYPE BLOOD Article Open access 30 March 2023 THE
RETAINING Β-KDO GLYCOSYLTRANSFERASE WBBB USES A DOUBLE-DISPLACEMENT MECHANISM WITH AN INTERMEDIATE ADDUCT REARRANGEMENT STEP Article Open access 21 October 2022 _AKKERMANSIA MUCINIPHILA_
EXOGLYCOSIDASES TARGET EXTENDED BLOOD GROUP ANTIGENS TO GENERATE ABO-UNIVERSAL BLOOD Article 29 April 2024 ACCESSION CODES ACCESSIONS PROTEIN DATA BANK * 1LZ0 * 1LZ7 * 1LZI * 1LZJ REFERENCES
* Landsteiner, K. _Wein Klin. Wschr._ 14, 1132–1134 (1901). Google Scholar * Watkins, W.M. & Morgan, W.T.J. _Nature_ 180, 1038–1040 (1957). Article CAS Google Scholar * Kabat, E.A.
_Blood Group Substances: Their Chemistry and Immunochemistry_ (Academic Press, New York; 1956). Google Scholar * Watkins, W.M. & Morgan, W.T.J. _Vox. Sang._ 4, 97–119 (1959). Article
CAS Google Scholar * Tuppy, H. & Staudenbauer, W.L. _Nature_ 210, 316–317 (1966). Article CAS Google Scholar * Hearn, V.M., Smith, Z.G. & Watkins, W.M. _Biochem. J._ 109,
315–317 (1968). Article CAS Google Scholar * Kobata, A., Grollman, E.F. & Ginsburg, V. _Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun._ 32, 272–277 (1968). Article CAS Google Scholar * Yamamoto,
F., Clausen, H., White, T., Marken, J. & Hakomori, S. _Nature_ 345, 229–233 (1990). Article CAS Google Scholar * Gastinel, L.N. et al. _EMBO J._ 20, 638–649 (2001). Article CAS
Google Scholar * Boix, E. et al. _J. Biol. Chem._ 276, 48608–48614 (2001). Article CAS Google Scholar * Breton, C., Bettler, E., Joziasse, D.H., Geremia, R.A. & Imberty, A. _J.
Biochem._ 123, 1000–1009 (1998). Article CAS Google Scholar * Busch, C. et al. _J. Biol. Chem._ 273, 19566–19572 (1998). Article CAS Google Scholar * Persson, K. et al. _Nature Struct.
Biol._ 8, 166–175 (2001). Article CAS Google Scholar * Charnock, S.J. & Davies, G.J. _Biochemistry_ 38, 6380–6385 (1999). Article CAS Google Scholar * Ünligil, U.M. et al. _EMBO
J._ 19, 5269–5280 (2000). Article Google Scholar * Pedersen, L.C. et al. _J. Biol. Chem._ 275, 34580–34585 (2000). Article CAS Google Scholar * Gastinel, L.N., Cambillau, C. &
Bourne, Y. _EMBO J._ 18, 3546–3557 (1999). Article CAS Google Scholar * Lowary, T.L. & Hindsgaul, O. _Carbhydr. Res._ 249, 163–195 (1993). Article CAS Google Scholar * Lowary, T.L.
& Hindsgaul, O. _Carbhydr. Res._ 251, 33–67 (1994). Article CAS Google Scholar * Mukherjee, A., Palcic, M.M. & Hindsgaul, O. _Carbhydr. Res._ 326, 1–21 (2000). Article CAS
Google Scholar * Kamath, V.P., Seto, N.O.L., Compston, C.A., Hindsgaul, O. & Palcic, M.M. _Glycoconj. J._ 16, 599–606 (1999). Article CAS Google Scholar * Seto, N.O.L. et al. _J.
Biol. Chem._ 272, 14133–14138 (1997). Article CAS Google Scholar * Seto, N.O.L. et al. _Eur. J. Biochem._ 259, 770–775 (1999). Article CAS Google Scholar * Vrielink, A., Rüger, W.,
Driessen, H.P.C. & Freemont, P.S. _EMBO J._ 13, 3413–3422 (1994). Article CAS Google Scholar * Moréra, S., Imberty, A., Aschke-Sonnenborn, U., Rüger, W. & Freemont, P.S. _J. Mol.
Biol._ 292, 717–730 (1999). Article Google Scholar * Takayama, S. et al. _Bioorg. Med. Chem._ 7, 401–409 (1999). Article CAS Google Scholar * Davies, G.J., Sinnott, M.L. & Withers,
S.G. in _Comprehensive Biological Catalysis_ Vol. I (ed. Sinnott, M.L.) 119–209 (Academic Press, San Diego; 1998). Google Scholar * Sinnott, M.L. _Chem. Rev._ 90, 1171–1202 (1990) Article
CAS Google Scholar * Ly, H.D. & Withers, S.G. _Annu. Rev. Biochem._ 68, 487–522 (1999). Article CAS Google Scholar * Seto, N.O.L., Compston, C.A., Szpacenko, A. & Palcic, M.M.
_Carbohydr. Res._ 324, 161–169 (2000). Article CAS Google Scholar * Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. _Methods Enzymol._ 276, 307–326 (1997). Article CAS Google Scholar * Smith, G.D.,
Nagar, B., Rini, J.M., Hauptman, H.A & Blessing, R.H. _Acta Crystallogr. D_ 54, 799–804 (1998). Article CAS Google Scholar * Brünger, A.T. et al. _Acta Crystallogr. D_ 54, 905–921
(1998). Article Google Scholar * van Asselt, E.J., Perrakis, A., Kalk, K.H., Lamzin, V.S. & Dijkstra, B.W. _Acta Crystallogr. D_ 54, 58–73 (1998). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Evans, S.V. _J. Mol. Graph._ 11, 134–138 (1993). Article CAS Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS S.I.P. and S.V.E. thank the Canadian Institutes of Health Research for
salary support and funding. M.M.P. thanks the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada for funding. The authors thank D.R. Bundle and O. Hindsgaul for helpful discussions,
as well as C. Weeks, J. Berendzen and R.W. Grosse-Kuntsleeve for help while at Brookhaven National Laboratories beamlines X4A, X8C and X12C. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS *
Department of Biochemistry, Microbiology and Immunology, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, K1H 8M5, Canada Sonia I. Patenaude, Nina O.L. Seto, Svetlana N. Borisova & Stephen V. Evans *
Institute for Biological Sciences, National Research Council of Canada, Ottawa, K1A 0R6, Canada Nina O.L. Seto * Department of Chemistry, University of Alberta, Edmonton, T6G 2G2, Canada
Adam Szpacenko, Sandra L. Marcus & Monica M. Palcic Authors * Sonia I. Patenaude View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Nina O.L. Seto
View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Svetlana N. Borisova View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google
Scholar * Adam Szpacenko View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Sandra L. Marcus View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * Monica M. Palcic View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Stephen V. Evans View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Stephen V. Evans. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing financial
interests. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Patenaude, S., Seto, N., Borisova, S. _et al._ The structural basis for specificity in human
ABO(H) blood group biosynthesis. _Nat Struct Mol Biol_ 9, 685–690 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb832 Download citation * Received: 22 April 2002 * Accepted: 17 July 2002 * Published: 19
August 2002 * Issue Date: 01 September 2002 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb832 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable
link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative









