- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
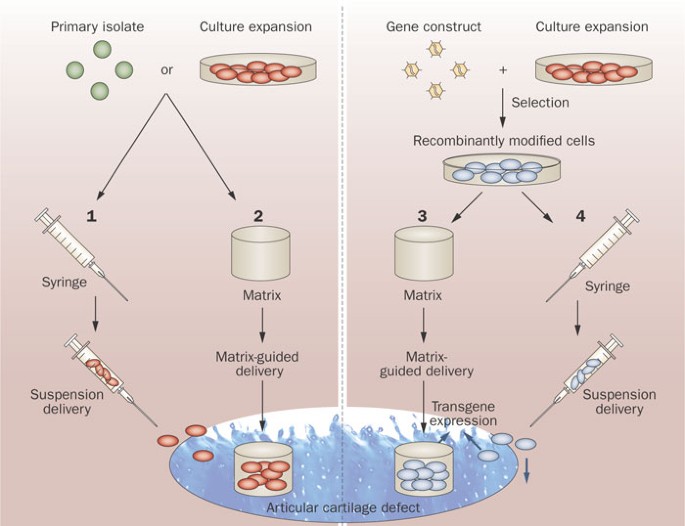
New research reports that primary human dermal fibroblasts seeded into a three-dimensional biodegradable matrix can differentiate _in vitro_ into osteoblasts and chondrocytes, and form
three-dimensional bone-like and cartilage-like constructs, respectively. Is skeletal tissue engineering from skin biopsy tissue on the horizon? Access through your institution Buy or
subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online
access $209.00 per year only $17.42 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which
are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support REFERENCES * Sommar, P. _ et al_.
Engineering three-dimensional cartilage- and bone-like tissues using human dermal fibroblasts and macroporous gelatine microcarriers. _J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg._
doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2009.02.072. Article Google Scholar * Tuan, R. S., Lee, F. Y., Kontinnen, T. Y., Wilkinson, J. M. & Smith, R. L. What are the local and systemic biologic reactions
and mediators to wear debris, and what host factors determine or modulate the biological response to wear particles? _J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg._ 16 (Suppl. 1), S42–S48 (2008). Article
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Atala, A., Lanza, R., Thomson, J. A. & Nerem, R. M. (Eds) _Principles of Regenerative Medicine_. (Academic Press, London, 2008). Google Scholar
* Hee, C. K., Jonikas, M. A. & Nicoll, S. B. Influence of three-dimensional scaffold on the expression of osteogenic differentiation markers by human dermal fibroblasts. _Biomaterials_
27, 875–884 (2006). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Mizuno, S. & Glowacki, J. Three-dimensional composite of demineralized bone powder and collagen for _in vitro_ analysis of
chondroinduction of human dermal fibroblasts. _Biomaterials_ 17, 1819–1825 (1996). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Pittenger M. F. _ et al_. Multilineage potential of adult human
mesenchymal stem cells. _Science_ 284, 143–147 (1999). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Elisseeff, J., Ferran, A., Hwang, S., Varghese, S. & Zhang, Z. The role of biomaterials in
stem cell differentiation: applications in the musculoskeletal system. _Stem Cells Dev._ 15, 295–303 (2006). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Mauck, R. L., Yuan, X. & Tuan, R. S.
Chondrogenic differentiation and functional maturation of bovine mesenchymal stem cells in long-term agarose culture. _Osteoarthritis Cartilage_ 14, 179–189 (2005). Article PubMed Google
Scholar * Noth, U., Steinert, A. F. & Tuan, R. S. Technology insight: adult mesenchymal stem cells for osteoarthritis therapy. _Nat. Clin. Pract. Rheumatol._ 4, 371–380 (2008). Article
PubMed Google Scholar * Sherwood, J. K. _ et al_. A three-dimensional osteochondral composite scaffold for articular cartilage repair. _Biomaterials_ 23, 4739–4751 (2002). Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar Download references AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, USA Rocky S. Tuan
Authors * Rocky S. Tuan View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Rocky S. Tuan. ETHICS DECLARATIONS
COMPETING INTERESTS The author declares no competing financial interests. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Tuan, R. Skin and bones (and
cartilage): the dermal fibroblast connection. _Nat Rev Rheumatol_ 5, 471–472 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2009.170 Download citation * Issue Date: September 2009 * DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2009.170 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not
currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative








