- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
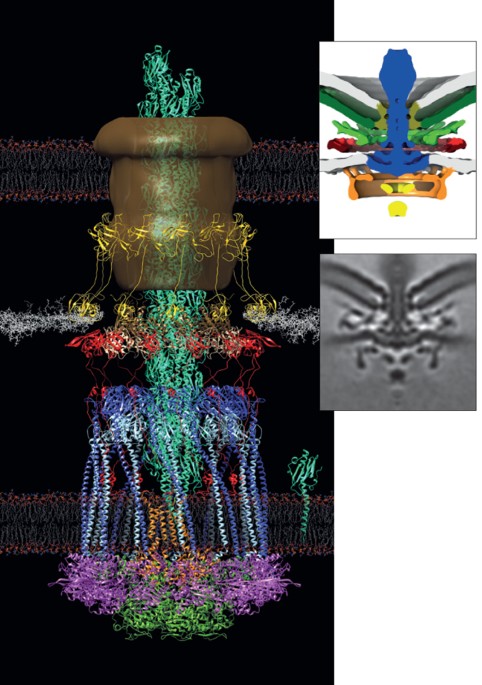
Access through your institution Buy or subscribe Embedded in the cell envelope, flagellar motors harness a proton-motive or sodium-motive force to rotate the flagellum, which is a helical
filament that is composed of flagellin subunits. Each flagellar motor contains a rotor and a stator; the heterooligomers of the stator form a ring structure that exerts a force on the rotor,
which in turn transmits torque to the filament to generate the rotating motion. Despite a conserved core structure of the motor, the swimming ability of flagellated bacteria varies between
species. To better understand the molecular bases for these differences, Beeby _et al_. studied wild-type bacterial cells from three different species (_Salmonella enterica_, _Vibrio
fischeri_ and _Campylobacter jejuni_), together with genetic mutants that lack individual components of the flagellar motor. The torque exerted by the _S. enterica_ motor has been estimated
to be in the range of 1,300−2,000 pN nm, whereas the _Vibrio_ spp. motor, which has more ready access to power owing to the sodium gradient in its marine environment, exerts an estimated
torque of 2,000−4,000 pN nm. As _C. jejuni_ has adapted to the high-viscosity environment of the epithelial mucus, its motor is expected to exert an even higher torque than that of _V.
fischeri_. The ECT images showed that the stoichiometry of stator complexes in the stator ring differs between species, with 11 in _S. enterica_ subsp. _enterica s_erovar Typhimurium, 13 in
_V. fischeri_ and 17 in _C. jejuni_. Furthermore, the 'C-ring' (the cytoplasmic ring of the rotor) was wider in _C. jejuni_, with a radius of 26 nm, than in _S_. Typhimurium and
_V. fischeri_ (with radii of 22 nm and 23 nm, respectively). The authors had previously shown that some flagellar motors have 'disc' complexes, of uncharacterized function, which
are not found in enteric bacteria such as _S_. Typhimurium. The ECT images showed that _V. fischeri_ and _C. jejuni_ have a basal disc that is associated with the periplasmic face of the
outer membrane; notably, the disc was wider in _C. jejuni_ (with a radius of 42 nm) than in _V. fischeri_ (with a radius of 28 nm). In the _V. fischeri_ motor, the previously described
T-ring and H-ring were present in addition to the basal disc. The _C. jejuni_ disc complex also had additional components, a disc associated with the inner membrane and a periplasmic disc,
but these were composed of different proteins to the T-ring and H-ring in _V. fischeri_, and also differed in complex architecture. This is a preview of subscription content, access via your
institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $209.00 per year only $17.42 per issue Learn more Buy this
article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in
* Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support REFERENCES * Beeby, M. et al. Diverse high-torque bacterial flagellar motors assemble wider stator rings
using a conserved protein scaffold. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1518952113 (2016) * Chang, Y. W. et al. Architecture of the type IVa pilus machine. _Science_
351, aad2001 (2016) Article Google Scholar Download references Authors * Naomi Attar View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar RELATED LINKS
RELATED LINKS RELATED LINKS IN NATURE RESEARCH Oikonomou, C. M. & Jensen, G. J. A new view into prokaryotic cell biology from electron cryotomography. _Nat. Rev. Microbiol._ 14, 205–220
(2016) RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Attar, N. ECT joins the rotary club. _Nat Rev Microbiol_ 14, 265 (2016).
https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2016.51 Download citation * Published: 12 April 2016 * Issue Date: May 2016 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2016.51 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share
the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer
Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(216x0:218x2)/benedict-cumberbatch-1-435-4-20cc736017b24435a3498a49d7c22b0e.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(584x489:586x491)/bill-gates-01-122122-3dca1a10ca5b4473af97402696129443.jpg)




