- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT Type 1 diabetes mellitus in pregnant women increases the risk of adverse outcomes for mother and offspring. Careful preconception counselling and screening is important, with
particular focus on glycaemic control, indications for antihypertensive therapy, screening for diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy and thyroid dysfunction, as well as review of other
medications. Supplementation with folic acid should be initiated before conception in order to minimize the risk of fetal malformations. Obtaining and maintaining tight control of blood
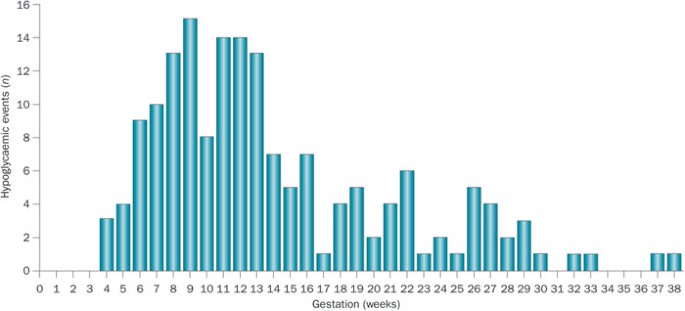
glucose and blood pressure before and during pregnancy is crucial for optimizing outcomes; however, the risk of severe hypoglycaemia during pregnancy is a major obstacle. Although pregnancy
does not result in deterioration of kidney function in women with diabetic nephropathy and normal serum creatinine levels, pregnancy complications such as pre-eclampsia and preterm delivery
are more frequent in these women than in women with T1DM and normal kidney function. Rapid-acting insulin analogues are considered safe to use in pregnancy and studies on long-acting insulin
analogues have provided reassuring results. Immediately after delivery the insulin requirement declines to approximately 60% of the prepregnancy dose, and remains 10% lower than before
pregnancy during breastfeeding. KEY POINTS * Tight maternal glycaemic and blood pressure control is crucial, and hypoglycaemia must be avoided during pregnancy * Insulin analogues can be
used before and during pregnancy * Folic acid supplementation should be initiated before conception and continued to the end of the first trimester * Maternal screening for retinopathy and
nephropathy should be carried out * Close surveillance of fetus and newborn baby is important Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content,
access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $209.00 per year only $17.42 per issue Learn
more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS
OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS METFORMIN IN GESTATIONAL DIABETES: PHYSIOLOGICAL
ACTIONS AND CLINICAL APPLICATIONS Article 25 October 2024 PRECISION GESTATIONAL DIABETES TREATMENT: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND META-ANALYSES Article Open access 05 October 2023 EARLY PREGNANCY
HYPERGLYCAEMIA AMONG PREGNANT WOMEN WITH RISK FACTORS FOR GESTATIONAL DIABETES INCREASES THE RISK OF PREGNANCY COMPLICATIONS Article Open access 24 October 2024 REFERENCES * Boulot, P. _ et
al_. French multicentric survey of outcome of pregnancy in women with pregestational diabetes. _Diabetes Care_ 26, 2990–2993 (2003). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Casson, I. F. _ et
al_. Outcomes of pregnancy in insulin dependent diabetic women: results of a five year population cohort study. _BMJ_ 315, 275–278 (1997). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google
Scholar * Confidential Enquiry into Maternal and Child Health. _Pregnancy in Women with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes in 2002–3, England, Wales and Northern Ireland_ (CEMACH, London, 2005). *
Evers, I. M., de Valk, H. W. & Visser, G. H. Risk of complications of pregnancy in women with type 1 diabetes: nationwide prospective study in the Netherlands. _BMJ_ 328, 915 (2004).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Hawthorne, G. _ et al_. Prospective population based survey of outcome of pregnancy in diabetic women: results of the Northern Diabetic
Pregnancy Audit, 1994. _BMJ_ 315, 279–281 (1997). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Jensen, D. M. _ et al_. Outcomes in type 1 diabetic pregnancies: a nationwide,
population-based study. _Diabetes Care_ 27, 2819–2823 (2004). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Lapolla, A. _ et al_. Outcome of pregnancy in type 1 diabetic patients treated with insulin
lispro or regular insulin: an Italian experience. _Acta Diabetol._ 45, 61–66 (2008). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Macintosh, M. C. _ et al_. Perinatal mortality and congenital
anomalies in babies of women with type 1 or type 2 diabetes in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland: population based study. _BMJ_ 333, 177 (2006). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google
Scholar * Penney, G. C., Mair, G. & Pearson, D. W. Outcomes of pregnancies in women with type 1 diabetes in Scotland: a national population-based study. _BJOG_ 110, 315–318 (2003).
Article PubMed Google Scholar * Platt, M. J. _ et al_. St Vincent's Declaration 10 years on: outcomes of diabetic pregnancies. _Diabet. Med._ 19, 216–220 (2002). Article CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Yang, J., Cummings, E. A., O'Connell, C. & Jangaard, K. Fetal and neonatal outcomes of diabetic pregnancies. _Obstet. Gynecol._ 108, 644–650 (2006). Article
PubMed Google Scholar * Lapolla, A. _ et al_. A multicenter Italian study on pregnancy outcome in women with diabetes. _Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis._ 18, 291–297 (2008). Article PubMed
Google Scholar * Persson, M., Norman, M. & Hanson, U. Obstetric and perinatal outcomes in type 1 diabetic pregnancies: A large, population-based study. _Diabetes Care_ 32, 2005–2009
(2009). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Boney, C. M., Verma, A., Tucker, R. & Vohr, B. R. Metabolic syndrome in childhood: association with birth weight, maternal
obesity, and gestational diabetes mellitus. _Pediatrics_ 115, e290–e296 (2005). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Esakoff, T. F., Cheng, Y. W., Sparks, T. N. & Caughey, A. B. The
association between birthweight 4000 g or greater and perinatal outcomes in patients with and without gestational diabetes mellitus. _Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol._ 200, 672–674 (2009). Article
PubMed Google Scholar * Schaefer-Graf, U. M. _ et al_. Birth weight and parental BMI predict overweight in children from mothers with gestational diabetes. _Diabetes Care_ 28, 1745–1750
(2005). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Vohr, B. R., McGarvey, S. T. & Tucker, R. Effects of maternal gestational diabetes on offspring adiposity at 4–7 years of age. _Diabetes Care_
22, 1284–1291 (1999). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hod, M. _ et al_. Fetal and perinatal outcomes in type 1 diabetes pregnancy: a randomized study comparing insulin aspart with
human insulin in 322 subjects. _Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol._ 198, 186–187 (2008). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hernandez, T. L., Friedman, J. E., van Pelt, R. E. & Barbour, L. A.
Patterns of glycemia in normal pregnancy: should the current therapeutic targets be challenged? _Diabetes Care_ 34, 1660–1668 (2011). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar *
Damm, P., Mathiesen, E., Clausen, T. D. & Petersen, K. R. Contraception for women with diabetes mellitus. _Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord._ 3, 244–249 (2005). Article PubMed Google
Scholar * Varughese, G. I., Chowdhury, S. R., Warner, D. P. & Barton, D. M. Preconception care of women attending adult general diabetes clinics—are we doing enough? _Diabetes Res.
Clin. Pract._ 76, 142–145 (2007). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Mathiesen, E. R. & Damm, P. Pregnancy—pharmacological problems. in _Pharmacotherapy of Diabetes: New
Developments_. (Ed. Mogensen, C. E.) 249–255 (Springer, New York, 2009). Google Scholar * Temple, R. C., Aldridge, V. J. & Murphy, H. R. Prepregnancy care and pregnancy outcomes in
women with type 1 diabetes. _Diabetes Care_ 29, 1744–1749 (2006). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Tieu, J., Middleton, P. & Crowther, C. A. Preconception care for diabetic women for
improving maternal and infant health. _Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2010_ Issue 12. Art No.: CD007776 http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD007776.pub2 * Murphy, H. R. _ et al_.
Effectiveness of a regional prepregnancy care program in women with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: benefits beyond glycemic control. _Diabetes Care_ 33, 2514–2520 (2010). Article PubMed
PubMed Central Google Scholar * Inkster, M. E. _ et al_. Poor glycated haemoglobin control and adverse pregnancy outcomes in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review of
observational studies. _BMC Pregnancy Childbirth_, 6 30 (2006). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * International Diabetes Federation. _Global Guidelines on Pregnancy and
Diabetes_ [online] (2009). * Guideline Development Group. Management of diabetes from preconception to the postnatal period: summary of NICE guidance. _BMJ_ 336, 714–717 (2008). * National
Institute of Health and Clinical Excellence. _Diabetes in pregnancy: management of diabetes and its complications from pre-conception to the post-natal period_ [online] (2008). * Nielsen, L.
R. _ et al_. Hypoglycemia in pregnant women with type 1 diabetes: predictors and role of metabolic control. _Diabetes Care_ 31, 9–14 (2008). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Wilson, R. D.
_ et al_. The use of folic acid for the prevention of neural tube defects and other congenital anomalies. _J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Can._ 25, 959–973 (2003). Article PubMed Google Scholar *
Capel, I. & Corcoy, R. What dose of folic acid should be used for pregnant diabetic women? _Diabetes Care_ 30, e63 (2007). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Bar, J., _ et al_. Pregnancy
outcome in patients with insulin dependent diabetes mellitus and diabetic nephropathy treated with ACE inhibitors before pregnancy. _J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab._ 12, 659–665 (1999).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Cooper, W. O. _ et al_. Major congenital malformations after first-trimester exposure to ACE inhibitors. _N. Engl. J. Med._ 354, 2443–2451 (2006).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Porta, M. _ et al_. Exposure to candesartan during the first trimester of pregnancy in type 1 diabetes: experience from the placebo-controlled
Diabetic Retinopathy Candesartan Trials. _Diabetologia_ 54 1298–1303 (2011). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Li, D. K., Yang, C., Andrade, S., Tavares, V. & Ferber, J. R.
Maternal exposure to angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors in the first trimester and risk of malformations in offspring: a retrospective cohort study. _BMJ_ 343, d5931 (2011). Article
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Shotan, A., Widerhorn, J., Hurst, A. & Elkayam, U. Risks of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition during pregnancy: experimental and clinical
evidence, potential mechanisms, and recommendations for use. _Am. J. Med._ 96, 451–456 (1994). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Tabacova, S., Little, R., Tsong, Y., Vega, A. &
Kimmel, C.A. Adverse pregnancy outcomes associated with maternal enalapril antihypertensive treatment. _Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug. Saf._ 12, 633–646 (2003). Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Sibai, B. M. Chronic hypertension in pregnancy. _Obstet. Gynecol._ 100, 369–377 (2002). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Nielsen, L. R., Muller, C., Damm, P. & Mathiesen, E.
R. Reduced prevalence of early preterm delivery in women with Type 1 diabetes and microalbuminuria—possible effect of early antihypertensive treatment during pregnancy. _Diabet. Med._ 23,
426–431 (2006). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Nielsen, L. R., Damm, P. & Mathiesen, E. R. Improved pregnancy outcome in type 1 diabetic women with microalbuminuria or diabetic
nephropathy: effect of intensified antihypertensive therapy? _Diabetes Care_ 32, 38–44 (2009). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Vestgaard, M. _ et al_.
Pregnancy-induced sight-threatening diabetic retinopathy in women with Type 1 diabetes. _Diabet. Med._ 27, 431–435 (2010). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Vestgaard, M., Nielsen, L.
R., Rasmussen, A. K., Damm, P. & Mathiesen, E. R. Thyroid peroxidase antibodies in pregnant women with type 1 diabetes: impact on thyroid function, metabolic control and pregnancy
outcome. _Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand._ 87, 1336–1342 (2008). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Haddow, J. E. _ et al_. Maternal thyroid deficiency during pregnancy and subsequent
neuropsychological development of the child. _N. Engl. J. Med._ 341, 549–555 (1999). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Abalovich, M. _ et al_. Management of thyroid dysfunction during
pregnancy and postpartum: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. _J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab._ 92, S1–S47 (2007). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kitzmiller, J. L. _ et
al_. Managing preexisting diabetes for pregnancy: summary of evidence and consensus recommendations for care. _Diabetes Care_ 31, 1060–1079 (2008). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Jovanovic, L. & Inturissi, M. Assessment of glycemic control. In _Managing Preexisting Diabetes Mellitus for Pregnancy_. (Ed. Kitzmiller, J. L.) 9–15 (American Diabetes Association,
2008). Google Scholar * Kerssen A, de Valk, H. W. & Visser, G. H. Do HbA1c levels and the self-monitoring of blood glucose levels adequately reflect glycaemic control during pregnancy
in women with type 1 diabetes mellitus? _Diabetologia_ 49, 25–28 (2006). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Garcia-Patterson, A. _ et al_. Insulin requirements throughout pregnancy in
women with type 1 diabetes mellitus: three changes of direction. _Diabetologia_ 53, 446–451 (2010). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Mathiesen, E. R. _ et al_. Insulin dose during
glucocorticoid treatment for fetal lung maturation in diabetic pregnancy: test of an algorithm. _Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand._ 81, 835–839 (2002). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Murphy,
H. R. _ et al_. Effectiveness of continuous glucose monitoring in pregnant women with diabetes: randomised clinical trial. _BMJ_ 337, a1680 (2008). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google
Scholar * Worm, D., Nielsen, L. R., Mathiesen, E. R. & Norgaard, K. Continuous glucose monitoring system with an alarm: a tool to reduce hypoglycemic episodes in pregnancy with
diabetes. _Diabetes Care_ 29, 2759–2760 (2006). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Mosca, A. _ et al_. Reference intervals for hemoglobin A1c in pregnant women: data from an Italian
multicenter study. _Clin. Chem._ 52, 1138–1143 (2006). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Nielsen, L. R. _ et al_. HbA1c levels are significantly lower in early and late pregnancy.
_Diabetes Care_ 27, 1200–1201 (2004). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Mills, J. L. _ et al_. Physiological reduction in fasting plasma glucose concentration in the first trimester of
normal pregnancy: the diabetes in early pregnancy study. _Metabolism_ 47, 1140–1144 (1998). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lurie, S. & Danon, D. Life span of erythrocytes in
late pregnancy. _Obstet. Gynecol._ 80, 123–126 (1992). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kerssen, A., de Valk, H. W. & Visser, G. H. Forty-eight-hour first-trimester glucose profiles in
women with type 1 diabetes mellitus: a report of three cases of congenital malformation. _Prenat. Diagn._ 26, 123–127 (2006). Article PubMed Google Scholar * British Medical Association
and Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain. _British National Formulary_. (London, 2006). * FDA NovoLog label [online] (2008). * FDA Humalog label [online] (2011). * EMA Novolog label
[online] (2009). * EMA Humalog label. http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Information/human/000088/WC500050332.pdf (2006). * Mathiesen, E. R. _ et al_.
Maternal glycemic control and hypoglycemia in Type 1 diabetic pregnancy: a randomized trial of insulin aspart versus human insulin in 322 pregnant women. _Diabetes Care_ 30, 771–776 (2007).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Mathiesen, E. R. _ et al_. Maternal efficacy and safety outcomes in a randomized, controlled trial comparing insulin detemir with NPH insulin in 310
pregnant women with type 1 diabetes. http://dx.doi.org/10.2337/dc11-2264 * FDA detemir label [online] (2005). * Gallen, I. W., Jaap, A., Roland, J. M. & Chirayath, H. H. Survey of
glargine use in 115 pregnant women with Type 1 diabetes. _Diabet. Med._ 25, 165–169 (2008). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lapolla, A. _ et al_. Use of insulin detemir in pregnancy:
a report on 10 Type 1 diabetic women. _Diabet. Med._ 26, 1181–1182 (2009). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Poyhonen-Alho, M., Ronnemaa, T., Saltevo, J., Ekblad, U. & Kaaja, R.
J. Use of insulin glargine during pregnancy. _Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand._ 86, 1171–1174 (2007). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Gabbe, S. G., Carpenter, L. B. & Garrison, E. A. New
strategies for glucose control in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus in pregnancy. _Clin. Obstet. Gynecol._ 50, 1014–1024 (2007). Article PubMed Google Scholar * McCance,
D. & Holmes, V. A. Insulin regimens in pregnancy in _A practical Manual of Diabetes in Pregnancy_ 99–109 (Blackwell Publishing Ltd, Oxford, UK, 2010). Book Google Scholar * Workgroup
on Hypoglycaemia, American Diabetes Association. Defining and reporting hypoglycemia in diabetes: a report from the American Diabetes Association Workgroup on Hypoglycemia. _Diabetes Care_
28, 1245–1249 (2005). * Rosenn, B. M., Miodovnik, M., Holcberg, G., Khoury, J. C. & Siddiqi, T. A. Hypoglycemia: the price of intensive insulin therapy for pregnant women with
insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. _Obstet. Gynecol._ 85, 417–422 (1995). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kimmerle, R., Heinemann, L., Delecki, A. & Berger, M. Severe
hypoglycemia incidence and predisposing factors in 85 pregnancies of type I diabetic women. _Diabetes Care_ 15, 1034–1037 (1992). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Leinonen, P. J.,
Hiilesmaa, V. K., Kaaja, R. J. & Teramo, K. A. Maternal mortality in type 1 diabetes. _Diabetes Care_ 24, 1501–1502 (2001). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Evers, I. M. _ et al_.
Risk indicators predictive for severe hypoglycemia during the first trimester of type 1 diabetic pregnancy. _Diabetes Care_ 25, 554–559 (2002). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Robertson,
H., Pearson, D. W. & Gold, A. E. Severe hypoglycaemia during pregnancy in women with Type 1 diabetes is common and planning pregnancy does not decrease the risk. _Diabet. Med._ 26,
824–826 (2009). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Buchanan, T. A., Schemmer, J. K. & Freinkel, N. Embryotoxic effects of brief maternal insulin-hypoglycemia during organogenesis in
the rat. _J. Clin. Invest._ 78, 643–649 (1986). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Kawaguchi, M., Tanigawa, K., Tanaka, O. & Kato, Y. Embryonic growth impaired by
maternal hypoglycemia during early organogenesis in normal and diabetic rats. _Acta Diabetol._ 31, 141–146 (1994). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Smoak, I. W. & Sadler, T. W.
Embryopathic effects of short-term exposure to hypoglycemia in mouse embryos _in vitro_. _Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol._ 163, 619–624 (1990). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * [No authors
listed] Pregnancy outcomes in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. _Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol._ 174, 1343–1353 (1996). * Ringholm, L., Pedersen-Bjergaard, U., Thorsteinsson, B., Damm,
P. & Mathiesen, E. R. Hypoglycaemia during pregnancy in women with Type 1 diabetes. _Diabet. Med._ 29, 558–566 (2012). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Garcia-Dominguez, M. _ et
al_. Use of insulin lispro during pregnancy in women with pregestational diabetes mellitus. _Med. Clin. (Barc.)_ 137, 581–586 (2011). Article Google Scholar * Heller, S. R. _ et al_.
Hypoglycaemia with insulin aspart: a double-blind, randomised, crossover trial in subjects with Type 1 diabetes. _Diabet. Med._ 21, 769–775 (2004). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Imbergamo, M. P. _ et al_. Use of glargine in pregnant women with type 1 diabetes mellitus: a case–control study. _Clin. Ther._ 30, 1476–1484 (2008). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Secher, A. L. _ et al_. Patient satisfaction and barriers to initiating real-time continuous glucose monitoring in early pregnancy in women with diabetes. _Diabet. Med._ 29, 272–277 (2012).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hegaard, H. K., Pedersen, B. K., Nielsen, B. B. & Damm, P. Leisure time physical activity during pregnancy and impact on gestational diabetes
mellitus, pre-eclampsia, preterm delivery and birth weight: a review. _Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand._ 86, 1290–1296 (2007). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Jovanovic, L. G. Using
meal-based self-monitoring of blood glucose as a tool to improve outcomes in pregnancy complicated by diabetes. _Endocr. Pract._ 14, 239–247 (2008). Article PubMed Google Scholar *
Leontos, C. Implementing the American Diabetes Association's nutrition recommendations. _J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc._ 103, S17–S20 (2003). PubMed Google Scholar * Hanson, U. &
Persson, B. Epidemiology of pregnancy-induced hypertension and preeclampsia in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic pregnancies in Sweden. _Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand._ 77, 620–624 (1998).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Holmes, V. A. _ et al_. Optimal glycemic control, pre-eclampsia, and gestational hypertension in women with type 1 diabetes in the diabetes and
pre-eclampsia intervention trial. _Diabetes Care_ 34, 1683–1688 (2011). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Siddiqi, T., Rosenn, B., Mimouni, F., Khoury, J. & Miodovnik,
M. Hypertension during pregnancy in insulin-dependent diabetic women. _Obstet. Gynecol._ 77, 514–519 (1991). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Bartha, J. L., Romero-Carmona, R.,
Torrejon-Cardoso, R., Comino-Delgado, R. Insulin, insulin-like growth factor-1, and insulin resistance in women with pregnancy-induced hypertension. _Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol._ 187, 735–740
(2002). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Seely, E. W. & Solomon, C. G. Insulin resistance and its potential role in pregnancy-induced hypertension. _J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab._
88, 2393–2398 (2003). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Sierra-Laguado, J. _ et al_. Determination of insulin resistance using the homeostatic model assessment (HOMA) and its relation
with the risk of developing pregnancy-induced hypertension. _Am. J. Hypertens._ 20, 437–442 (2007). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Solomon, C. G. & Seely, E. W. Brief review:
hypertension in pregnancy: a manifestation of the insulin resistance syndrome? _Hypertension_ 37, 232–239 (2001). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Ferriss, J. B. The causes of raised
blood pressure in insulin-dependent and non-insulin-dependent diabetes. _J. Hum. Hypertens._ 5, 245–254 (1991). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Leguizamon, G. F., Zeff, N. P. Fernandez A:
Hypertension and the pregnancy complicated by diabetes. _Curr. Diab. Rep._ 6, 297–304 (2006). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Ekbom, P. _ et al_. Pregnancy outcome in type 1 diabetic
women with microalbuminuria. _Diabetes Care_ 24, 1739–1744 (2001). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Rossing, K. _ et al_. Pregnancy and progression of diabetic nephropathy.
_Diabetologia_ 45, 36–41 (2002). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Sibai, B. M. Diabetic nephropathy in pregnancy. in _A Practical Manual of Diabetes in Pregnancy_. 153–156 (Blackwell
Publishing, Oxford, 2008). Google Scholar * [No authors listed] Blood glucose control and the evolution of diabetic retinopathy and albuminuria. A preliminary multicenter trial. The Kroc
Collaborative Study Group. _N. Engl. J. Med._ 311, 365–372 (1984). * [No authors listed] The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term
complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. _N. Engl. J. Med._ 329, 977–986 (1993). * Lawson, P. M. _ et al_.
Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) does not prevent progression of proliferative and preproliferative retinopathy. _Br. J. Ophthalmol._ 66, 762–766 (1982). Article CAS PubMed
PubMed Central Google Scholar * Chew, E. Y. _ et al_. Metabolic control and progression of retinopathy. The Diabetes in Early Pregnancy Study. National Institute of Child Health and
Human Development Diabetes in Early Pregnancy Study. _Diabetes Care_ 18, 631–637 (1995). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Okosieme, O. E., Marx, H. & Lazarus, J. H. Medical
management of thyroid dysfunction in pregnancy and the postpartum. _Expert Opin. Pharmacother._ 9, 2281–2293 (2008). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Mathiesen, E. R., Ringholm, L.
& Damm, P. Stillbirth in diabetic pregnancies. _Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol._ 25, 105–111 (2011). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Conway, D. L. & Catalano, P. M.
Obstetrical management of women with preexisting diabetes mellitus. In _Managing Preexisting Diabetes and Pregnancy. American Diabetes Association Technical Reviews and Consensus
Recommendations for Care_. (Ed. Kitzmiller, J. L.) 561–601 (American Diabetes Association, 2008). Google Scholar * Jovanovic, L. Glucose and insulin requirements during labor and delivery:
the case for normoglycemia in pregnancies complicated by diabetes. _Endocr. Pract._ 10, (Suppl. 2) 40–45 (2004). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Stage, E., Mathiesen, E. R., Emmersen, P.
B., Greisen, G. & Damm, P. Diabetic mothers and their newborn infants—rooming-in and neonatal morbidity. _Acta Paediatr._ 99, 997–999 (2010). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Inturris, M. Benefits and concerns of breast-feeding in women with diabetes. In _Managing Preexisting Diabetes and Pregnancy_. (Ed. Kitzmiller, J. L.) 697–727 (American Diabetes Association,
2008). Google Scholar * Stage, E., Norgard, H., Damm, P. & Mathiesen, E. Long-term breast-feeding in women with type 1 diabetes. _Diabetes Care_ 29, 771–774 (2006). Article PubMed
Google Scholar * [No authors listed] Preparing pregnant women with diabetes for special breast-feeding challenges. _J. Am. Diet. Assoc._ 98, 648 (1998). * Hummel, S. _ et al_. Breastfeeding
habits in families with Type 1 diabetes. _Diabet. Med._ 24, 671–676 (2007). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Sorkio, S. _ et al_. Breastfeeding patterns of mothers with type 1
diabetes: results from an infant feeding trial. _Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev._ 26, 206–211 (2010). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Riviello, C., Mello, G. & Jovanovic, L.
G. Breastfeeding and the basal insulin requirement in type 1 diabetic women. _Endocr. Pract._ 15, 187–193 (2009). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Beardmore, K. S., Morris, J. M. &
Gallery, E. D. Excretion of antihypertensive medication into human breast milk: a systematic review. _Hypertens. Pregnancy_ 21, 85–95 (2002). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Shannon,
M. E., Malecha, S. E. & Cha, A. J. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) and lactation: an update. _J. Hum. Lact._ 16, 152–155
(2000). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Shannon, M. E., Malecha, S. E. & Cha, A. J. Beta blockers and lactation: an update. _J. Hum. Lact._ 16, 240–245 (2000). Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * [No authors listed] American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Drugs: The transfer of drugs and other chemicals into human milk. _Pediatrics_ 93, 137–150 (1994).
Download references AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Center for Pregnant Women with Diabetes, Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen, Blegdamsvej 9, Copenhagen Ø, DK 2100,
Denmark Lene Ringholm, Elisabeth R. Mathiesen, Louise Kelstrup & Peter Damm Authors * Lene Ringholm View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar *
Elisabeth R. Mathiesen View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Louise Kelstrup View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * Peter Damm View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS L. Ringholm contributed to researching and discussing
content, writing the manuscript and editing the article before submission. E. R. Mathiesen, L. Kelstrup and P. Damm contributed substantially to discussions of the content and reviewing
and/or editing of the manuscript before submission. CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Lene Ringholm. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS P. Damm and E. R Mathiesen have acted as
consultants for and received grant support from Novo Nordisk. E. R. Mathiesen has also received honoraria from Novo Nordisk. L. Ringholm and L. Kelstrup declare no competing interests.
RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Ringholm, L., Mathiesen, E., Kelstrup, L. _et al._ Managing type 1 diabetes mellitus in pregnancy—from
planning to breastfeeding. _Nat Rev Endocrinol_ 8, 659–667 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2012.154 Download citation * Published: 11 September 2012 * Issue Date: November 2012 * DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2012.154 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not
currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative







