- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
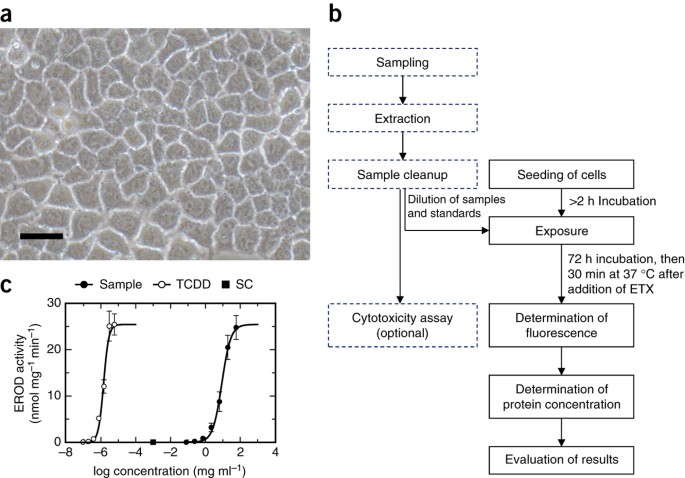
ABSTRACT This protocol describes a quantitative and robust 96-well-plate-reader–based assay for the measurement of ethoxyresorufin-_O_-deethylase (EROD) activity using the rat hepatoma cell
line H4IIE. The assay can be used to determine the cytochrome P450 subfamily 1A (CYP1A)-inducing potential of single substances, as well as of mixtures and extracts of samples. It is based
on the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR)–mediated induction of cytochrome P450 enzymes (subfamily 1A) in cells after exposure to dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. One enzymatic reaction
catalyzed by CYP1A is the deethylation of the exogenous substrate 7-ethoxyresorufin to the fluorescent product resorufin, which is measured as EROD activity in the assay. The CYP1A-inducing
potential of a sample can be reliably quantified by comparing the EROD activity with the concentration-response curve of the standard substance 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-_p_-dioxin, which
can be detected at concentrations down to the picogram per liter range. A researcher familiar with the procedure can process up to 160 samples with four wells each within 3 d. The series
described uses four plates with three concentrations per sample, which can be easily scaled to accommodate different sample sizes. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a
preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $259.00 per
year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated
during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS
HIGH-THROUGHPUT TOXICOGENOMIC SCREENING OF CHEMICALS IN THE ENVIRONMENT USING METABOLICALLY COMPETENT HEPATIC CELL CULTURES Article Open access 27 January 2021 FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE THE
QUALITY OF METABOLOMICS DATA IN IN VITRO CELL TOXICITY STUDIES: A SYSTEMATIC SURVEY Article Open access 11 November 2021 TOLTERODINE IS A NOVEL CANDIDATE FOR ASSESSING CYP3A4 ACTIVITY
THROUGH METABOLIC VOLATILES TO PREDICT DRUG RESPONSES Article Open access 20 January 2025 REFERENCES * Sinkkonen, S. & Paasivirta, J. Degradation half-life times of PCDDs, PCDFs and PCBs
for environmental fate modeling. _Chemosphere_ 40, 943–949 (2000). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Weber, R. et al. Dioxin- and POP-contaminated sites—contemporary and future relevance and
challenges. _Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int._ 15, 363–393 (2008). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Brack, W. Effect-directed analysis: a promising tool for the identification of organic
toxicants in complex mixtures? _Anal. Bioanal. Chem._ 377, 397–407 (2003). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Theelen, R.M.C., Liem, A.K.D., Slob, W. & Van Wijnen, J.H. Intake of
2,3,7,8-chlorine-substituted dioxins, furans, and planar PCBs from food in the Netherlands: Median and distribution. _Chemosphere_ 27, 1625–1635 (1993). CAS Google Scholar * Spagnoli, J.J.
& Skinner, L.C. PCBs in fish from selected waters of New York State. _Pestic. Monit. J._ 11, 69–87 (1977). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * La Rocca, C. & Mantovani, A. From
environment to food: the case of PCB. _Ann. Ist. Super. Sanità_ 42, 410–416 (2006). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Denison, M.S. & Heath-Pagliuso, S. The Ah receptor: a regulator of the
biochemical and toxicological actions of structurally diverse chemicals. _Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol._ 61, 557–568 (1998). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Denison, M.S. & Nagy, S.R.
Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor by structurally diverse exogenous and endogenous chemicals. _Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol._ 43, 309–334 (2003). CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Brouwer, A. et al. Functional aspects of developmental toxicity of polyhalogenated aromatic hydrocarbons in experimental animals and human infants. _Eur. J. Pharmacol._ 293, 1–40 (1995). CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Van den Berg, M. et al. Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for PCBs, PCDDs, PCDFs for humans and wildlife. _Environ. Health Perspect._ 106, 775–792 (1998). CAS
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Poland, A. & Knutson, J.C. 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-_p_-dioxin and related halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons: examination of the mechanism of
toxicity. _Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol._ 22, 517–554 (1982). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Giesy, J.P., Ludwig, J.P. & Tillitt, D.E. Deformities in birds of the Great Lakes region.
Assigning causality. _Environ. Sci. Technol._ 28, 128A–135A (1994). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Dencker, L. The role of receptors in 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-_p_-dioxin (TCDD) toxicity.
_Arch. Toxicol. Suppl._ 8, 43–60 (1985). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Huang, H. & Buekens, A. On the mechanisms of dioxin formation in combustion processes. _Chemosphere_ 31,
4099–4117 (1995). CAS Google Scholar * Lallas, P.L. The Stockholm Convention on persistent organic pollutants. _Am. J. Int. Law_ 692–708 (2001). Google Scholar * Covaci, A. et al. The
Belgian PCB/dioxin crisis—8 years later: an overview. _Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol._ 25, 164–170 (2008). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Abraham, K. et al. Review: incidents regarding dioxin
in feedstuff in Germany 2011–a consumer health risk? _Arch. Lebensmittelhyg._ 62, 108–115 (2011). CAS Google Scholar * European Commission. _The Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed 2013:
Annual Report._ Report No. 978-92-79-38196-6, (OP, 2014). * European Commission. _The Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed 2012: Annual Report._ Report No. 978-92-79-28611-7, (OP, 2013). *
European Commission. Communication of 16 April 2002 from the Commission to the Council, the European parliament, the Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the regions: Towards a
thematic strategy for soil protection. _Official Journal of the European Union, L series (OJ L)_ 179 (2002). * European Commission. Commission Regulation (EC) No. 1881/2006 of 19 December
2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. _OJ L_ 364 (2006). * European Commission. Commission Recommendation (EC) No. 711/2013 of 3 December 2013 on the reduction
of the presence of dioxins, furans and PCBs in feed and food. _OJ L_ 323 (2013). * European Commission. Commission Recommendation (EC) No. 663/2014 of 11 September 2014 amending the Annex to
Recommendation 2013/711/EU on the reduction of the presence of dioxins, furans and PCBs in feed and food. _OJ L_ 272 (2014). * European Commission. Commission Regulation (EC) No. 277/2012
of 28 March 2012 amending Annexes I and II to Directive 2002/32/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards maximum levels and action thresholds for dioxins and
polychlorinated biphenyls. _OJ L_ 91 (2012). * European Commission. Commission Regulation (EC) No. 589/2014 of 2 June 2014 laying down methods of sampling and analysis for the control of
levels of dioxins, dioxin-like PCBs and non-dioxin-like PCBs in certain foodstuffs and repealing Regulation (EU) No. 252/2012. _OJ L_ 164 (2014). * European Commission. Commission Regulation
(EC) No 278/2012 of 28 March 2012 amending Regulation (EC) No. 152/2009 as regards the determination of the levels of dioxins and polychlorinated biphenyls. _OJ L_ 91 (2012). * Jordaan, I.
et al. The Contribution of dioxin-like compounds from platinum mining and processing samples. _Miner. Eng._ 20, 191–193 (2007). CAS Google Scholar * Nieuwoudt, C. et al. A pilot-study of
dioxin-like compounds in soil and sediment from residential and industrial areas in central South Africa. _Chemosphere_ 76, 744–783 (2008). Google Scholar * Wölz, J. et al. Changes in
toxicity and Ah receptor agonist activity of suspended particulate matter during flood events at the rivers Neckar and Rhine—a mass balance approach using _in vitro_ methods and chemical
analysis. _Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res._ 15, 536–553 (2008). Google Scholar * Keiter, S. et al. Activities and identification of aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists in sediments from the
Danube river. _Anal. Bioanal. Chem._ 390, 2009–2019 (2008). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Olsman, H. et al. Relative differences in aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated response for 18
polybrominated and mixed halogenated dibenzo-_p_-dioxins and -furans in cell lines from four different species. _Environ. Toxicol. Chem._ 26, 2448–2454 (2007). CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Wernersson, A.-S. et al. The European technical report on aquatic effect-based monitoring tools under the water framework directive. _Env. Sci. Eur._ 27, 7 (2015). Google Scholar *
Behnisch, P.A., Hosoe, K. & Sakai, S.-i. Combinatorial bio/chemical analysis of dioxin and dioxin-like compounds in waste recycling, feed/food, humans/wildlife and the environment.
_Environ. Int._ 27, 495–519 (2001). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Eichbaum, K. et al. _In vitro_ bioassays for detecting dioxin-like activity—application potentials and limits of detection,
a review. _Sci. Total Environ._ 487, 37–48 (2014). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Van den Berg, M. et al. The 2005 World Health Organization reevaluation of human and mammalian toxic
equivalency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. _Toxicol. Sci._ 93, 223–241 (2006). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Novotna, A., Pavek, P. & Dvorak, Z. Novel stably transfected
gene reporter human hepatoma cell line for assessment of aryl hydrocarbon receptor transcriptional activity: construction and characterization. _Environ. Sci. Technol._ 45, 10133–10139
(2011). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Murk, A.J. et al. Chemical-ctivated Luciferase Gene Expression (CALUX): a novel _in vitro_ bioassay for Ah receptor active compounds in sediments and
pore water. _Fundam. Appl. Toxicol._ 33, 149–160 (1996). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Pitot, H.C., Peraino, C., Morse, P.A. Jr. & Potter, V.R. Hepatomas in tissue culture compared with
adapting liver _in vivo_. _J. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr._ 13, 229–245 (1964). CAS Google Scholar * Schwirzer, S.M. et al. Establishment of a simple cleanup procedure and bioassay for
determining 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin toxicity equivalents of environmental samples. _Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf._ 41, 77–82 (1998). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Thiem, I.,
Boehmler, G. & Thoms, B. Modification of the micro EROD-bioassay and validation for routine analysis demonstrated for beef and milk. _Organohalogen Compd._ 76, 161–164 (2014). CAS
Google Scholar * Thiem, I. & Boehmler, G. Step-by-step analysis of recovery rates of dioxin-like compounds in beef using the micro-EROD-bioassay. _Organohalogen Compd._ 73, 2128–2131
(2011). Google Scholar * Thiem, I. & Boehmler, G. Model for interpretation of coupled data from biotests based on the dioxin-like response of Ah-receptors. _Organohalogen Compd._ 73,
2124–2127 (2011). Google Scholar * Donato, M.T., Castell, J.V. & Gómez-Lechón, M.J. A rapid and sensitive method for measuring monooxygenase activities in hepatocytes cultured in
96-well plates. _J. Tissue Cult. Methods_ 14, 153–157 (1992). Google Scholar * Donato, M.T., Gomez-Lechon, M.J. & Castell, J.V. A microassay for measuring cytochrome P450IA1 and
P450IIB1 activities in intact human and rat hepatocytes cultured on 96-well plates. _Anal. Biochem._ 213, 29–33 (1993). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Safe, S. Development of bioassays and
approaches for the risk assessment of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-_p_-dioxin and related compounds. _Environ. Health Perspect._ 101 (suppl. 3): 317–325 (1993). CAS PubMed PubMed Central
Google Scholar * Tillitt, D.E., Giesy, J.P. & Ankley, G.T. Characterization of the H4IIE rat hepatoma cell bioassay as a tool for assessing toxic potency of planar halogenated
hydrocarbons in environmental samples. _Environ. Sci. Technol._ 25, 87–92 (1991). CAS Google Scholar * Sanderson, J.T. et al. Comparison of Ah receptor-mediated luciferase and
ethoxyresorufin-_O_-deethylase induction in H4IIE cells: Implications for their use as bioanalytical tools for the detection of polyhalogenated aromatic hydrocarbons. _Toxicol. Appl.
Pharmacol._ 137, 316–325 (1996). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Whyte, J., Schmitt, C. & Tillitt, D. The H4IIE cell bioassay as an indicator of dioxin-like chemicals in wildlife and the
environment. _Crit. Rev. Toxicol._ 34, 1–83 (2004). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Gizzi, G., Hoogenboom, L.A.P., Von Holst, C., Rose, M. & Anklam, E. Determination of dioxins
(PCDDs/PCDFs) and PCBs in food and feed using the DR CALUX (R) bioassay: results of an international validation study. _Food Addit. Contam._ 22, 472–481 (2005). CAS PubMed Google Scholar
* Safe, S., Rodriguez, L. & Goldstein, L. Toxic equivalency factor approach for risk assessment of combustion by-products. _Toxicol. Environ. Chem._ 49, 181–191 (1995). CAS Google
Scholar * Villeneuve, D.L., Blankenship, A.L. & Giesy, J.P. Derivation and application of relative potency estimates based on _in vitro_ bioassay results. _Environ. Toxicol. Chem._ 19,
2835–2843 (2000). CAS Google Scholar * Hädrich, J. et al. Considerations on the working range in bioassays dose-response curves: curve fit and assay background response. _Organohalogen
Compd._ 74, 177–181 (2012). Google Scholar * Radenac, G., Coteur, G., Danis, B., Dubois, P. & Warnau, M. Measurement of EROD activity: caution on spectral properties of standards used.
_Mar. Biotechnol._ 6, 307–311 (2004). CAS Google Scholar * Repetto, G., del Peso, A. & Zurita, J.L. Neutral red uptake assay for the estimation of cell viability/cytotoxicity. _Nat.
Protoc._ 3, 1125–1131 (2008). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Smith, P.K. et al. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. _Anal. Biochem._ 150, 76–85 (1985). CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Hanberg, A., Stahlberg, M., Georgellis, A., de Wit, C. & Ahlborg, U.G. Swedish dioxin survey: evaluation of the H-4-IIE bioassay for screening environmental samples for
dioxin-like enzyme induction. _Pharmacol. Toxicol._ 69, 442–449 (1991). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Peters, A. et al. Effects of polybrominated diphenyl ethers on basal and TCDD-induced
ethoxyresorufin activity and cytochrome P450-1A1 expression in MCF-7, HepG2, and H4IIE cells. _Toxicol. Sci._ 82, 488–496 (2004). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Schmitz, H.-J. et al.
CYP1A1-inducing potency in H4IIE cells and chemical composition of technical mixtures of polychlorinated biphenyls. _Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol._ 1, 73–79 (1996). CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Behnisch, P.A., Hosoe, K., Brouwer, A. & Sakai, S.-i. Screening of dioxin-like toxicity equivalents for various matrices with wildtype and recombinant rat hepatoma H4IIE
cells. _Toxicol. Sci._ 69, 125–130 (2002). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Gale, R.W., Long, E.R., Schwartz, T.R. & Tillitt, D.E. Evaluation of planar halogenated and polycyclic aromatic
hydrocarbons in estuarine sediments using ethoxyresorufin-_O_-deethylase Induction of H4IIE cells. _Environ. Toxicol. Chem._ 19, 1348–1359 (2000). CAS Google Scholar * Li, W., Wu, W.Z.,
Barbara, R.B., Schramm, K.W. & Kettrup, A. A new enzyme immunoassay for PCDD/F TEQ screening in environmental samples: comparison to micro-EROD assay and to chemical analysis.
_Chemosphere_ 38, 3313–3318 (1999). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hewitt, L.M. et al. Characteristics of ligands for the Ah receptor and sex steroid receptors in hepatic tissues of fish
exposed to bleached kraft mill effluent. _Environ. Sci. Technol._ 34, 4327–4334 (2000). CAS Google Scholar * Jiang, Q.T. et al. Human health risk assessment of organochlorines associated
with fish consumption in a coastal city in China. _Environ. Pollut._ 136, 155–165 (2005). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Summer, C.L., Bursian, S.J. & Kubiak, T.J. Effects induced by
feeding organochlorine contaminated carp from Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron to laying White Leghorn hens. I Effects on health of adult hens egg production and fertility. _J. Toxicol. Environ.
Health_ 49, 389–408 (1996). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Valdovinosa, C., Sotomayora, P., Stecha, R., Schoffera, J. & Bustos-Lópezb, C. Application of the EROD-H4IIE bioassay for the
determination of dioxins in pork in comparison to high resolution gas chromatography coupled to high resolution mass spectrometry. _Arch. Med. Vet._ 45, 173–181 (2013). Google Scholar *
Schramm, K.W., Klimm, C., Hofmaier, A. & Kettrup, A. Comparison of dioxin-like-response _in vitro_ and chemical analysis of emissions and materials. _Chemosphere_ 42, 551–557 (2001). CAS
PubMed Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This protocol was applied within the §64-LFGB working group 'Wirkungsbezogene Analytik' (effect directed analysis)
for a pre–round robin test. The authors acknowledge the federal office of Consumer Protection and Food Safety (BVL) for their support in this project. The protocol was used and further
adopted in context of the project 'DioRAMA—Assessment of the dioxin-like activity in sediments and fish for sediment evaluation' that received funds from the German Federal
Ministry of Transport and Digital Infrastructure. The authors acknowledge the German National Academic Foundation ('Studienstiftung des deutschen Volkes') for a personal
scholarship granted to M.B. H.H. was supported by the Chinese 111 Program (College of Environmental Science and Engineering and Key Laboratory of Yangze Water environment, Ministry of
Education, Tongji University). AUTHOR INFORMATION Author notes * Andreas Schiwy and Markus Brinkmann: These authors contributed equally to this work. AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of
Ecosystem Analysis, Institute for Environmental Research, Aachen Biology and Biotechnology (ABBt), Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule Aachen (RWTH) Aachen University, Aachen,
Germany Andreas Schiwy, Markus Brinkmann, Kerstin Winkens, Kathrin Eichbaum, Leonie Nüßer, Beat Thalmann, Thomas-Benjamin Seiler & Henner Hollert * Food and Veterinary Institute
Braunschweig/Hannover, Lower Saxony State Office for Consumer Protection and Food Safety (LAVES), Braunschweig, Germany Ines Thiem, Gabriele Guder & Brigitte Thoms * Department G3:
Biochemistry, Federal Institute of Hydrology (BFG), Ecotoxicology, Koblenz, Germany Sebastian Buchinger & Georg Reifferscheid * College of Resources and Environmental Science, Chongqing
University, Chongqing, China Henner Hollert * College of Environmental Science and Engineering and State Key Laboratory of Pollution Control and Resource Reuse, Tongji University, Shanghai,
China Henner Hollert * State Key Laboratory of Pollution Control and Resource Reuse, School of the Environment, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China Henner Hollert Authors * Andreas Schiwy
View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Markus Brinkmann View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar *
Ines Thiem View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Gabriele Guder View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google
Scholar * Kerstin Winkens View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Kathrin Eichbaum View author publications You can also search for this
author inPubMed Google Scholar * Leonie Nüßer View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Beat Thalmann View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Sebastian Buchinger View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Georg Reifferscheid View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Thomas-Benjamin Seiler View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar *
Brigitte Thoms View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Henner Hollert View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed
Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS All authors contributed extensively to the work presented in this paper, read and edited it, and gave their final approval for publication. A.S. and M.B. have
contributed equally to the work and share first authorship. A.S. has adopted the protocol from an initial version of I.T., G.G. and B.T., and established it together with K.W., L.N. and K.E.
in our laboratory. M.B. and A.S. wrote the manuscript and compiled the protocol. T.-B.S. B.T., S.B., G.R. and H.H. gave technical support and conceptual advice. CORRESPONDING AUTHOR
Correspondence to Henner Hollert. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing financial interests. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS
ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Schiwy, A., Brinkmann, M., Thiem, I. _et al._ Determination of the CYP1A-inducing potential of single substances, mixtures and extracts of samples in the micro-EROD
assay with H4IIE cells. _Nat Protoc_ 10, 1728–1741 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2015.108 Download citation * Published: 08 October 2015 * Issue Date: November 2015 * DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2015.108 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not
currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative