- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
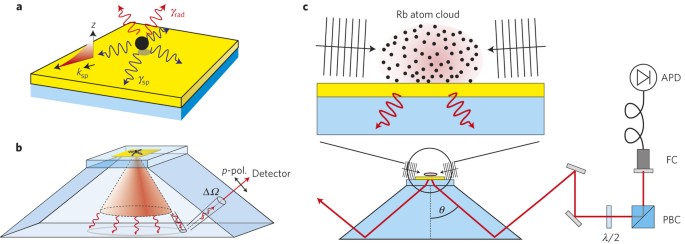
Cooperative coupling between optical emitters and light fields is one of the outstanding goals in quantum technology. It is both fundamentally interesting for the extraordinary radiation
properties of the participating emitters and has many potential applications in photonics. Although this goal has been achieved using high-finesse optical cavities, attention has turned to
broadband, easy to build cavity-free approaches. Here we demonstrate cooperative coupling of ultracold atoms with surface plasmons propagating on a plane gold surface. While the atoms are
moving towards the surface they are excited by an external laser pulse. The interaction between the excited atom fluorescence and surface plasmons is probed by detecting the photons emitted
into the substrate when the plasmon excitations decay. A maximum Purcell factor of ηP = 4.9 is reached at an optimum distance of z = 250 nm from the surface. The coupling leads to the
observation of a Fano-like resonance in the spectrum.
C.Z. gratefully acknowledges financial support by the DFG. C.S. was supported by Carl-Zeiss Stiftung Baden-Württemberg. S.S. is indebted to the Baden-Württemberg Stiftung for the financial
support of this research project by the Eliteprogramm for Postdocs.
Physikalisches Institut and Center for Collective Quantum Phenomena in LISA+, Universität Tübingen, Auf der Morgenstelle 14, D-72076 Tübingen, Germany
C.Z. provided the laboratory and experimental facilities, C.S. made the measurements, and S.S. analysed the data and wrote the paper.
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: