- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
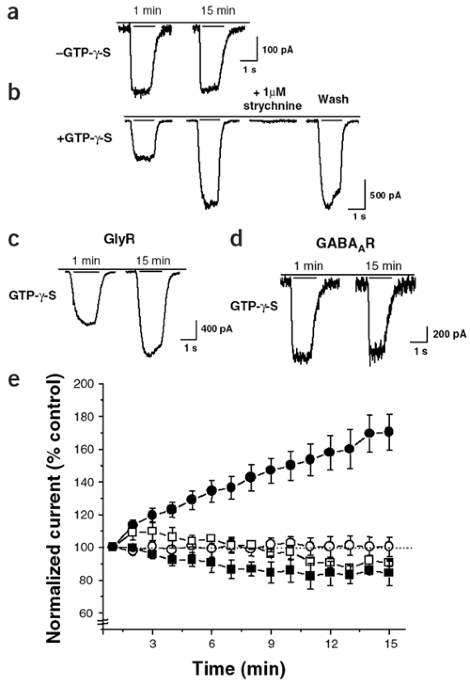
ABSTRACT Glycine receptors (GlyRs), together with GABAA and nicotinic acetylcholine (ACh) receptors, form part of the ligand-activated ion channel superfamily and regulate the excitability
of the mammalian brain stem and spinal cord. Here we report that the ability of the neurotransmitter glycine to gate recombinant and native ionotropic GlyRs is modulated by the G protein βγ
dimer (Gβγ). We found that the amplitude of the glycine-activated Cl− current was enhanced after application of purified Gβγ or after activation of a G protein–coupled receptor.
Overexpression of three distinct G protein α subunits (Gα), as well as the Gβγ scavenger peptide ct-GRK2, significantly blunted the effect of G protein activation. Single-channel recordings
from isolated membrane patches showed that Gβγ increased the GlyR open probability (_nP_o). Our results indicate that this interaction of Gβγ with GlyRs regulates both motor and sensory
functions in the central nervous system. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through
your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $209.00 per year only $17.42 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant
access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions *
Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS CONFORMATIONAL TRANSITIONS AND ALLOSTERIC MODULATION IN A HETEROMERIC GLYCINE RECEPTOR Article Open access 13
March 2023 MOLECULAR MECHANISM OF LIGAND GATING AND OPENING OF NMDA RECEPTOR Article 31 July 2024 GLUA2-CONTAINING AMPA RECEPTORS FORM A CONTINUUM OF CA2+-PERMEABLE CHANNELS Article 19 March
2025 REFERENCES * Betz, H. Glycine receptors: heterogeneous and widespread in the mammalian brain. _Trends Neurosci._ 14, 458–461 (1991). Article CAS Google Scholar * Legendre, P. The
glycinergic inhibitory synapse. _Cell. Mol. Life Sci._ 58, 760–793 (2001). Article CAS Google Scholar * Schmid, K., Bohmer, G. & Gebauer, K. Glycine receptor-mediated fast synaptic
inhibition in the brainstem respiratory system. _Respir. Physiol._ 84, 351–361 (1991). Article CAS Google Scholar * Harris, R.A. Ethanol actions on multiple ion channels: which are
important? _Alcohol: Clin. Exp. Res._ 23, 1563–1570 (1999). CAS Google Scholar * Mihic, S.J. et al. Sites of alcohol and volatile anaesthetic action on GABAA and glycine receptors.
_Nature_ 389, 385–389 (1997). Article CAS Google Scholar * Song, Y. & Huang, L.Y. Modulation of glycine receptor chloride channels by cAMP dependent protein kinase in spinal
trigeminal neurons. _Nature_ 348, 242–245 (1990). Article CAS Google Scholar * Vaello, M.L., Ruiz-Gomez, A., Lerma, J. & Mayor, F. Modulation of inhibitory glycine receptors by
phosphorylation by protein kinase C and cAMP-dependent protein kinase. _J. Biol. Chem._ 269, 2002–2008 (1994). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Ahmadi, S., Lippross, S., Neuhuber, W.L. &
Zeilhofer, H.U. PGE2 selectively blocks inhibitory glycinergic neurotransmission onto rat superficial dorsal horn neurons. _Nat. Neurosci._ 5, 34–40 (2002). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Gilman, A.G. Nobel Lecture: G proteins and regulation of adenylyl cyclase. _Biosci. Rep._ 15, 65–97 (1995). Article CAS Google Scholar * Hamm, H.E. The many faces of G protein signaling.
_J. Biol. Chem._ 273, 669–672 (1998). Article CAS Google Scholar * Clapham, D.E. & Neer, E.J. G protein βγ subunits. _Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol._ 37, 167–203 (1997). Article CAS
Google Scholar * Ikeda, S.R. & Dunlap, K. Voltage-dependent modulation of N-type calcium channels: Role of G protein subunits. _Adv. Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res._ 33, 131–151
(1999). Article CAS Google Scholar * Dolphin, A.C. Mechanisms of modulation of voltage-dependent calcium channels by G proteins. _J. Physiol._ 506, 3–11 (1998). Article CAS Google
Scholar * Mark, M.D. & Herlitze, S. G-protein mediated gating of inward-rectifier K+ channels. _Eur. J. Biochem._ 267, 5830–5836 (2000). Article CAS Google Scholar * De Ward, M. et
al. Direct binding of G-protein βγ complex to voltage-dependent calcium channels. _Nature_ 385, 446–450 (1997). Article Google Scholar * Canti, C., Page, K.M., Stephens, G.J. &
Dolphin, A.C. Identification of residues in the N terminus of alpha1B critical for inhibition of the voltage-dependent calcium channel by Gβγ. _J. Neurosci._ 19, 6855–6864 (1999). Article
CAS Google Scholar * Krapivinsky, G., Krapivinsky, L., Wickman, K. & Clapham, D.E. Gβγ binds directly to the G protein-gated K+ channel, IKACh . _J. Biol. Chem._ 270, 29059–29062
(1995). Article CAS Google Scholar * Ruegg, U.T. & Burgess, G.M. Staurosporine, K-252 and UCN-01: potent but nonspecific inhibitors of protein kinases. _Trends Pharmacol. Sci._ 10,
218–220 (1989). Article CAS Google Scholar * Jeong, S.W. & Ikeda, S.R. Sequestration of G-protein βγ subunits by different G-protein α subunits blocks voltage-dependent modulation of
Ca2+ channels in rat sympathetic neurons. _J. Neurosci._ 19, 4755–4761 (1999). Article CAS Google Scholar * Daaka, Y. et al. Receptor and Gβγ isoform-specific interactions with G
protein-coupled receptor kinases. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 94, 2180–2185 (1997). Article CAS Google Scholar * Blackmer, T. et al. G protein βγ subunit-mediated presynaptic inhibition:
regulation of exocytotic fusion downstream of Ca2+ entry. _Science_ 292, 293–297 (2001). Article CAS Google Scholar * Kammermeier, P.J. & Ikeda, S.R. Expression of RGS2 alters the
coupling of metabotropic glutamate receptor 1a to M-type K+ and N-type Ca2+ channels. _Neuron_ 22, 819–829 (1999). Article CAS Google Scholar * Diverse-Pierluissi, M. et al. Selective
coupling of G protein βγ complexes to inhibition of Ca2+ channels. _J. Biol. Chem._ 275, 28380–28385 (2000). Article CAS Google Scholar * Hille, B. Modulation of ion-channel function by
G-protein-coupled receptors. _Trends Neurosci._ 17, 531–536 (1994). Article CAS Google Scholar * Logothetis, D.E., Kurachi, Y., Galper, J., Neer, E.J. & Clapham, D.E. The beta gamma
subunits of GTP-binding proteins activate the muscarinic K+ channel in heart. _Nature_ 28, 321–326 (1987). Article Google Scholar * Wickman, K.D. et al. Recombinant G-protein βγ-subunits
activate the muscarinic-gated atrial potassium channel. _Nature_ 368, 255–257 (1994). Article CAS Google Scholar * Beato, M., Groot-Kormelink, P.J., Colquhoun, D. & Sivilotti, L.G.
Openings of the rat recombinant α1 homomeric glycine receptor as a function of the number of agonist molecules bound. _J. Gen. Physiol._ 119, 443–466 (2002). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Ruiz-Velasco, V. & Ikeda, S.R. Multiple G-protein βγ combinations produce voltage-dependent inhibition of N-type calcium channels in rat superior cervical ganglion neurons. _J.
Neurosci._ 20, 2183–2191 (2000). Article CAS Google Scholar * Ruiz-Velasco, V. & Ikeda, S.R. Functional expression and FRET analysis of green fluorescent proteins fused to G-protein
subunits in rat sympathetic neurons. _J. Physiol._ 537, 679–692 (2001). Article CAS Google Scholar * Couve, A., Moss, S.J. & Pangalos, M.N. GABAB receptors: a new paradigm in
G-protein signaling. _Mol. Cell. Neurosci._ 16, 296–312 (2000). Article CAS Google Scholar * Luscher, C., Jan, L.Y., Stoffel, M., Malenka, R.C. & Nicoll, R.A. G protein-coupled
inwardly rectifying K+ channels (GIRKs) mediate postsynaptic but not presynaptic transmitter actions in hippocampal neurons. _Neuron_ 19, 687–695 (1997). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Sawynok, J. GABAergic mechanisms in antinociception. _Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry_ 8, 581–586 (1984). Article CAS Google Scholar * Hwang, A.S. & Wilcox, G.L.
Baclofen, γ-aminobutyric acidB receptors and substance P in the mouse spinal cord. _J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther._ 248, 1026–1033 (1989). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kangrga, I., Jiang, M.C.
& Randic, M. Actions of (–)-baclofen on rat dorsal horn neurons. _Brain Res._ 562, 265–275 (1991). Article CAS Google Scholar * Towers, S. et al. GABAB receptor protein and mRNA
distribution in rat spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia. _Eur. J. Neurosci._ 12, 3201–3210 (2000). Article CAS Google Scholar * Scanziani, M. GABA spillover activates postsynaptic GABAB
receptors to control rhythmic hippocampal activity. _Neuron_ 25, 673–681 (2000). Article CAS Google Scholar * Jonas, P., Bischofberger, J. & Sandkuhler, J. Corelease of two fast
neurotransmitters at a central synapse. _Science_ 281, 419–424 (1998). Article CAS Google Scholar * Hille, B. _Ion Channels of Excitable Membranes_ (Sinauer, Sunderland, Massachusetts,
2001). Google Scholar * Colquhoun, D. Binding, gating, affinity and efficacy: the interpretation of structure- activity relationships for agonists and of the effects of mutating receptors.
_Br. J. Pharmacol._ 125, 924–947 (1998). Article CAS Google Scholar * Rogers, C.J., Twyman, R.E. & Macdonald, R.L. Benzodiazepine and beta-carboline regulation of single GABAA
receptor channels of mouse spinal neurones in culture. _J. Physiol._ 475, 69–82 (1994). Article CAS Google Scholar * Bean, B.P. Neurotransmitter inhibition of neuronal calcium currents by
changes in voltage dependence. _Nature_ 340, 153–156 (1989). Article CAS Google Scholar * Kneussel, M. & Betz, H. Clustering of inhibitory neurotransmitter receptors at developing
postsynaptic sites: the membrane activation model. _Trends Neurosci._ 23, 429–435 (2000). Article CAS Google Scholar * Tapia, J.C. et al. Early expression of glycine and GABAA receptors
in developing spinal cord neurons. Effects on neurite outgrowth. _Neuroscience_ 108, 493–506 (2001). Article CAS Google Scholar * van Zundert, B. et al. Glycine receptors involved in
synaptic transmission are selectively regulated by the cytoskeleton in mouse spinal neurons. _J. Neurophysiol._ 87, 640–644 (2002). Article CAS Google Scholar * Geiman, E.J., Zheng, W.,
Fritschy, J.M. & Alvarez, F.J. Glycine and GABAA receptor subunits on Renshaw cells: relationship with presynaptic neurotransmitters and postsynaptic gephyrin clusters. _J. Comp.
Neurol._ 444, 275–289 (2002). Article CAS Google Scholar * Asano, T., Morishita, R., Ueda, H. & Kato, K. Selective association of G protein β4 with γ5 and γ12 subunits in bovine
tissues. _J. Biol. Chem._ 274, 21425–21429 (1999). Article CAS Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank S.R. Ikeda and N.L. Harrison for the plasmids, S.R. Ikeda for
critically reading the manuscript, and L.J. Aguayo, A. Ghazanfari and J.T. Healey for technical assistance. This work was supported by Fondecyt, GIA-DIUC (L.G.A. and J.O.), and by the
National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism intramural program (R.W.P.). AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Physiology, Laboratory of Neurophysiology, Box
160-C, University of Concepción, Chile Gonzalo E Yevenes, Juan C Tapia, Jorge Parodi & Luis G Aguayo * Unit on Cellular Neuropharmacology, Laboratory of Molecular and Cellular
Neurobiology, National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, National Institutes of Health, Park 5 Building., Room. 150, 12420 Parklawn Dr., Bethesda, 20892-8115, Maryland, USA Robert W
Peoples * Department of Molecular Biology, Laboratory of Molecular Genetics, Box 160-C, University of Concepción, Chile Ximena Soto & Juan Olate Authors * Gonzalo E Yevenes View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Robert W Peoples View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Juan C
Tapia View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Jorge Parodi View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
* Ximena Soto View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Juan Olate View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google
Scholar * Luis G Aguayo View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Luis G Aguayo. ETHICS DECLARATIONS
COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing financial interests. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Yevenes, G., Peoples, R.,
Tapia, J. _et al._ Modulation of glycine-activated ion channel function by G-protein βγ subunits. _Nat Neurosci_ 6, 819–824 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1095 Download citation *
Received: 29 April 2003 * Accepted: 23 May 2003 * Published: 13 July 2003 * Issue Date: 01 August 2003 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1095 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following
link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature
SharedIt content-sharing initiative