- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
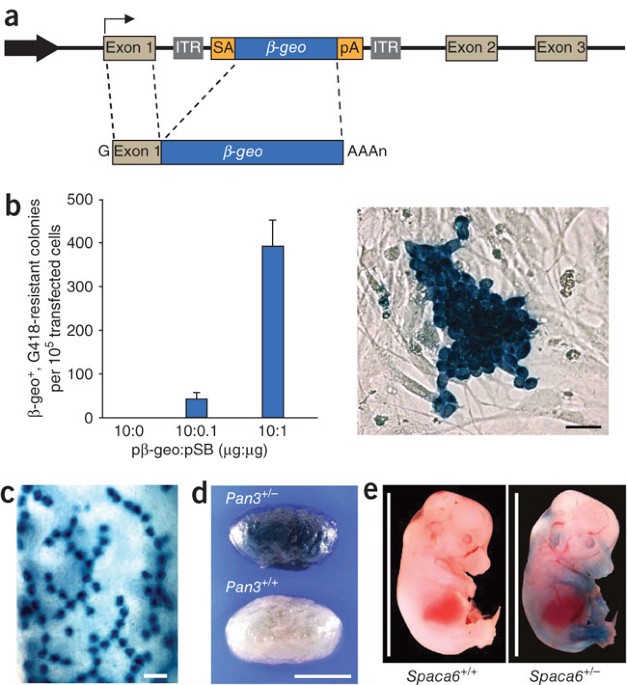
ABSTRACT Disrupting genes in the rat on a genome-wide scale will allow the investigation of many biological processes linked to human health. Here we used transposon-mediated mutagenesis to
knock out genes in rat spermatogonial stem cells. Given the capacity of the testis to support spermatogenesis from thousands of transplanted, genetically manipulated spermatogonia, this
approach paves a way for high-throughput functional genomic studies in the laboratory rat. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access
via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy
this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: *
Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS GENOMIC STABILITY OF MOUSE SPERMATOGONIAL STEM CELLS IN
VITRO Article Open access 17 December 2021 THE_ MC4R_ GENE IS RESPONSIBLE FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF EXPERIMENTALLY INDUCED TESTICULAR TERATOMAS Article Open access 01 May 2023 CRISPR/CAS9-BASED
GENETIC SCREEN OF SCNT-REPROGRAMMING RESISTANT GENES IDENTIFIES CRITICAL GENES FOR MALE GERM CELL DEVELOPMENT IN MICE Article Open access 29 July 2021 REFERENCES * Capecchi, M.R. _Nat. Rev.
Genet._ 6, 507–512 (2005). Article CAS Google Scholar * Hamra, F.K. et al. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 102, 17430–17435 (2005). Article CAS Google Scholar * Ryu, B.Y., Kubota, H.,
Avarbock, M.R. & Brinster, R.L. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 102, 14302–14307 (2005). Article CAS Google Scholar * Buehr, M. et al. _Cell_ 135, 1287–1298 (2008). Article CAS Google
Scholar * Li, P. et al. _Cell_ 135, 1299–1310 (2008). Article CAS Google Scholar * Orwig, K.E., Shinohara, T., Avarbock, M.R. & Brinster, R.L. _Biol. Reprod._ 66, 944–949 (2002).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Hamra, F.K. et al. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 99, 14931–14936 (2002). Article CAS Google Scholar * Ivics, Z. et al. _Nat. Methods_ 6, 415–422 (2009).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Ivics, Z., Hackett, P.B., Plasterk, R.H. & Izsvak, Z. _Cell_ 91, 501–510 (1997). Article CAS Google Scholar * Kitada, K. et al. _Nat. Methods_ 4,
131–133 (2007). Article CAS Google Scholar * Lu, B. et al. _Mamm. Genome_ 18, 338–346 (2007). Article CAS Google Scholar * Horie, K. et al. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 98, 9191–9196
(2001). Article CAS Google Scholar * Dupuy, A.J., Fritz, S. & Largaespada, D.A. _Genesis_ 30, 82–88 (2001). Article CAS Google Scholar * Richardson, T.E., Chapman, K.M., Dann,
C.T., Hammer, R.E. & Hamra, F.K. _PLoS One_ 4, e6308 (2009). Article Google Scholar * Mates, L., Izsvak, Z. & Ivics, Z. _Genome Biol._ 8 (Suppl. 1), S1 (2007). Article Google
Scholar * Wu, Z. et al. _Biol. Reprod._ 81, 77–86 (2009). Article CAS Google Scholar * Cronkhite, J.T. et al. _Dev. Biol._ 284, 171–183 (2005). Article CAS Google Scholar * Dann,
C.T., Alvarado, A.L., Hammer, R.E. & Garbers, D.L. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 103, 11246–11251 (2006). Article CAS Google Scholar * Hamra, F.K. et al. _Dev. Biol._ 269, 393–410
(2004). Article CAS Google Scholar * Vigdal, T.J., Kaufman, C.D., Izsvak, Z., Voytas, D.F. & Ivics, Z. _J. Mol. Biol._ 323, 441–452 (2002). Article CAS Google Scholar * Schnutgen,
F. et al. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 102, 7221–7226 (2005). Article Google Scholar * Friedrich, G. & Soriano, P. _Genes Dev._ 5, 1513–1523 (1991). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Izsvak, Z. et al. _J. Biol. Chem._ 277, 34581–34588 (2002). Article CAS Google Scholar * Sanes, J.R., Rubenstein, J.L. & Nicolas, J.F. _EMBO J._ 5, 3133–3142 (1986). Article CAS
Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank T. Nguyen, T.E. Richardson, G. Mendrano and L.M. Thompson for help with these studies, N. Hübner, D.J. Mangelsdorf and M.H. Cobb
for discussions and for critical reading of the manuscript, and EURATools–EURATrans consortium for sponsoring Z. Izsvák and F.K.H to attend annual meetings (grant HEALTH-F4-2010-241504).
This work was supported by US National Institutes of Health grants R21RR023958 from the National Center for Research Resources and RO1HD036022 from the National Institute of Child Health and
Human Development to F.K.H., by the Bundesministerium fur Bildung und Forschung (grant NGFN-2) to Z. Ivics, European Young Investigator award to Z. Izsvák and by the Cecil H. and Ida Green
Center for Reproductive Biology Sciences at University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Max Delbrück Center for Molecular
Medicine, Berlin, Germany Zsuzsanna Izsvák, Janine Fröhlich, Ivana Grabundzija & Zoltán Ivics * University of Debrecen, Debrecen, Hungary Zsuzsanna Izsvák & Zoltán Ivics * Department
of Pharmacology and Cecil H. and Ida Green Center for Reproductive Biology Sciences, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, Texas, USA James R Shirley, Heather M Powell,
Karen M Chapman & F Kent Hamra Authors * Zsuzsanna Izsvák View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Janine Fröhlich View author publications
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Ivana Grabundzija View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * James R Shirley View
author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Heather M Powell View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar *
Karen M Chapman View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Zoltán Ivics View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed
Google Scholar * F Kent Hamra View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS I.G., J.F., H.M.P., J.R.S., K.M.C. and F.K.H. performed the
research; Z. Izsvák, Z. Ivics and F.K.H. designed research; all authors analyzed the data; Z. Izsvák, Z. Ivics and F.K.H. wrote the manuscript. Correspondence should be addressed to F.K.H.
regarding spermatogonial technology or Z. Ivics regarding transposon technology. CORRESPONDING AUTHORS Correspondence to Zoltán Ivics or F Kent Hamra. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing financial interests. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY TEXT AND FIGURES Supplementary Figures 1–8, Supplementary Tables 1–5 and Supplementary
Discussion (PDF 2237 kb) RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Izsvák, Z., Fröhlich, J., Grabundzija, I. _et al._ Generating knockout rats by
transposon mutagenesis in spermatogonial stem cells. _Nat Methods_ 7, 443–445 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1461 Download citation * Received: 09 January 2010 * Accepted: 16 April
2010 * Published: 16 May 2010 * Issue Date: June 2010 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1461 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative

