- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
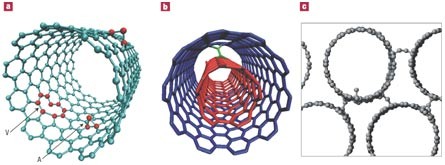
ABSTRACT Irradiating solids with energetic particles is usually thought to introduce disorder, normally an undesirable phenomenon. But recent experiments on electron or ion irradiation of
various nanostructures demonstrate that it can have beneficial effects and that electron or ion beams may be used to tailor the structure and properties of nanosystems with high precision.
Moreover, in many cases irradiation can lead to self-organization or self-assembly in nanostructures. In this review we survey recent advances in the rapidly evolving area of irradiation
effects in nanostructured materials, with particular emphasis on carbon systems because of their technological importance and the unique ability of graphitic networks to reconstruct under
irradiation. We dwell not only on the physics behind irradiation of nanostructures but also on the technical applicability of irradiation for nanoengineering of carbon and other systems.
Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this
journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer
support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS ENHANCING THE ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF GRAPHITE NANOFLAKE THROUGH GAMMA-RAY IRRADIATION Article Open access 01 September 2022 A MULTIFUNCTIONAL
CHEMICAL TOOLBOX TO ENGINEER CARBON DOTS FOR BIOMEDICAL AND ENERGY APPLICATIONS Article 16 February 2022 DIRECT OBSERVATION OF THE FORMATION AND STABILIZATION OF METALLIC NANOPARTICLES ON
CARBON SUPPORTS Article Open access 11 December 2020 REFERENCES * Cook, I. Materials research for fusion energy. _Nature Mater._ 5, 77–80 (2006). CAS Google Scholar * Nastasi, M., Mayer,
J. & Hirvonen, J. _Ion–solid Interactions: Fundamentals and Applications_ (Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, 1996). Google Scholar * Ugarte, D. Curling and closure of graphitic networks
under electron-beam irradiation. _Nature_ 359, 707–709 (1992). CAS Google Scholar * Banhart, F. & Ajayan, P. M. Carbon onions as nanoscopic pressure cells for diamond formation,
_Nature_ 382, 433–435 (1996). CAS Google Scholar * Smith, B. W., Monthioux, M. & Luzzi, D. E. Encapsulated C60 in carbon nanotubes. _Nature_ 396, 323–323 (1998). CAS Google Scholar *
Kis, A. et al. Reinforcement of single-walled carbon nanotube bundles by intertube bridging. _Nature Mater._ 3, 153–157 (2004). CAS Google Scholar * Gómez-Navarro, G. et al. Tuning the
conductance of single-walled carbon nanotubes by ion irradiation in the Anderson localization regime. _Nature Mater._ 4, 534–539 (2005). Google Scholar * Terrones, M., Terrones, H.,
Banhart, F., Charlier, J.-C. & Ajayan, P. M. Coalescence of single-walled carbon nanotubes. _Science_ 288, 1226–1229 (2000). CAS Google Scholar * Hashimoto, A., Suenaga, K., Gloter,
A., Urita, K. & Iijima, S. Direct evidence for atomic defects in graphene layers. _Nature_ 430, 870–873 (2004). CAS Google Scholar * Mickelson, W., Aloni, S., Han, W. Q., Cumings, J.
& Zettl, A. Packing C60 in boron nitride nanotubes. _Science_ 300, 467–469 (2003). CAS Google Scholar * Terrones, M. et al. Molecular junctions by joining single-walled carbon
nanotubes. _Phys. Rev. Lett._ 89, 075505 (2002). CAS Google Scholar * Sun, L. et al. Carbon nanotubes as high-pressure cylinders and nanoextruders. _Science_ 312, 1199–1202 (2006). CAS
Google Scholar * Wesolowski, P., Lyutovich, Y., Banhart, F., Carstanjen, H. D. & Kronmüller, H. Formation of diamond in carbon onions under MeV ion irradiation. _Appl. Phys. Lett._ 71,
1948–1950 (1997). CAS Google Scholar * Lifshitz, Y. et al. The mechanism of diamond nucleation from energetic species. _Science_ 297, 1531–1533 (2002). CAS Google Scholar * Yao, Y. et
al. Diamond nucleation by energetic pure carbon bombardment. _Phys. Rev. B_ 72, 035402 (2005). Google Scholar * Stahl, H., Appenzeller, J., Martel, R., Avouris, P. & Lengeler, B.
Intertube coupling in ropes of SWNTs. _Phys. Rev. Lett._ 85, 5186–5189 (2000). CAS Google Scholar * Wei, B. Q., D'Arcy-Gall, J., Ajayan, P. M. & Ramanath, G. Tailoring structure
and electrical properties of carbon nanotubes using kilo-electron-volt ions. _Appl. Phys. Lett._ 83, 3581–3583 (2003). CAS Google Scholar * Raghuveer, M. S. et al. Nanomachining carbon
nanotubes with ion beams _Appl. Phys. Lett._ 84, 4484–4486 (2004). CAS Google Scholar * Talapatra, S. et al. Irradiation-induced magnetism in carbon nanostructures. _Phys. Rev. Lett._ 95,
097201 (2005). CAS Google Scholar * Esquinazi, P., Spearmann, D., Höhne, R., Setzer, A. & Butz, T. Induced magnetic ordering by proton irradiation in graphite. _Phys. Rev. Lett._ 91,
227201 (2003). CAS Google Scholar * Chappert, C. et al. Planar patterned magnetic media obtained by ion irradiation. _Science_ 280, 1919–1922 (1998). CAS Google Scholar * Bernas, H. et
al. Ordering intermetallic alloys by ion irradiation: a way to tailor magnetic media. _Phys. Rev. Lett._ 91, 077203 (2003). CAS Google Scholar * Akcöltekin, E. et al. Creation of multiple
nanodots by single ions. _Nature Nanotechnol._ 2, 290–294 (2007). Google Scholar * Dhar, S., Davis, R. P. & Feldman, L. C. A novel technique for the fabrication of nanostructures on
silicon carbide using amorphization and oxidation, _Nanotechnology_ 17, 4514–4518 (2006). CAS Google Scholar * Heinig, K. H., Muller, T., Schmidt, B., Strobel, M. & Möller, W.
Interfaces under ion irradiation: growth and taming of nanostructures. _Appl. Phys. A_ 77, 17–25 (2003). CAS Google Scholar * Klaumünzer, S. Modification of nanostructures by high-energy
ion beams. _Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B_ 244, 1–7 (2006). Google Scholar * Kroto, H. W., Heath, J. R., O'Brien, S. C., Curl, R. F. & Smalley, R. E. C60: Buckminsterfullerene. _Nature_
318, 162–163 (1985). CAS Google Scholar * Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. _Nature_ 354, 56–58 (1991). CAS Google Scholar * Geim, A. K. & Novoselov, K. S. The
rise of grapheme. _Nature Mater._ 6, 183–191 (2007). CAS Google Scholar * Nasibulin, A. G. et al. A novel hybrid carbon material. _Nature Nanotechnol._ 2, 156–161 (2007). CAS Google
Scholar * Banhart, F. Irradiation effects in carbon nanostructures. _Rep. Prog. Phys._ 62, 1181–1221 (1999). CAS Google Scholar * Pomoell, J., Krasheninnikov, A. V. & Nordlund, K. Ion
ranges and irradiation-induced defects in multi-walled carbon nanotubes. _J. Appl. Phys._ 96, 2864–2871 (2004). CAS Google Scholar * Kunert, T. & Schmidt, R. Excitations and
fragmentation mechanisms in ion–fullerene collisions, _Phys. Rev. Lett._ 86, 5258–5261 (2001). CAS Google Scholar * Ding, F., Jiao, K., Wu, M. & Yakobson, B. I. Pseudoclimb and
dislocation dynamics in superplastic nanotubes. _Phys. Rev. Lett._ 98, 075503 (2007). Google Scholar * Osváth, Z. et al. Atomically resolved STM images of carbon nanotube defects produced
by Ar+ irradiation. _Phys. Rev. B_ 72, 045429 (2005). Google Scholar * Urita, K., Suenaga, K., Sugai, T., Shinohara, H. & Iijima, S. In situ observation of thermal relaxation of
interstitial-vacancy pair defects in a graphite gap. _Phys. Rev. Lett._ 94, 155502 (2005). Google Scholar * Raghuveer, M. S. et al. Site-selective functionalization of carbon nanotubes.
_Adv. Mater._ 18, 547–552 (2006). CAS Google Scholar * Jung, Y. J. et al. Straightening suspended singlewalled carbon nanotubes by ion irradiation. _Nano Lett._ 4, 1109–1113 (2004). CAS
Google Scholar * Kim, D.-H. et al. Enhancement of the field emission of carbon nanotubes straightened by application of argon ion irradiation. _Chem. Phys. Lett._ 378, 232–237 (2003). CAS
Google Scholar * Ni, B. et al. A combined computational and experimental study of ion-beam modification of carbon nanotube bundles. _J. Phys. Chem. B_ 105, 12719–12725 (2001). CAS Google
Scholar * Yang, D. Q., Rochette, J. & Sacher, E. Controlled chemical functionalization of multiwalled carbon nanotubes by kiloelectronvolt argon ion treatment and air exposure.
_Langmuir_ 21, 8539–8545 (2005). CAS Google Scholar * Zhu, Y., Yi, T., Zheng, B. & Cao, L. The interaction of C60 fullerene and carbon nanotube with Ar ion beam. _Appl. Surf. Sci._
137, 83–90 (1999). CAS Google Scholar * Krasheninnikov, A. V., Nordlund, K. & Keinonen, J. Production of defects in supported carbon nanotubes under ion irradiation. _Phys. Rev. B_ 65,
165423 (2002). Google Scholar * Lu, A. J. & Pan, B. C. Nature of single vacancy in achiral carbon nanotubes. _Phys. Rev. Lett._ 92, 105504 (2004). CAS Google Scholar * Rossato, J.,
Baierle, R. J., Fazzio, A. & Mota, R. Vacancy formation process in carbon nanotubes: First-principles approach. _Nano Lett._ 5, 197–200 (2005). CAS Google Scholar * Krasheninnikov, A.
V., Lehtinen, P. O., Foster, A. S. & Nieminen, R. M. Bending the rules: contrasting vacancy energetics and migration in graphite and carbon nanotubes. _Chem. Phys. Lett._ 418, 132–136
(2006). CAS Google Scholar * Lehtinen, P. O., Foster, A. S., Ma, Y., Krasheninnikov, A. V. & Nieminen, R. M. Irradiation-induced magnetism in graphite: a density functional study.
_Phys. Rev. Lett._ 93, 187202 (2004). CAS Google Scholar * Telling, R., Ewels, C., El-Barbary, A. & Heggie, M. Wigner defects bridge the graphite gap. _Nature Mater._ 2, 333–337
(2003). CAS Google Scholar * El-Barbary, A. A., Telling, R. H., Ewels, C. P., Heggie, M. I. & Briddon, P. R. Structure and energetics of the vacancy in graphite. _Phys. Rev. B_ 68,
144107 (2003). Google Scholar * Kotakoski, J., Krasheninnikov, A. V. & Nordlund, K. Energetics, structure, and long-range interaction of vacancy-type defects in carbon nanotubes:
atomistic simulations. _Phys. B_ 74, 245420 (2006). Google Scholar * Kis, A., Jensen, K., Aloni, S., Mickelson, W. & Zettl, A. Interlayer forces and ultralow sliding friction in
multiwalled carbon nanotubes. _Phys. Rev. Lett._ 97, 025501 (2006). CAS Google Scholar * Stone, A. J. & Wales, D. J. Theoretical-studies of icosahedral C60 and some related species.
_Chem. Phys. Lett._ 128, 501–503 (1986). CAS Google Scholar * Sammalkorpi, M., Krasheninnikov, A., Kuronen, A., Nordlund, K. & Kaski, K. Mechanical properties of carbon nanotubes with
vacancy-like defects. _Phys. Rev. B_ 70, 245416 (2004). Google Scholar * da Silva, A., Fazzio, A. & Antonelli, A. Bundling up carbon nanotubes through Wigner defects. _Nano Lett._ 5,
1045–1049 (2005). CAS Google Scholar * Banhart, F., Li, J. X. & Krasheninnikov, A. V. Carbon nanotubes under electron irradiation: stability of the tubes and their action as pipes for
atom transport. _Phys. Rev. B_ 71, 241408(R) (2005). Google Scholar * Yuzvinsky, T. D. et al. Shrinking a carbon nanotubes. _Nano Lett._ 6, 2718–2722 (2006). CAS Google Scholar * Li, J.
X. & Banhart, F. The engineering of hot carbon nanotubes with an electron beam. _Nano Lett._ 4, 1143–1146 (2004). CAS Google Scholar * Banhart, F., Li, J. X. & Terrones, M. Cutting
single-walled carbon nanotubes with an electron beam: evidence for atom migration inside nanotubes. _Small_ 1, 953–956 (2005). CAS Google Scholar * Yuzvinsky, T. D., Fennimore, A. M.,
Mickelson, W., Esquivias, C. & Zettl, A. Precision cutting of nanotubes with a low-energy electron beam. _Appl. Phys. Lett._ 86, 053109 (2005). Google Scholar * Yoon, M. et al. Zipper
mechanism of nanotube fusion: theory and experiment. _Phys. Rev. Lett._ 92, 075504 (2004). Google Scholar * Suzuki, M., Ishibashi, K., Toratani, K., Tsuya, D. & Aoyagi, Y. Tunnel
barrier formation using argon-ion irradiation and single quantum dots in multiwall carbon nanotubes. _Appl. Phys. Lett._ 81, 2273–2275 (2002). CAS Google Scholar * Maehashi, K. et al.
Formation of single quantum dot in single-walled carbon nanotube channel using focused-ion-beam technique. _Appl. Phys. Lett._ 90, 023103 (2007). Google Scholar * Ishibashi, K., Tsuya, D.,
Suzuki, M. & Aoyagi, Y. Fabrication of a single-electron inverter in multiwall carbon nanotubes. _Appl. Phys. Lett._ 82, 3307–3309 (2003). CAS Google Scholar * Mikó, C. et al. Effect
of electron irradiation on the electrical properties of fibers of aligned single-walled carbon nanotubes. _Appl. Phys. Lett._ 83, 4622–4624 (2003). Google Scholar * Kim, H. M. et al.
Morphological change of multiwalled carbon nanotubes through high-energy (MeV) ion irradiation. _J. Appl. Phys._ 97, 026103 (2005). Google Scholar * Schittenhelm, H. et al. Synthesis and
characterization of single-wall carbon nanotube amorphous diamond thin-film composites. _Appl. Phys. Lett._ 81, 2097–2099 (2002). CAS Google Scholar * Kumar, A. et al. Synthesis of
confined electrically conducting carbon nanowires by heavy ion irradiation of fullerene thin film. _J. Appl. Phys._ 101, 014308 (2007). Google Scholar * Kumar, A., Avasthi, D. K., Pivin, J.
C., Tripathi, A. & Singh, F. Ferromagnetism induced by heavy-ion irradiaiton in fullerene films. _Phys. Rev. B_ 74, 153409 (2006). Google Scholar * Basiuk, V. A., Kobayashi, K.,
Negishi, T. K. Y., Basiuk, E. V. & Saniger-Blesa, J. M., Irradiation of single-walled carbon nanotubes with high-energy protons. _Nano Lett._ 2, 789–791 (2002). CAS Google Scholar *
Neupane, P. P., Manasreh, M. O., Weaver, B. D., Landi, B. J. & Raffaelle, R. P. Proton irradiation effect on single-wall carbon nanotubes in a poly(3-octylthiophene) matrix. _Appl. Phys.
Lett._ 86, 221908 (2005). Google Scholar * Jang, I., Sinnott, S. B., Danailov, D. & Keblinski, P. Molecular dynamics simulation study of carbon nanotubes welding under electron beam
irradiation. _Nano Lett._ 4, 109–114 (2004). CAS Google Scholar * Krasheninnikov, A. V., Nordlund, K., Keinonen, J. & Banhart, F. Ion-irradiation induced welding of carbon nanotubes.
_Phys. Rev. B_ 66, 245403 (2002). Google Scholar * Luzzi, D. E. & Smith, B. W. Carbon cage structures in single wall carbon nanotubes: a new class of materials. _Carbon_ 38, 1751–1756
(2000). CAS Google Scholar * Hernández, E. et al. Fullerene coalescence in nanopeapods: a path to novel tubular carbon. _Nano Lett._ 3, 1037–1042 (2003). Google Scholar * Sun, L.,
Rodríguez-Manzo, J. A. & Banhart, F., Elastic deformation of nanometer-sized metal crystals in graphitic shells. _Appl. Phys. Lett._ 89, 263104 (2006). Google Scholar * Li, J. X. &
Banhart, F. The deformation of single, nanometer-sized metal crystals in graphitic shells. _Adv. Mater._ 17, 1539–1542 (2005). CAS Google Scholar * Banhart, F., Hernández, E. &
Terrones, M. Extreme superheating and supercooling of encapsulated metals in fullerene-like shells. _Phys. Rev. Lett._ 90, 185502 (2003). CAS Google Scholar * Zhang, S. et al. Mechanics of
defects in carbon nanotubes: atomistic and multiscale simulations. _Phys. Rev. B_ 71, 115403 (2005). Google Scholar * Dumitrica, T., Hua, M. & Yakobson, B. I. Symmetry-, time-, and
temperature-dependent strength of carbon nanotubes. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 103, 6105–6109 (2006). CAS Google Scholar * Åström, J. A., Krasheninnikov, A. V. & Nordlund, K. Carbon
nanotube mats and fibers with irradiation-improved mechanical characteristics: a theoretical model. _Phys. Rev. Lett._ 93, 215503 (2004). Google Scholar * Skákalová, V., Woo, Y., Osváth,
Z., Biró, L. P. & Roth, S. Electron transport in Ar-irradiated single wall carbon nanotubes. _Phys. Status Solidi B_ 243, 3346–3350 (2006). Google Scholar * Krasheninnikov, A. V.
Predicted scanning microscopy images of carbon nanotubes with atomic vacancies. _Solid State Commun._ 118, 361–365 (2001). CAS Google Scholar * Krasheninnikov, A. V., Nordlund, K., Sirviö,
M., Salonen, E. & Keinonen, J. Formation of ion irradiation-induced atomic-scale defects on walls of carbon nanotubes. _Phys. Rev. B_ 63, 245405 (2001). Google Scholar * Makarova, T.
& Palacio, F. (eds) _Carbon Based Magnetism_ (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2006). Google Scholar * Andriotis, A. N., Menon, M., Sheetz, R. M. & Chernozatonskii, L. Magnetic properties of
C60 polymers. _Phys. Rev. Lett._ 90, 026801 (2003). Google Scholar * Chan, J. A., Montanari, B., Gale, J. D., Taylor, S. M. B. J. W. & Harrison, N. M. Magnetic properties of polymerized
C60: the influence of defects and hydrogen. _Phys. Rev. B_ 70, 041403(R) (2004). Google Scholar * Zaiser, M. & Banhart, F. Radiation-induced transformation of graphite to diamond.
_Phys. Rev. Lett._ 79, 3680–3683 (1997). CAS Google Scholar * Lyutovich, Y. & Banhart, F. Low-pressure transformation of graphite to diamond under irradiation. _Appl. Phys. Lett._ 74,
659–660 (1999). CAS Google Scholar * Zaiser, M., Lyutovich, Y. & Banhart, F., Irradiation-induced transformation of graphite to diamond: a quantitative study. _Phys. Rev. B_ 62,
3058–3064 (2000). CAS Google Scholar * Terrones, M. & Terrones, H. The role of defects in graphitic structures. _Fullerene Sci. Technol._ 4, 517–522 (1996). CAS Google Scholar *
Rodríguez-Manzo, J. A. et al. In situ nucleation of carbon nanotubes by the injection of carbon atoms into metal particles. _Nature Nanotechnol._ 2, 307–311 (2007). Google Scholar *
Stolojan, V., Tison, Y., Chen, G. Y. & Silva, R. Controlled growth-reversal of catalytic carbon nanotubes under electron-beam irradiation. _Nano Lett._ 6, 1837–1841 (2006). CAS Google
Scholar * Golberg, D. & Bando, Y. Electron irradiation-induced solid state phase transformations: application to the study of fullerenes and nanotubes in the B-C-N system. _Recent Res.
Dev. Appl. Phys._ 2, 1–14 (1999). CAS Google Scholar * Zobelli, A. et al. Defective structure of BN nanotubes: from single vacancies to dislocation lines. _Nano Lett._ 6, 1955–1960 (2006).
CAS Google Scholar * Xu, S. et al. Nanometer-scale modification and welding of silicon and metallic nanowires with a high-intensity electron beam. _Small_ 1, 1221–1229 (2005). CAS Google
Scholar * Zhan, J., Bando, Y., Hu, J. & Golberg, D. Nanofabrication of ZnO nanowires. _Appl. Phys. Lett._ 89, 243111 (2006). Google Scholar * Castro, M., Cuerno, R., Vázquez, L. &
Gago, R. Self-organized ordering of nanostructures produced by ion-beam sputtering. _Phys. Rev. Lett._ 94, 016102 (2005). Google Scholar * Mohanta, S. K., Sonia, R. K., Tripathy, S. &
Chua, S. J. Ordered InP nanostructures fabricated by Ar-ion irradiation. _Appl. Phys. Lett._ 88, 043101 (2006). Google Scholar * Kluth, P. et al. Disorder and cluster formation during ion
irradiation of Au nanoparticles in SiO2 . _Phys. Rev. B_ 74, 014202 (2006). Google Scholar * McEuen, P. L. Carbon-based electronics. _Nature_ 393, 15–17 (1998). CAS Google Scholar *
Miyamoto, Y., Berber, S., Yoon, M., Rubio, A. & Tománek, D. Can photo excitations heal defects in carbon nanotubes? _Chem. Phys. Lett._ 392, 209–213 (2004). CAS Google Scholar *
Krasheninnikov, A. V., Nordlund, K. & Keinonen, J. Carbon nanotubes as masks against ion irradiation: an insight from atomistic simulations. _Appl. Phys. Lett._ 81, 1101–1103 (2002). CAS
Google Scholar * Wang, Y.-N. & Mišković, Z. L. Interactions of fast ions with carbon nanotubes: self-energy and stopping power. _Phys. Rev. A_ 69, 022901 (2004). Google Scholar *
Ziegler, J. F., Biersack, J. P. & Littmark, U. _The Stopping and Range of Ions in Matter_ (Pergamon, New York, 1985). Google Scholar * Banhart, F. Formation and transformation of carbon
nanoparticles under electron irradiation. _Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A_ 362, 2205–2222 (2004). CAS Google Scholar * Salonen, E., Krasheninnikov, A. V. & Nordlund, K. Beam
interactions with materials and atoms. _Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B_ 193, 603–608 (2002). CAS Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank K. Nordlund, R. M. Nieminen, J.
Keinonen, A. S. Foster, J. Kotakoski, M. Sammalkorpi, J. X. Li, L. Sun, J. A. Rodríguez-Manzo, M. Terrones, P. M. Ajayan and other co-workers for many years of collaboration. The preparation
of this review was supported by the Academy of Finland through the Centre of Excellence program. Support from the DAAD and ETC (D05/51651) is gratefully acknowledged. AUTHOR INFORMATION
Author notes * F. Banhart Present address: Present address: Institut de Physique et Chimie des Matériaux de Strasbourh, Université de Strasbourg, 23 rue de loess, 67034 Strasbourg, France,
AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Accelerator Laboratory, P.O. Box 43, FI-00014 University of Helsinki, Finland A. V. Krasheninnikov * Laboratory of Physics, P.O. Box 1100, FI-02015 Helsinki
University of Technology, Finland A. V. Krasheninnikov * Institut für Physikalische Chemie, Universität Mainz, Mainz, D-55099, Germany F. Banhart Authors * A. V. Krasheninnikov View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * F. Banhart View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar RIGHTS AND
PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Krasheninnikov, A., Banhart, F. Engineering of nanostructured carbon materials with electron or ion beams. _Nature
Mater_ 6, 723–733 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1996 Download citation * Issue Date: October 2007 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1996 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the
following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer
Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(319x0:321x2)/people_social_image-60e0c8af9eb14624a5b55f2c29dbe25b.png)



