- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
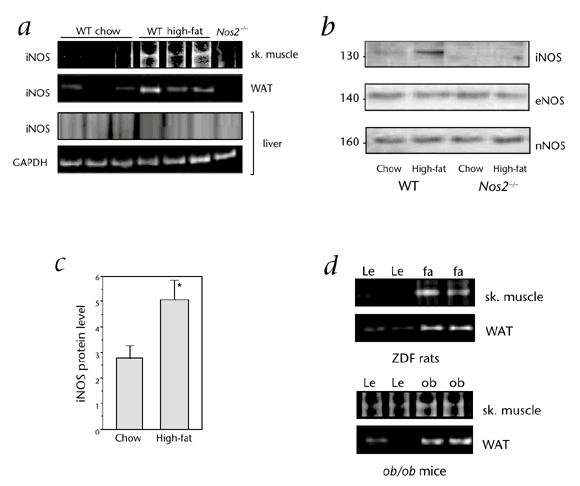
Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) is induced by inflammatory cytokines in skeletal muscle and fat. It has been proposed that chronic iNOS induction may cause muscle insulin resistance.
Here we show that iNOS expression is increased in muscle and fat of genetic and dietary models of obesity. Moreover, mice in which the gene encoding iNOS was disrupted (Nos2−/− mice) are
protected from high-fat–induced insulin resistance. Whereas both wild-type and Nos2−/− mice developed obesity on the high-fat diet, obese Nos2−/− mice exhibited improved glucose tolerance,
normal insulin sensitivity in vivo and normal insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in muscles. iNOS induction in obese wild-type mice was associated with impairments in phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase and Akt activation by insulin in muscle. These defects were fully prevented in obese Nos2−/− mice. These findings provide genetic evidence that iNOS is involved in the development
of muscle insulin resistance in diet-induced obesity.
We thank B. Marcotte and J. Lalonde for technical assistance; F. Tremblay for help with the determination of PI 3-kinase activity; R. Labrecque for help with the maintenance and care of the
transgenic mice lines; C. Nathan for advice; and Y. Deshaies and C.H. Côté for critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by grants from the Canadian Institutes for Health
Research (to A.M.).
Department of Anatomy and Physiology, Lipid Research Unit and Research Center on Energy Metabolism, Laval University Hospital Research Center, Ste-Foy, Québec, Canada
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:









