- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT FAS LIGAND (FASL) TRIGGERS APOPTOSIS DURING CYTOTOXICITY MEDIATED BY CYTOTOXIC T LYMPHOCYTES AND DURING IMMUNE DOWNREGULATION 1 . THE ABILITY OF T CELLS AND NATURAL KILLER CELLS TO
TRIGGER APOPTOSIS THROUGH THIS MECHANISM IS CONTROLLED BY THE CELL SURFACE EXPRESSION OF FASL ( ref. 2 ). BECAUSE FASL EXPRESSION IS UPREGULATED ON ACTIVATION 2, 3 , FASL WAS THOUGHT TO BE
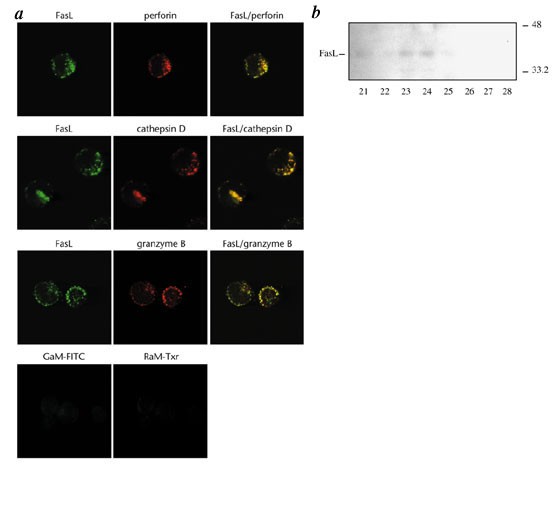
DELIVERED DIRECTLY TO THE CELL SURFACE. HERE WE SHOW THAT NEWLY SYNTHESIZED FASL IS STORED IN SPECIALIZED SECRETORY LYSOSOMES IN BOTH CD4 + AND CD8 + T CELLS AND NATURAL KILLER CELLS, AND
THAT POLARIZED DEGRANULATION CONTROLS THE DELIVERY OF FASL TO THE CELL SURFACE. IN THIS WAY, FASL-MEDIATED APOPTOSIS IS FINELY CONTROLLED BY RECEPTOR-MEDIATED TARGET-CELL RECOGNITION. THE
CYTOPLASMIC TAIL OF FASL CONTAINS SIGNALS THAT SORT FASL TO SECRETORY LYSOSOMES IN HEMOPOIETIC CELLS. THIS PATHWAY MAY PROVIDE A GENERAL MECHANISM FOR CONTROLLING THE CELL SURFACE APPEARANCE
OF PROTEINS INVOLVED IN IMMUNE REGULATION. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access
through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $209.00 per year only $17.42 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink *
Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional
subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS TROGOCYTIC MOLTING OF T CELL MICROVILLI UPREGULATES T CELL RECEPTOR SURFACE EXPRESSION AND
PROMOTES CLONAL EXPANSION Article Open access 24 May 2023 DIFFERENCES IN CD80 AND CD86 TRANSENDOCYTOSIS REVEAL CD86 AS A KEY TARGET FOR CTLA-4 IMMUNE REGULATION Article Open access 23 August
2022 TIM-3 DRIVES TEMPORAL DIFFERENCES IN RESTIMULATION-INDUCED CELL DEATH SENSITIVITY IN EFFECTOR CD8+ T CELLS IN CONJUNCTION WITH CEACAM1 Article Open access 14 April 2021 REFERENCES *
Nagata, S. & Golstein, P. The Fas death factor. _Science_ 267, 1449–1456 (1995). Article CAS Google Scholar * Suda, T. et al. Expression of the Fas ligand in cells of T cell lineage.
_J. Immunol._ 154, 3806–3813 (1995). CAS Google Scholar * Vignaux, F. et al. TCR/CD3 coupling to Fas-based cytotoxicity. _J. Exp. Med._ 181, 781–786 (1995). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Suda, T., Takahashi, T., Golstein, P. & Nagata, S. Molecular cloning and expression of the Fas ligand, a novel member of the tumor necrosis factor family. _Cell_ 75, 1169–1178 (1993).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Watanabe-Fukunaga, R. et al. The cDNA structure, expression, and chromosomal assignment of the mouse Fas antigen. _J Immunol_. 148, 1274–1279 (1992). CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Montel, A.H., Bochan, M.R., Hobbs, J.A., Lynch, D.H. & Brahmi, Z. Fas involvement in cytotoxicity mediated by human NK cells. _Cell. Immunol._ 166, 236–246
(1995). Article CAS Google Scholar * Griffith, T.S., Brunner, T., Fletcher, S.M., Green, D.R. & Ferguson, T.A. Fas ligand-induced apoptosis as a mechanism of immune priviledge [see
comments]. _Science_ 270, 1189–1192 (1995). Article CAS Google Scholar * Peters, P.J. et al. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte granules are secretory lysosomes, containing both perforin and
granzymes. _J. Exp. Med._ 173, 1099–1109 (1991). Article CAS Google Scholar * Yodoi, J. et al. TCGF (IL 2)-receptor inducing factor(s). I. Regulation of IL 2 receptor on a natural
killer-like cell line (YT cells). _J. Immunol._ 134, 1623–1630 (1985). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kayagaki, N. et al. Metalloproteinase-mediated release of human Fas ligand. _J. Exp.
Med._ 182, 1777–1783 (1995). Article CAS Google Scholar * Mariani, S.M., Matiba, B., Baumler, C. & Krammer, P.H. Regulation of cell surface APO-1/Fas (CD95) ligand expression by
metalloproteases. _Eur. J. Immunol._ 25, 2303–2307 (1995). Article CAS Google Scholar * Isaaz, S., Baetz, K., Olsen, K., Podack, E. & Griffiths, G.M. Serial killing by cytotoxic T
lymphocytes: T cell receptor triggers degranulation, re-filling of the lytic granules and secretion of lytic proteins via a non-granule pathway. _Eur. J. Immunol._ 25, 1071–1079 (1995).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Peters, P.J. et al. Molecules relevant for T cell-target cell interaction are present in cytolytic granules of human T lymphocytes. _Eur. J. Immunol._ 19,
1469–1475 (1989). Article CAS Google Scholar * Valitutti, S., Muller, S., Dessing, M. & Lanzavecchia, A. Different responses are elicited in cytotoxic T lymphocytes by different
levels of T cell receptor occupancy. _J. Exp. Med._ 183, 1917–1921 (1996). Article CAS Google Scholar * Stokes, T.A. et al., Fiedler, P., Schaetzlein, C.E. & Eibel, H. & Stassi,
G. et al. Technical Comments. _Science_ 279, 2015 (1998). Article Google Scholar * Griffiths, G.M. Secretory lysosomes- a special mechanism of regulated secretion in hemopoietic in cells.
_Trends Cell Biol._ 6, 329–332 (1996). Article CAS Google Scholar * Griffiths, G.M. Protein sorting and secretion during CTL killing. _Semin. Immunol._ 9, 109–115 (1997). Article CAS
Google Scholar * Shiver, J.W. & Henkart, P.A. A noncytotoxic mast cell tumor line exhibits potent IgE-dependent cytotoxicity after transfection with the cytolysin/perforin gene. _Cell_
64, 1175–1181 (1991). Article CAS Google Scholar * Hara, T., Jung, L.K., Bjorndahl, J.M. & Fu, S.M. Human T cell activation. III. Rapid induction of a phosphorylated 28 kD/32 kD
disulfide-linked early activation antigen (EA 1) by 12-o- tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate, mitogens, and antigens. _J. Exp. Med._ 164, 1988–2005 (1986). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Ziegler, S.F. et al. Molecular characterization of the early activation antigen CD69: a type II membrane glycoprotein related to a family of natural killer cell activation antigens. _Eur. J.
Immunol._ 23, 1643–1648 (1993). Article CAS Google Scholar * Takayama, H. & Sitkovsky, M.V. Antigen receptor-regulated exocytosis in cytotoxic T lymphocytes. _J. Exp. Med._ 166,
725–743 (1987). Article CAS Google Scholar * Uellner, R. et al. Perforin is activated by a proteolytic cleavage during biosynthesis which reveals a phospholipid-binding C2 domain. _EMBO
J._ 16, 7287–7296 (1997). Article CAS Google Scholar * Henkart, P.A., Millard, P.J., Reynolds, C.W. & Henkart, M.P. Cytolytic activity of purified cytoplasmic granules from cytotoxic
rat large granular lymphocyte tumors. _J. Exp. Med._ 160, 75–93 (1984). Article CAS Google Scholar * Kiener, P.A. et al. Human monocytic cells contain high levels of intracellular Fas
ligand: rapid release following cellular activation. _J. Immunol._ 159, 1594–1598 (1997). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Marks, M.S., Ohno, H., Kirchhausen, T. & Bonifacino, J.S. Protein
sorting by tyrosine-based signals: adapting to the Ys and wherefores. _Trends Cell Biol._ 7, 124–128 (1997). Article CAS Google Scholar * Henn, V. et al. CD40 ligand on activated
platelets triggers an inflammatory reaction of endothelial cells. _Nature_ 391, 591–594 (1998). Article CAS Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The authors thank J.
Kaufman, G. MacPherson, J. Stinchcombe and H. Waldmann for critical reading of the manuscript and discussions. The work was supported by grants from the Wellcome Trust (040825 and 050613).
AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Sir William Dunn School of Pathology, University of Oxford, South Parks Road, Oxford, OX1 3RE G. Bossi & G.M. Griffiths Authors * G. Bossi
View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * G.M. Griffiths View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to G.M. Griffiths. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Bossi, G., Griffiths, G. Degranulation plays an
essential part in regulating cell surface expression of Fas ligand in T cells and natural killer cells. _Nat Med_ 5, 90–96 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/4779 Download citation * Received:
27 October 1998 * Accepted: 18 November 1998 * Issue Date: January 1999 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/4779 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read
this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative



![Ms r anghel -v- middlesex university: [2022] eat 176](https://www.gov.uk/assets/static/govuk-opengraph-image-03837e1cec82f217cf32514635a13c879b8c400ae3b1c207c5744411658c7635.png)



