- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT AUTOIMMUNITY TO ANTIGENS OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM IS USUALLY CONSIDERED DETRIMENTAL. T CELLS SPECIFIC TO A CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM SELF ANTIGEN, SUCH AS MYELIN BASIC PROTEIN,
CAN INDEED INDUCE EXPERIMENTAL AUTOIMMUNE ENCEPHALOMYELITIS, BUT SUCH T CELLS MAY NEVERTHELESS APPEAR IN THE BLOOD OF HEALTHY INDIVIDUALS. WE SHOW HERE THAT AUTOIMMUNE T CELLS SPECIFIC TO
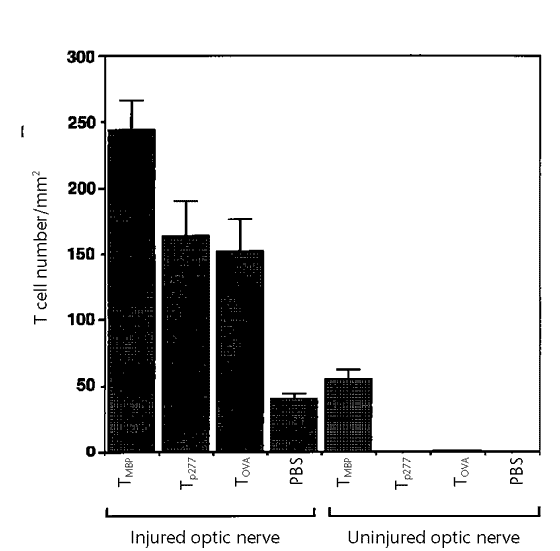
MYELIN BASIC PROTEIN CAN PROTECT INJURED CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM NEURONS FROM SECONDARY DEGENERATION. AFTER A PARTIAL CRUSH INJURY OF THE OPTIC NERVE, RATS INJECTED WITH ACTIVATED ANTI–MYELIN
BASIC PROTEIN T CELLS RETAINED APPROXIMATELY 300% MORE RETINAL GANGLION CELLS WITH FUNCTIONALLY INTACT AXONS THAN DID RATS INJECTED WITH ACTIVATED T CELLS SPECIFIC FOR OTHER ANTIGENS.
ELECTROPHYSIOLOGICAL ANALYSIS CONFIRMED THIS FINDING AND SUGGESTED THAT THE NEUROPROTECTION COULD RESULT FROM A TRANSIENT REDUCTION IN ENERGY REQUIREMENTS OWING TO A TRANSIENT REDUCTION IN
NERVE ACTIVITY. THESE FINDINGS INDICATE THAT T–CELL AUTOIMMUNITY IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM, UNDER CERTAIN CIRCUMSTANCES, CAN EXERT A BENEFICIAL EFFECT BY PROTECTING INJURED NEURONS FROM
THE SPREAD OF DAMAGE. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution
Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $209.00 per year only $17.42 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full
article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs *
Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS B CELLS ORCHESTRATE TOLERANCE TO THE NEUROMYELITIS OPTICA AUTOANTIGEN AQP4 Article Open access 21 February 2024 CD8+ T CELLS
SPECIFIC FOR CRYPTIC APOPTOSIS-ASSOCIATED EPITOPES EXACERBATE EXPERIMENTAL AUTOIMMUNE ENCEPHALOMYELITIS Article Open access 29 October 2021 MICROGLIA-MEDIATED DEMYELINATION PROTECTS AGAINST
CD8+ T CELL-DRIVEN AXON DEGENERATION IN MICE CARRYING PLP DEFECTS Article Open access 30 October 2023 REFERENCES * Streilein, J.W. Immune privilege as the result of local tissue barriers and
immunosuppressive microenvironments. _Curr. Opin. Immunol._ 5, 428–432 (1993). Article CAS Google Scholar * Streilein, J.W. Unraveling immune privilege. _Science_ 270, 1158–1159 (1995).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Lazarov Spiegler, O. _ et al._ Transplantation of activated macrophages overcomes central nervous system regrowth failure. _FASEB J._ 10, 1296–1302 (1996).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Rapalino, O. _ et al._ Implantation of stimulated homologous macrophages results in partial recovery of paraplegic rats. _Nature Med._ 4, 814–821 (1998).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Hickey, W.F., Hsu, B.L. & Kimura, H. T7–lymphocyte entry into the central nervous system. _J. Neurosci. Res._ 28, 254– 260 (1991). Article CAS Google
Scholar * Ben Nun, A., Wekerle, H. & Cohen, I.R. The rapid isolation of clonable antigen–specific T lymphocyte lines capable of mediating autoimmune encephalomyelitis. _ Eur. J.
Immunol._ 11, 195–199 (1981). Article CAS Google Scholar * Ota, K. et al. T–cell recognition of an immunodominant myelin basic protein epitope in multiple sclerosis. _Nature_ 346, 183–187
(1990). Article CAS Google Scholar * Martin, R. Immunological aspects of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis and their application for new therapeutic
strategies. _ J. Neural Transm. Suppl._ 49, 53–67 (1997). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Burns, J., Rosenzweig, A., Zweiman, B. & Lisak, R.P. Isolation of myelin basic protein–reactive
T–cell lines from normal human blood. _Cell. Immunol._ 81, 435– 440 (1983). Article CAS Google Scholar * Pette, M. _et al._ Myelin autoreactivity in multiple sclerosis: recognition of
myelin basic protein in the context of HLA–DR2 products by T lymphocytes of multiple–sclerosis patients and healthy donors. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 87, 7968–7972 (1990). Article CAS
Google Scholar * Martin, R. _ et al._ Fine specificity and HLA restriction of myelin basic protein–specific cytotoxic T cell lines from multiple sclerosis patients and healthy individuals.
_J. Immunol._ 145, 540–548 (1990). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Schluesener, H.J. & Wekerle, H. Autoaggressive T lymphocyte lines recognizing the encephalitogenic region of myelin
basic protein: in vitro selection from unprimed rat T lymphocyte populations. _ J. Immunol._ 135, 3128–3133 (1985). CAS Google Scholar * Hirschberg, D.L. _ et al._ Accumulation of
passively transferred primed T cells independently of their antigen specificity following central nervous system trauma. _ J. Neuroimmunol._ 89, 88–96 (1998). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Faden, A.I. & Salzman, S. Pharmacological strategies in CNS trauma. _Trends Pharmacol. Sci._ 13, 29– 35 (1992). Article CAS Google Scholar * Faden, A.I. Experimental neurobiology of
central nervous system trauma. _Crit. Rev. Neurobiol._ 7, 175–186 (1993). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * McIntosh, T.K. Novel pharmacologic therapies in the treatment of experimental
traumatic brain injury: a review. _J. Neurotrauma_ 10, 215 –261 (1993). Article CAS Google Scholar * Lynch, D.R. & Dawson, T.M. Secondary mechanisms in neuronal trauma. _Curr. Opin.
Neurol._ 7, 510– 516 (1994). Article CAS Google Scholar * Bazan, N.G., Rodriguez de Turco, E.B. & Allan, G. Mediators of injury in neurotrauma: intracellular signal transduction and
gene expression. _J. Neurotrauma_ 12, 791–814 (1995). Article CAS Google Scholar * Liu, D., Yang, R., Yan, X. & McAdoo, D.J. Hydroxyl radicals generated in vivo kill neurons in the
rat spinal cord: electrophysiological, histological, and neurochemical results. _J. Neurochem._ 62, 37–44 (1994). Article CAS Google Scholar * Yoshino, A., Hovda, D.A., Kawamata, T.,
Katayama, Y. & Becker, D.P. Dynamic changes in local cerebral glucose utilization following cerebral concussion in rats: evidence of a hyper– and subsequent hypometabolic state. _Brain
Res._ 561, 106–119 (1991). Article CAS Google Scholar * Hovda, D.A., Yoshino, A., Kawamata, T., Katayama, Y. & Becker, D.P. Diffuse prolonged depression of cerebral oxidative
metabolism following concussive brain injury in the rat: a cytochrome oxidase histochemistry study. _Brain Res._ 567, 1–10 (1991). Article CAS Google Scholar * Zivin, J.A. & Choi,
D.W. Stroke therapy. _Sci. Am. _ 265, 56–63 ( 1991). Article CAS Google Scholar * Yoles, E. _et al._ GM1 reduces injury–induced metabolic deficits and degeneration in the rat optic nerve.
_Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci._ 33, 3586–3591 (1992). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Yoles, E. & Schwartz, M. N–methyl–D–aspartate–receptor antagonist protects neurons from secondary
degeneration after partial optic nerve crush. _J. Neurotrauma_ 14, 665– 675 (1997). Article CAS Google Scholar * Yoles, E. & Schwartz, M. Degeneration of spared axons following
partial white matter lesion: Implications for optic nerve neuropathies. _ Exp. Neurol._ 153, 1–7 ( 1998). Article CAS Google Scholar * Naparstek, Y. _ et al._ T lymphocyte lines producing
or vaccinating against autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). Functional activation induces peanut agglutinin receptors and accumulation in the brain and thymus of line cells. _Eur. J.
Immunol._ 13, 418–423 ( 1983). Article CAS Google Scholar * Popovich, P.G., Stokes, B.T. & Whitacre, C.C. Concept of autoimmunity following spinal cord injury: possible roles for T
lymphocytes in the traumatized central nervous system. _J. Neurosci. Res._ 45, 349– 363 (1996). Article CAS Google Scholar * Mor, F. & Cohen, I.R. Pathogenicity of T cells responsive
to diverse cryptic epitopes of myelin basic protein in the Lewis rat. _ J. Immunol._ 155, 3693–3699 (1995). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Savio, T. & Schwab, M.E. Rat CNS white matter,
but not gray matter, is nonpermissive for neuronal cell adhesion and fiber outgrowth. _ J. Neurosci._ 9, 1126–1133 (1989). Article CAS Google Scholar * Lotan, M. & Schwartz, M. Cross
talk between the immune system and the nervous system in response to injury: implications for regeneration. _FASEB J._ 8, 1026–1033 (1994). Article CAS Google Scholar * Zamvil, S.S. &
Steinman, L. The T lymphocyte in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. _Annu. Rev. Immunol._ 8, 579–621 (1990). Article CAS Google Scholar * Palladini, G., Grossi, M., Maleci, A.,
Lauro, G.M. & Guidetti, B. Immunocomplexes in rat and rabbit spinal cord after injury. _Exp. Neurol._ 95, 639– 651 (1987). Article CAS Google Scholar * Mizrachi, Y. _ et al._ Systemic
humoral factors participating in the course of spinal cord injury. _Paraplegia_ 21, 287– 293 (1983). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Cohen, I.R. Autoimmunity to chaperonins in the
pathogenesis of arthritis and diabetes. _Annu. Rev. Immunol._ 9, 567– 589 (1991). Article CAS Google Scholar * Mor, F. & Cohen, I.R. T cells in the lesion of experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis. Enrichment for reactivities to myelin basic protein and to heat shock proteins. _J. Clin. Invest._ 90, 2447–2455 (1992). Article CAS Google Scholar * Ransom, B.R.,
Stys, P.K. & Waxman, S.G. The pathophysiology of anoxic injury in central nervous system white matter. _Stroke_ 21, 11 (suppl), III52–57 (1990). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Barone,
F.C., Feuerstein, G.Z. & White, R.F. Brain cooling during transient focal ischemia provides complete neuroprotection. _Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev._ 21, 31–44 (1997). Article CAS Google
Scholar * Yarom, Y. _et al._ Immunospecific inhibition of nerve conduction by T lymphocytes reactive to basic protein of myelin. _Nature_ 303, 246–247 (1983). Article CAS Google Scholar
* Koller, H., Siebler, M. & Hartung, H.P. Immunologically induced electrophysiological dysfunction: implications for inflammatory diseases of the CNS and PNS. _Prog. Neurobiol._ 52, 1–26
( 1997). Article CAS Google Scholar * Meeson, A.P., Piddlesden, S., Morgan, B.P. & Reynolds, R. The distribution of inflammatory demyelinated lesions in the central nervous system of
rats with antibody–augmented demyelinating experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. _Exp. Neurol._ 129, 299 –310 (1994). Article CAS Google Scholar * Ehrhard, P.B., Erb, P., Graumann, U.
& Otten, U. Expression of nerve growth factor and nerve growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase Trk in activated CD4–positive T–cell clones. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 90, 10984–10988
( 1993). Article CAS Google Scholar * Lambiase, A. _ et al._ Human CD4+ T cell clones produce and release nerve growth factor and express high–affinity nerve growth factor receptors. _ J.
Allergy Clin. Immunol._ 100, 408– 414 (1997). Article CAS Google Scholar * Santambrogio, L. _ et al._ Nerve growth factor production by lymphocytes. _ J. Immunol._ 153, 4488–4495 (1994).
CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Cohen, I.R. The cognitive paradigm and the immunological homunculus. _Immunol. Today_ 13, 490–494 ( 1992). Article CAS Google Scholar * Lider, O., Reshef,
T., Beraud, E., Ben Nun, A. & Cohen, I.R. Anti–idiotypic network induced by T cell vaccination against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. _Science_ 239, 181–183 (1988). Article
CAS Google Scholar * Matzinger, P. Tolerance, danger, and the extended family. _Annu. Rev. Immunol. _ 12, 991–1045 ( 1994). Article CAS Google Scholar * Hirshfeld, H., Teitelbaum, D.,
Arnon, R. & Sela, M. Basic encephalitogenic protein: a simplified purification on sulfoethyl–Sephadex. _FEBS Lett._ 7, 317 ( 1970). Article CAS Google Scholar * Elias, D. _et al._
Vaccination against autoimmune mouse diabetes with a T–cell epitope of the human 65–kDa heat shock protein. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 88, 3088–3091 (1991). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Mor, F. & Cohen, I.R. Shifts in the epitopes of myelin basic protein recognized by Lewis rat T cells before, during, and after the induction of experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis. _J. Clin. Invest._ 92, 2199–2206 ( 1993). Article CAS Google Scholar * Gillis, S., Ferm, M.M., Ou, W. & Smith, K.A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production
and a quantitative microassay for activity. _J. Immunol._ 120, 2027– 2032 (1978). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Duvdevani, R. _ et al._ Graded crush of the rat optic nerve as a brain injury
model: combining electrophysiological, histological and behavioral outcome. _ Restor. Neurol. Neurosci._ 2, 31–38 (1990). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hunig, T., Wallny, H.J., Hartley,
J.K., Lawetzky, A. & Tiefenthaler, G. A monoclonal antibody to a constant determinant of the rat T cell antigen receptor that induces T cell activation. Differential reactivity with
subsets of immature and mature T lymphocytes. _J. Exp. Med._ 169, 73– 86 (1989). Article CAS Google Scholar * Yoles, E., Belkin, M. & Schwartz, M. HU–211, a nonpsychotropic
cannabinoid, produces short– and long–term neuroprotection after optic nerve axotomy. _J. Neurotrauma_ 13, 49– 57 (1996). Article CAS Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank S. Smith and P. Taylor for editorial assistance, and I. Friedmann for help with graphics. I.R. Cohen is the incumbent of the Mauerberger Chair in Immunology, the director of the
Robert Koch–Minerva Center for Research in Autoimmune Disease and the director of the Center for the Study of Emerging Diseases. M.S. holds the Maurice and Ilse Katz Professorial Chair in
Neuroimmunology. AUTHOR INFORMATION Author notes * Gila Moalem, Felix Mor and Irun R. Cohen: Department of Immunology, The Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot, Israel G.M. & R.L.–A.
contributed equally to the work. AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Neurobiology, The Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot, Israel Gila Moalem, Raya Leibowitz–Amit, Eti Yoles &
Michal Schwartz Authors * Gila Moalem View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Raya Leibowitz–Amit View author publications You can also search
for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Eti Yoles View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Felix Mor View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Irun R. Cohen View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Michal Schwartz View author publications
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Michal Schwartz. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE
THIS ARTICLE Moalem, G., Leibowitz–Amit, R., Yoles, E. _et al._ Autoimmune T cells protect neurons from secondary degeneration after central nervous system axotomy. _Nat Med_ 5, 49–55
(1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/4734 Download citation * Received: 24 August 1998 * Accepted: 03 November 1998 * Issue Date: January 1999 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/4734 SHARE THIS
ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(383x0:385x2)/suave-768-1-ba61227cd9f741fcb2c1627fe4857037.jpg)

