- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT Severe thrombocytopenia frequently occurs in patients receiving chemotherapy and in patients with autoimmune disorders. Thrombocytopenia is associated with bleeding, which may be
serious and life threatening1,2,3. Current treatment strategies for thrombocytopenia may require transfusion of allogeneic platelets, which is associated with serious drawbacks4. These
include the occurrence of anti-platelet antibodies, which may result in refractoriness to further platelet transfusions, and the potential risk of transfer of blood-borne diseases5,6.
Therefore, we have recently developed a platelet substitute product (Synthocytes), which is composed of human albumin microcapsules with fibrinogen immobilized on their surface. Here we show
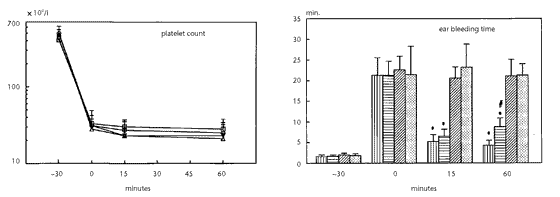
that the intravenous administration of these microcapsules not only corrects the prolonged bleeding time in rabbits rendered thrombocytopenic either by anti-platelet antibodies or by
chemotherapy, but also reduces bleeding from surgical wounds inflicted in the abdominal skin and musculature. No potential systemic prothrombotic effect of the microcapsules was observed in
a model of rabbit venous thrombosis. As for the mechanism of action, experiments with normal and thrombocytopenic human blood in an endothelial cell matrix-coated perfusion chamber
demonstrated an interaction between the fibrinogen-coated albumin microcapsules and native platelets. It was shown that the fibrinogen-coated albumin microcapsules could facilitate platelet
adhesion to endothelial cell matrix and correct the impaired formation of platelet aggregates in relatively platelet-poor blood. This study indicates that fibrinogen-coated albumin
microcapsules can act to improve primary hemostasis under thrombocytopenic conditions and may eventually be a promising agent for prophylaxis and treatment of bleeding in patients with
severe thrombocytopenia. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your
institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $209.00 per year only $17.42 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access
to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read
our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS IMPACT OF G FORCE AND TIMING ON THE CHARACTERISTICS OF PLATELET-RICH FIBRIN MATRICES Article Open access 16 March
2021 THERAPEUTIC POTENTIAL OF FIBRINOGEN Γ-CHAIN PEPTIDE-COATED, ADP-ENCAPSULATED LIPOSOMES AS A HAEMOSTATIC ADJUVANT FOR POST-CARDIOPULMONARY BYPASS COAGULOPATHY Article Open access 09 July
2020 HEMOSTATIC CAPABILITY OF ULTRAFILTRATED FRESH FROZEN PLASMA COMPARED TO CRYOPRECIPITATE Article Open access 07 December 2023 REFERENCES * Roy, A.J., Jaffe, N. & Djerassi, I.
Prophylactic platelet transfusions in children with acute leukemia. A dose response study. _Transfusion_ 13, 283–290 (1973). Article CAS Google Scholar * Rebulla, P. _ et al._ The
threshold for prophylactic platelet transfusions in adults with acute myeloid leukemia. _N. Engl. J. Med._ 337, 1870–1875 (1997). Article CAS Google Scholar * National Institute of Health
Consensus Conference. Platelet transfusion therapy._Transfus. Med. Rev._ 1, 195 –200 (1987). * Slichter, S.J. _ in_ _Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice_ 2nd edn. (eds. Hoffman, R. et
al. ) 419–421 (Churchill Livingstone, New York, 1995). Google Scholar * The Trial to Reduce Alloimmunization to Platelets Study Group. Leucocyte reduction and ultraviolet B irradiation of
platelets to prevent alloimmunization and refractoriness to platelet transfusions. _ N. Engl. J. Med._ 337, 1861–1869 (1997). * Dodd, R.Y. The risk of transfusion-transmitted infection. _N.
Engl. J. Med. _ 327, 419–421 ( 1992). Article CAS Google Scholar * Yen, R.C.K., & Ho, T.W.C. Blajchman M.A. A novel approach to correcting the bleeding time in thrombocytopenic
rabbits. _Transfusion _ 35, 41S (1995). Google Scholar * Rodgers, R.P. & Levin, J. A critical reappraisal of the bleeding time. _Semin. Thromb. Hemost._ 16, 1– 20 (1990). Article CAS
Google Scholar * Evatt, B.L., Levin, J. & Algazy, K.M. Partial purification of thrombopoietin from the plasma of thrombocytopenic rabbits. _Blood_ 54, 377 –388 (1979). CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Blajchman, M.A. & Lee, D.H. The thrombocytopenic rabbit bleeding time model to evaluate the in vivo hemostatic efficacy of platelets and platelet substitutes. _Transf.
Med. Rev._ 11, 99–105 (1997). Google Scholar * Kuter, D.J. & Rosenberg, R.D. The reciprocal relationship of thrombopoietin (c-Mpl ligand) to changes in the platelet mass during
busulfan-induced thrombocytopenia in the rabbit. _Blood_ 85, 2710–2730 (1995). Google Scholar * Blajchman, M.A. _ et al_. Shortening of the bleeding time in rabbits by hydrocortisone caused
inhibition of prostacyclin generation by the vessel wall. _ J. Clin. Invest._ 63, 1026–1035 (1979). Article CAS Google Scholar * Benedict, C.R. _ et al._ New variant of human tissue
plasminogen activator (TPA) with enhanced efficacy and lower incidence of bleeding compared with recombinant human TPA. _Circulation_ 92, 3032– 3040 (1995). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Levi, M., Biemond, B.J., van Zonneveld, A.J., ten Cate, J.W. & Pannekoek, H. : Inhibition of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1) activity results in promotion of endogenous
thrombolysis and inhibition of thrombus extension in models of experimental thrombosis. _Circulation_ 85, 305–312 (1992). Article CAS Google Scholar * Sakariassen, K.S., Aarts, P.A., de
Groot, P.G., Houdijk, W.P. & Sixma, J.J. A perfusion chamber developed to investigate platelet interaction in flowing blood with human vessel wall cells, their extracellular matrix, and
purified components. _J. Lab. Clin. Med._ 102, 522–535 ( 1983). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Zwaginga, J.J. _ et al._ Thrombogenicity of vascular cells. Comparison between endothelial
cells isolated from different sources and smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts. _Arteriosclerosis_ 10, 437– 448 (1990). Article CAS Google Scholar * van Breugel, H.F., de Groot, P.G.,
Heethaar, R.M. & Sixma, J.J. Role of plasma viscosity in platelet adhesion. _Blood_ 80, 953–959 (1992). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Saelman, E.U.M. _ et al_. Aggregate formation is
more strongly inhibited at high shear rates by dRGDW, a synthetic RGD-containing peptide. _Arterioscler. Thromb._ 13, 1164–1170 ( 1993). Article CAS Google Scholar Download references
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The assistance of A. van de Wardt is acknowledged. M.L. is a fellow of the Royal Dutch Academy of Arts and Sciences. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Center for
Hemostasis, Thrombosis, Atherosclerosis and Inflammation Research, Academic Medical Center, University of Amsterdam , Meibergdreef 9, Amsterdam, 1105, AZ, The Netherlands Marcel Levi,
Philip W. Friederich, Bart J. Biemond & Jan Wouter ten Cate * Andaris, 1 Mere Way, Ruddington , NG11 6JS, Nottingham, United Kingdom Sarah Middleton & Roy Harris * Department of
Hematology, University of Utrecht, P.O. Box 85500, Utrecht, 3508, GA, The Netherlands Philip G. de Groot, Ya Ping Wu & Harry F.G. Heijnen * Department of Laboratory Medicine, University
of California School of Medicine, and VA Medical Center, 4150 Clement Street , San Francisco, 94121, California, USA Jack Levin Authors * Marcel Levi View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Philip W. Friederich View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Sarah Middleton View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Philip G. de Groot View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Ya Ping
Wu View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Roy Harris View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar *
Bart J. Biemond View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Harry F.G. Heijnen View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * Jack Levin View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Jan Wouter ten Cate View author publications You can also search
for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Marcel Levi. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Levi, M.,
Friederich, P., Middleton, S. _et al._ Fibrinogen-coated albumin microcapsules reduce bleeding in severely thrombocytopenic rabbits. _Nat Med_ 5, 107–111 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/4795
Download citation * Received: 17 August 1998 * Accepted: 09 November 1998 * Issue Date: January 1999 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/4795 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following
link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature
SharedIt content-sharing initiative





