- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
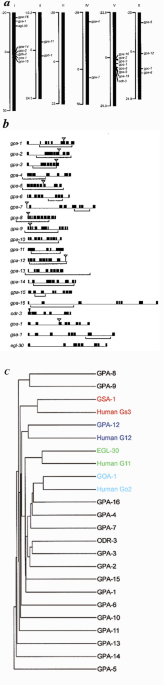
ABSTRACT _Caenorhabditis elegans_ is the first animal whose genomic sequence has been determined1. One of the new possibilities in post-sequence genetics is the analysis of complete gene
families at once. We studied the family of heterotrimeric G proteins2. _C. elegans_ has 20 Gα, 2 Gβ and 2 Gγ genes. There is 1 homologue of each of the 4 mammalian classes of Gα genes,
Gi/Goα, Gsα, Gqα and G12α, and there are 16 new α genes. Although the conserved Gα subunits are expressed in many neurons and muscle cells3,4,5,6,7, GFP fusions indicate that 14 new Gα genes
are expressed almost exclusively in a small subset of the chemosensory neurons of _C. elegans_8,9. We generated loss-of-function alleles using target-selected gene inactivation10,11. None
of the amphid-expressed genes are essential for viability, and only four show any detectable phenotype (chemotaxis defects), suggesting extensive functional redundancy. On the basis of
functional analysis, the 20 genes encoding Gα proteins can be divided into two groups: those that encode subunits affecting muscle activity (homologues of Gi/Goα, Gsα and Gq; refs 3,4,5,6),
and those (14 new genes) that encode proteins most likely involved in perception. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your
institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $209.00 per year only $17.42 per issue Learn more Buy this
article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in
* Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS SIN-3 FUNCTIONS THROUGH MULTI-PROTEIN INTERACTION TO REGULATE
APOPTOSIS, AUTOPHAGY, AND LONGEVITY IN _CAENORHABDITIS ELEGANS_ Article Open access 22 June 2022 DISSECTING THE SEQUENTIAL EVOLUTION OF A SELFISH MITOCHONDRIAL GENOME IN _CAENORHABDITIS
ELEGANS_ Article Open access 05 July 2024 HOMEOBOX GENES AND THE SPECIFICATION OF NEURONAL IDENTITY Article 26 August 2021 REFERENCES * The _C. elegans_ Sequencing Consortium. Genome
sequence of the nematode _C. elegans_: a platform for investigating biology. _Science_ 282, 2012–2018 (1998). * Neer, E.J. Heterotrimeric G proteins: organizers of transmembrane signals. _
Cell_ 80, 249–257 ( 1995). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Mendel, J.E. _ et al._ Participation of the Go protein in multiple aspects of behavior in _C. elegans_. _Science_ 267,
1652–1655 (1995). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Ségalat, L., Elkes, D.A. & Kaplan, J.M. Modulation of serotonin controlled behaviors by G o in _Caenorhabditis elegans_.
_Science_ 267 , 1648–1651 (1995). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Brundage, L. _ et al._ Mutations in a _C. elegans_ Gqα gene disrupt movement, egg-laying and viability. _Neuron_ 16,
999–1009 (1996). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Korswagen, H.C., Park, J-H., Ohshima, Y. & Plasterk, R.H.A. An activating mutation in a _Caenorhabditis elegans_
Gs protein induces neuronal degeneration. _Genes Dev._ 11, 1493 –1503 (1997). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Park, J-H., Ohshima, S., Tani, T. & Ohshima, Y. Structure and
expression of the _gsa-1_ gene encoding a G protein α (s) subunit in _C. elegans_. _Gene_ 194, 183– 190 (1997). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Zwaal, R.R., Mendel, J.E., Sternberg,
P.W. & Plasterk, R.H.A. Two neuronal G proteins are involved in the chemosensation of dauer inducing pheromone by _C. elegans_. _Genetics_ 145, 715–727 (1997). CAS PubMed PubMed
Central Google Scholar * Roayaie, K., Gage Crump, J., Sagasti, A. & Bargmann, C.I. The Gα protein ODR-3 mediates olfactory and nociceptive function and controls cilium morphogenesis in
_C. elegans_ olfactory neurons. _ Neuron_ 20, 55–67 ( 1998). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Zwaal, R.R., Broeks, A., van Meurs, J., Groenen, J.T.M. & Plasterk, R.H.A. Target
selected gene inactivation by using a frozen transposon insertion mutant bank. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 90, 7431–7435 ( 1993). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar *
Jansen, G., Hazendonk, E., Thijssen, K.L. & Plasterk, R.H.A. Reverse genetics by chemical mutagenesis in _Caenorhabditis elegans_. _Nature Genet._ 17, 119– 121 (1997). Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Lochrie, M.A., Mendel, J.E., Sternberg, P.W. & Simon, M.I. Homologous and unique G protein α subunits in the nematode _Caenorhabditis elegans_. _Cell Regul._ 2,
135– 154 (1991). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Zwaal, R.R. _ et al._ G proteins are required for spatial orientation of early cell cleavage in _C. elegans_
embryos. _Cell_ 86 , 619–629 (1996). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Bargmann, C.I. & Mori, I. Chemotaxis and thermotaxis. in _C. elegans II_ (eds Riddle, D.L., Blumenthal, T.,
Meyer, B.J. & Priess, J.R.) 717–737 (Cold Spring Harbor Press, New York, 1997). Google Scholar * White, J.G., Southgate, E., Thomson, J.N. & Brenner, S. The structure of the nervous
system of the nematode _Caenorhabditis elegans _. _Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond._ 314, 1–340 (1986). Article CAS Google Scholar * Perkins, L.A., Hedgecock, E.M., Thomson, J.N. &
Culotti, J.G. Mutant sensory cilia in the nematode _Caenorhabditis elegans_. _ Dev. Biol._ 117, 456–487 (1986). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Ward, S. Chemotaxis by the nematode
_Caenorhabditis elegans_: identification of attractants and analysis of the response by use of mutants. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 70, 817–821 (1973). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central
Google Scholar * Culotti, J.G. & Russell, R.L. Osmotic avoidance defective mutants of the nematode _Caenorhabditis elegans_. _Genetics_ 90, 243–256 (1978). CAS PubMed PubMed Central
Google Scholar * Bargmann, C.I., Hartwieg, E. & Horvitz, H.R. Odorant-selective genes and neurons mediate olfaction in _C. elegans_. _Cell_ 74, 515– 527 (1993). Article CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Sengupta, P., Chou, J.H. & Bargmann, C.I. _odr-10_ encodes a seven transmembrane domain olfactory receptor required for responses to the odorant diacetyl. _ Cell_ 84,
899–909 ( 1994). Article Google Scholar * Troemel, E.R., Kimmel, B.E. & Bargmann, C.I. Reprogramming chemotaxis responses: sensory neurons define olfactory preferences in _C. elegans_.
_Cell_ 91, 161–169 (1997). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Buck, L.B. Information coding in the vertebrate olfactory system. _Annu. Rev. Neurosci._ 19, 517–544 ( 1996). Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Kaplan, J.M. & Horvitz, H.R. A dual mechanosensory and chemosensory neuron in _Caenorhabditis elegans_. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 90, 2227–2231 ( 1993).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Colbert, H.A. & Bargmann, C.I. Odorant-specific adaptation pathways generate olfactory plasticity in _C. elegans_. _Neuron_ 14,
803–812 (1995). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Troemel, E.R., Chou, J.H., Dwyer, N.D., Colbert, H.A. & Bargmann, C.I. Divergent seven transmembrane receptors are candidate
chemosensory receptors in _C. elegans_. _Cell_ 83 , 207–218 (1995). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Yu, S., Avery, L., Baude, E. & Garbers, D.L. Gyanylyl cyclase expression in
specific sensory neurons: a new family of chemosensory receptors. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 94, 3384– 3387 (1997). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Altschul, S.F.,
Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E.W. & Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. _J. Mol. Biol._ 215, 403–410 ( 1990). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Eeckman, F.H. &
Durbin, R. ACeDB and Macace. _Methods Cell Biol._ 48, 583–605 ( 1995). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Han, M. & Sternberg, P.W. Analysis of dominant negative mutations of the
_Caenorhabditis elegans let-60_ ras gene. _ Genes Dev._ 5, 2188–2198 (1991). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Bargmann, C.I. & Horvitz, H.R. Chemosensory neurons with overlapping
functions direct chemotaxis to multiple chemicals in _C. elegans_. _Neuron_ 7, 729– 742 (1991). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank C.
Bargmann for strains and help in identification of amphid neurons; L. Brundage and M. Simon for the communication of unpublished results; A. Coulson for cosmids; the Fire lab for
GFP-expression vectors; R. Zwaal, J. Neels, R. Korswagen and Y. Kato for the isolation of mutant strains; C. de Vries for help with behavioural assays; S. Wicks for help with statistical
analyses and behavioural assays; and C. van den Berg, P. Borst, R. Korswagen and S. Wicks for comments on the manuscript. This work was supported by grant NKI 94-809 from the Netherlands
Cancer Foundation, by grant NWO-GMW 90104094 from the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research, by grant 940-70-008 from the New Drugs Research Foundation to R.H.A.P., and by a
Biotechnology Research Training Grant from the European Commission (BIO4CT965072) to P.W. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Division of Molecular Biology, The Netherlands Cancer
Institute, Centre for Biomedical Genetics, Plesmanlaan 121, Amsterdam, 1066 CX, The Netherlands Gert Jansen, Karen L Thijssen, Pia Werner, Marieke van derHorst, Esther Hazendonk & Ronald
H A Plasterk Authors * Gert Jansen View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Karen L Thijssen View author publications You can also search for
this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Pia Werner View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Marieke van derHorst View author publications You can
also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Esther Hazendonk View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Ronald H A Plasterk View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Ronald H A Plasterk. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT
THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Jansen, G., Thijssen, K., Werner, P. _et al._ The complete family of genes encoding G proteins of _Caenorhabditis elegans_. _Nat Genet_ 21, 414–419 (1999).
https://doi.org/10.1038/7753 Download citation * Received: 16 December 1998 * Accepted: 04 March 1999 * Issue Date: 01 April 1999 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/7753 SHARE THIS ARTICLE
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided
by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative