- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
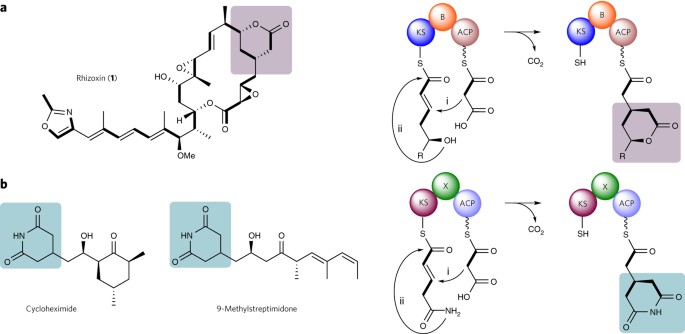
ABSTRACT Biosynthesis of rhizoxin in _Burkholderia rhizoxinica_ affords an unusual polyketide synthase module with ketosynthase and branching domains that install the δ-lactone, conferring
antimitotic activity. To investigate their functions in chain branching, we designed chimeric modules with structurally similar domains from a glutarimide-forming module and a dehydratase.
Biochemical, kinetic and mutational analyses reveal a structural role of the accessory domains and multifarious catalytic actions of the ketosynthase. Access through your institution Buy or
subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online
access $259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which
are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS
STRUCTURE AND MECHANISM OF A DEHYDRATASE/DECARBOXYLASE ENZYME COUPLE INVOLVED IN POLYKETIDE Β-METHYL BRANCH INCORPORATION Article Open access 18 September 2020 DIENE INCORPORATION BY A
DEHYDRATASE DOMAIN VARIANT IN MODULAR POLYKETIDE SYNTHASES Article 15 September 2022 DISCOVERY OF TYPE II POLYKETIDE SYNTHASE-LIKE ENZYMES FOR THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF CISPENTACIN Article Open
access 06 December 2023 ACCESSION CODES ACCESSIONS GENBANK/EMBL/DDBJ * CBW75249.1 * CCC21123.1 PROTEIN DATA BANK * 4KC5 REFERENCES * Hertweck, C. _Angew. Chem. Int. Ed._ 48, 4688–4716
(2009). Article CAS Google Scholar * Partida-Martinez, L.P. & Hertweck, C. _Nature_ 437, 884–888 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lackner, G., Partida-Martinez, L.P.
& Hertweck, C. _Trends Microbiol._ 17, 570–576 (2009). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Scherlach, K., Busch, B., Lackner, G., Paszkowski, U. & Hertweck, C. _Angew. Chem. Int.
Ed._ 51, 9615–9618 (2012). Article CAS Google Scholar * Partida-Martinez, L.P. & Hertweck, C. _ChemBioChem_ 8, 41–45 (2007). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Scherlach, K.,
Partida-Martinez, L.P., Dahse, H.-M. & Hertweck, C. _J. Am. Chem. Soc._ 128, 11529–11536 (2006). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Schmitt, I. et al. _ISME J._ 2, 632–641 (2008).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kusebauch, B., Scherlach, K., Kirchner, H., Dahse, H.M. & Hertweck, C. _ChemMedChem_ 6, 1998–2001 (2011). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Nguyen, T. et al. _Nat. Biotechnol._ 26, 225–233 (2008). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kusebauch, B., Busch, B., Scherlach, K., Roth, M. & Hertweck, C. _Angew. Chem. Int. Ed._ 48,
5001–5004 (2009). Article CAS Google Scholar * Bretschneider, T. et al. _Nature_ 502, 124–128 (2013). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Heine, D., Sundaram, S., Bretschneider, T.
& Hertweck, C. _Chem. Commun. (Camb.)_ 51, 9872–9875 (2015). Article CAS Google Scholar * Heine, D., Bretschneider, T., Sundaram, S. & Hertweck, C. _Angew. Chem. Int. Ed._ 53,
11645–11649 (2014). Article CAS Google Scholar * Rajski, S.R. & Shen, B. _ChemBioChem_ 11, 1951–1954 (2010). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Wang, B. et al.
_Org. Lett._ 15, 1278–1281 (2013). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lim, S.K. et al. _J. Biol. Chem._ 284, 29746–29756 (2009). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar *
Yin, M. et al. _Org. Lett._ 16, 3072–3075 (2014). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Chen, S. et al. _Chem. Biol._ 10, 1065–1076 (2003). Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Hothersall, J. et al. _J. Biol. Chem._ 282, 15451–15461 (2007). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Xu, Z. et al. _ChemBioChem_ 15, 1274–1279 (2014). Article CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Calderone, C.T. _Nat. Prod. Rep._ 25, 845–853 (2008). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Schneider-Poetsch, T. et al. _Nat. Chem. Biol._ 6, 209–217 (2010). Article
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Bretschneider, T. et al. _Nat. Chem. Biol._ 8, 154–161 (2012). Article CAS Google Scholar * Fuchs, S.W. et al. _Angew. Chem. Int. Ed._ 52,
4108–4112 (2013). Article CAS Google Scholar * Zocher, G. et al. _Chem. Sci._ 10.1039/C5SC02488A (6 August 2015). * Kelley, L.A. & Sternberg, M.J. _Nat. Protoc._ 4, 363–371 (2009).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Ji, X.-Y. et al. _Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo)_ 58, 1436–1441 (2010). Article CAS Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank A.
Perner for MS analyses and M. Poetsch for MALDI measurements. We are grateful for financial support by the International Leibniz Research School (to S.S.) and the Studienstiftung des
Deutschen Volkes (to D.H.). AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Biomolecular Chemistry, Leibniz Institute for Natural Product Research and Infection Biology (HKI),
Jena, Germany Srividhya Sundaram, Daniel Heine & Christian Hertweck * Chair of Natural Product Chemistry, Friedrich Schiller University, Jena, Germany Christian Hertweck Authors *
Srividhya Sundaram View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Daniel Heine View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed
Google Scholar * Christian Hertweck View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS S.S. and C.H. designed experiments; S.S. performed
genetic and biochemical experiments and analyzed data; D.H. synthesized substrates and reference compounds; and S.S. and C.H. wrote the manuscript. CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to
Christian Hertweck. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing financial interests. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY TEXT AND FIGURES Supplementary
Results, Supplementary Notes 1 and 2 and Supplementary Figures 1–10. (PDF 3399 kb) RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Sundaram, S., Heine,
D. & Hertweck, C. Polyketide synthase chimeras reveal key role of ketosynthase domain in chain branching. _Nat Chem Biol_ 11, 949–951 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1932
Download citation * Received: 07 July 2015 * Accepted: 28 August 2015 * Published: 19 October 2015 * Issue Date: December 2015 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1932 SHARE THIS ARTICLE
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative



![[withdrawn] maritime labour convention: wages guidance](https://www.gov.uk/assets/static/govuk-opengraph-image-03837e1cec82f217cf32514635a13c879b8c400ae3b1c207c5744411658c7635.png)