- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT Most of the metals (elements heavier than helium) produced by stars in the member galaxies of clusters currently reside within the hot, X-ray-emitting intra-cluster gas.
Observations of X-ray line emission from this intergalactic medium have suggested a relatively small cluster-to-cluster scatter outside the cluster centres1,2 and enrichment with iron out to
large radii3,4,5, leading to the idea that the metal enrichment occurred early in the history of the Universe3. Models with early enrichment predict a uniform metal distribution at large
radii in clusters, whereas those with late-time enrichment6,7 are expected to introduce significant spatial variations of the metallicity. To discriminate clearly between these competing
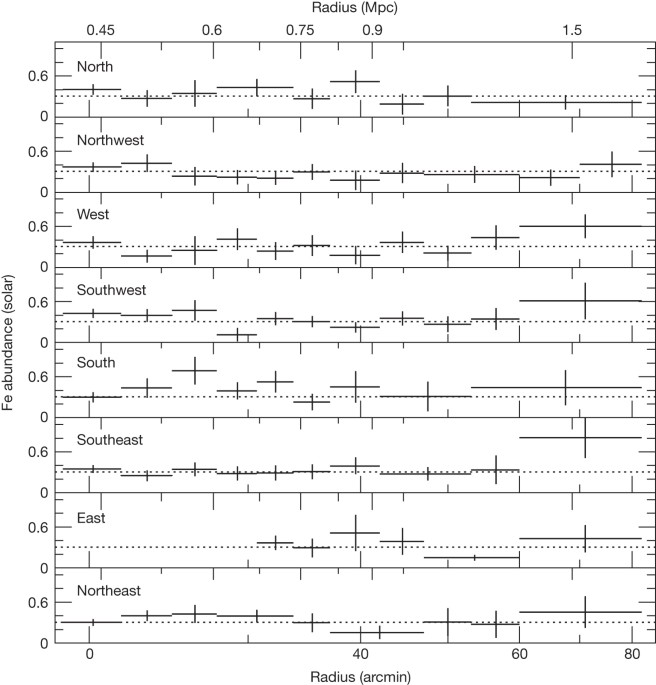
models, it is essential to test for potential inhomogeneities by measuring the abundances out to large radii along multiple directions in clusters, which has not hitherto been done. Here we
report a remarkably uniform iron abundance, as a function of radius and azimuth, that is statistically consistent with a constant value of _Z_Fe = 0.306 ± 0.012 in solar units out to the
edge of the nearby Perseus cluster. This homogeneous distribution requires that most of the metal enrichment of the intergalactic medium occurred before the cluster formed, probably more
than ten billion years ago, during the period of maximal star formation and black hole activity. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content,
access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 51 print issues and online access $199.00 per year only $3.90 per issue Learn
more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS
OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS LARGE METALLICITY VARIATIONS IN THE GALACTIC
INTERSTELLAR MEDIUM Article 08 September 2021 A DEPARTURE FROM THE MASS–METALLICITY RELATION IN MERGING GALAXIES DUE TO AN INFALL OF METAL-POOR GAS Article 08 January 2024 LOW GAS-PHASE
METALLICITIES OF ULTRALUMINOUS INFRARED GALAXIES ARE A RESULT OF DUST OBSCURATION Article 26 May 2022 REFERENCES * Matsushita, K. Radial profiles of Fe abundance in the intracluster medium
of nearby clusters observed with XMM-Newton. _Astron. Astrophys._ 527, 134–146 (2011) Article ADS Google Scholar * Leccardi, A. & Molendi, S. Radial metallicity profiles for a large
sample of galaxy clusters observed with XMM-Newton. _Astron. Astrophys._ 487, 461–466 (2008) Article ADS Google Scholar * Fujita, Y. et al. High metallicity of the X-ray gas up to the
virial radius of a binary cluster of galaxies: evidence of galactic superwinds at high-redshift. _Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn_ 60, 343–349 (2008) Article Google Scholar * Simionescu, A. et al.
Baryons at the edge of the X-ray–brightest galaxy cluster. _Science_ 331, 1576–1579 (2011) Article CAS ADS Google Scholar * Urban, O. et al. X-ray spectroscopy of the Virgo cluster out
to the virial radius. _Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc._ 414, 2101–2111 (2011) Article ADS Google Scholar * Balestra, I. et al. Tracing the evolution in the iron content of the intra-cluster
medium. _Astron. Astrophys._ 462, 429–442 (2007) Article CAS ADS Google Scholar * Maughan, B. J., Jones, C., Forman, W. & Van Speybroeck, L. Images, structural properties, and metal
abundances of galaxy clusters observed with Chandra ACIS-I at 0.1 < z < 1.3. _Astrophys. J._ 174, 117–135 (2008) Article CAS ADS Google Scholar * Urban, O. et al.
Azimuthally resolved X-ray spectroscopy of the Perseus cluster out to its edge. _Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc_ (submitted); http://arxiv.org/abs/1307.3592 (2013) * De Grandi, S., Ettori, S.,
Longhetti, M. & Molendi, S. On the iron content in rich nearby clusters of galaxies. _Astron. Astrophys._ 419, 7–18 (2004) Article CAS ADS Google Scholar * Feldman, U. Elemental
abundances in the upper solar atmosphere. _Phys. Scr._ 46, 202–220 (1992) Article CAS ADS Google Scholar * Gunn, J. E. & Gott, J. R., III On the infall of matter into clusters of
galaxies and some effects on their evolution. _Astrophys. J._ 176, 1–19 (1972) Article ADS Google Scholar * Domainko, W. et al. Enrichment of the ICM of galaxy clusters due to
ram-pressure stripping. _Astron. Astrophys._ 452, 795–802 (2006) Article ADS Google Scholar * Matsushita, K., Sakuma, E., Sasaki, T., Sato, K. & Simionescu, A. Metal-mass-to-light
ratios of the Perseus cluster out to the virial radius. _Astrophys. J._ 764, 147–156 (2013) Article ADS Google Scholar * Simionescu, A. et al. Large-scale motions in the Perseus galaxy
cluster. _Astrophys. J._ 757, 182–187 (2012) Article ADS Google Scholar * Voit, G. M., Kay, S. T. & Bryan, G. L. The baseline intracluster entropy profile from gravitational structure
formation. _Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc._ 364, 909–916 (2005) Article ADS Google Scholar * De Young, D. S. On the origin and evolution of iron-enriched gas in clusters of galaxies.
_Astrophys. J._ 223, 47–55 (1978) Article CAS ADS Google Scholar * Madau, P. et al. High-redshift galaxies in the Hubble Deep Field: colour selection and star formation history to z ∼ 4.
_Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc._ 283, 1388–1404 (1996) Article ADS Google Scholar * Brandt, W. N. & Hasinger, G. Deep extragalactic X-ray surveys. _Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys._ 43,
827–859 (2005) Article ADS Google Scholar * Fabjan, D. et al. Simulating the effect of active galactic nuclei feedback on the metal enrichment of galaxy clusters. _Mon. Not. R. Astron.
Soc._ 401, 1670–1690 (2010) Article CAS ADS Google Scholar * Mannucci, F., Della Valle, M. & Panagia, N. Two populations of progenitors for Type Ia supernovae? _Mon. Not. R. Astron.
Soc._ 370, 773–783 (2006) Article ADS Google Scholar * Maoz, D., Mannucci, F. & Brandt, T. D. The delay-time distribution of Type Ia supernovae from Sloan II. _Mon. Not. R. Astron.
Soc._ 426, 3282–3294 (2012) Article ADS Google Scholar * Böhringer, H., Matsushita, K., Churazov, E., Finoguenov, A. & Ikebe, Y. Implications of the central metal abundance peak in
cooling core clusters of galaxies. _Astron. Astrophys._ 416, L21–L25 (2004) Article ADS Google Scholar * Baldi, A. et al. An XMM-Newton spatially-resolved study of metal abundance
evolution in distant galaxy clusters. _Astron. Astrophys._ 537, 142–153 (2012) Article Google Scholar * Andreon, S. The enrichment history of the intracluster medium: a Bayesian approach.
_Astron. Astrophys._ 546, 6–17 (2012) Article ADS Google Scholar * Abraham, J. et al. Measurement of the depth of maximum of extensive air showers above 1018 eV. _Phys. Rev. Lett._ 104,
091101 (2010) Article CAS ADS Google Scholar * Norman, C. A., Melrose, D. B. & Achterberg, A. The origin of cosmic rays above 1018.5 eV. _Astrophys. J._ 454, 60–68 (1995) Article
ADS Google Scholar * Cen, R. & Ostriker, J. P. Where are the baryons? _Astrophys. J._ 514, 1–6 (1999) Article CAS ADS Google Scholar * Davé, R. et al. Baryons in the warm-hot
intergalactic medium. _Astrophys. J._ 552, 473–483 (2001) Article ADS Google Scholar * Anders, E. & Grevesse, N. Abundances of the elements—meteoritic and solar. _ Geochim. Cosmochim.
Acta_ 53, 197–214 (1989) Article CAS ADS Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We are grateful for discussions with other members of the Perseus cluster Suzaku Key project
collaboration, as well as with Y. Lu, P. Simeon and R. Blandford. This work was supported by the Suzaku grants NNX09AV64G and NNX10AR48G, the NASA ADAP grant NNX12AE05G, and by the US
Department of Energy under contract number DE-AC02-76SF00515. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, Stanford University, 452
Lomita Mall, Stanford, California 94305-4085, USA , Norbert Werner, Ondrej Urban, Aurora Simionescu & Steven W. Allen * Department of Physics, Stanford University, 382 Via Pueblo Mall,
Stanford, California 94305-4060, USA, Norbert Werner, Ondrej Urban, Aurora Simionescu & Steven W. Allen * SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, 2575 Sand Hill Road, Menlo Park, 94025,
California, USA Ondrej Urban & Steven W. Allen * Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS), JAXA, 3-1-1 Yoshinodai, Chuo-ku, Sagamihara, Kanagawa 252-5210, Japan , Aurora
Simionescu Authors * Norbert Werner View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Ondrej Urban View author publications You can also search for this
author inPubMed Google Scholar * Aurora Simionescu View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Steven W. Allen View author publications You can
also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS N.W. led the writing of the manuscript. O.U. reduced and analysed the data. A.S. and N.W. contributed to the data analysis.
S.W.A. contributed to the writing of the manuscript and is the principal investigator of the Suzaku Key Project data. All authors discussed all results, developed the interpretation and
commented on the manuscript. CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Norbert Werner. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing financial interests. POWERPOINT
SLIDES POWERPOINT SLIDE FOR FIG. 1 POWERPOINT SLIDE FOR FIG. 2 SOURCE DATA SOURCE DATA TO FIG. 1 SOURCE DATA TO FIG. 2 RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE
THIS ARTICLE Werner, N., Urban, O., Simionescu, A. _et al._ A uniform metal distribution in the intergalactic medium of the Perseus cluster of galaxies. _Nature_ 502, 656–658 (2013).
https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12646 Download citation * Received: 01 June 2013 * Accepted: 09 September 2013 * Published: 30 October 2013 * Issue Date: 31 October 2013 * DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12646 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently
available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(399x0:401x2)/james-feigen-800-09db67f52d8848ffbc29065c01b978b8.jpg)