- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
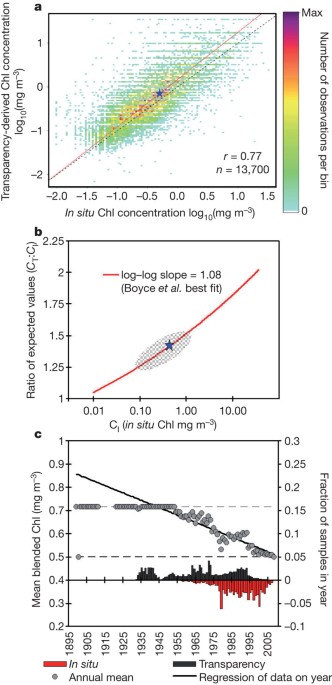
ABSTRACT Arising from D. G. Boyce, M. R. Lewis & B. Worm _Nature_ 466, 591–596 (2010)10.1038/nature09268; Boyce _et al._ reply Phytoplankton account for about half of global and nearly
all of marine primary productivity; consequently, any widespread drop in phytoplankton biomass would almost certainly have severe ecological consequences. Boyce _et al._1 have reported
strong (∼1% per year) and sustained declines in marine phytoplankton biomass at local, regional and global scales. However, I suggest that some or much of their reported declines are
attributable to bias between the two data types used by Boyce _et al._1. Although real changes may have occurred, their proper quantification requires removal of the bias component. Access
through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access $199.00 per year only $3.90 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may
be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support
SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS SEASONAL BIASES IN FLUORESCENCE-ESTIMATED CHLOROPHYLL-A DERIVED FROM BIOGEOCHEMICAL PROFILING FLOATS Article Open access 16 October 2024 WIDESPREAD
CHANGES IN SOUTHERN OCEAN PHYTOPLANKTON BLOOMS LINKED TO CLIMATE DRIVERS Article Open access 28 August 2023 MARINE PHYTOPLANKTON COMMUNITY DATA AND CORRESPONDING ENVIRONMENTAL PROPERTIES
FROM EASTERN NORWAY, 1896–2020 Article Open access 14 December 2022 REFERENCES * Boyce, D. G., Lewis, M. R. & Worm, B. Global phytoplankton decline over the past century. _Nature_ 466,
591–596 (2010) Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Siegel, D. A. & Franz, B. A. Century of phytoplankton change. _Nature_ 466, 569–571 (2010) Article ADS CAS Google Scholar *
Falkowski, P. & Wilson, C. Phytoplankton productivity in the North Pacific ocean since 1900 and implications for absorption of anthropogenic CO2 . _Nature_ 358, 741–743 (1992) Article
ADS Google Scholar Download references AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Institute of Ocean Sciences, Fisheries and Oceans Canada, PO Box 6000, Sidney, British Columbia, V8L
4B2, Canada David L. Mackas Authors * David L. Mackas View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to David L.
Mackas. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The author declares no competing financial interests. POWERPOINT SLIDES POWERPOINT SLIDE FOR FIG. 1 RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and
permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Mackas, D. Does blending of chlorophyll data bias temporal trend?. _Nature_ 472, E4–E5 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09951 Download
citation * Received: 01 October 2010 * Accepted: 01 February 2011 * Published: 13 April 2011 * Issue Date: 14 April 2011 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09951 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone
you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the
Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative