- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
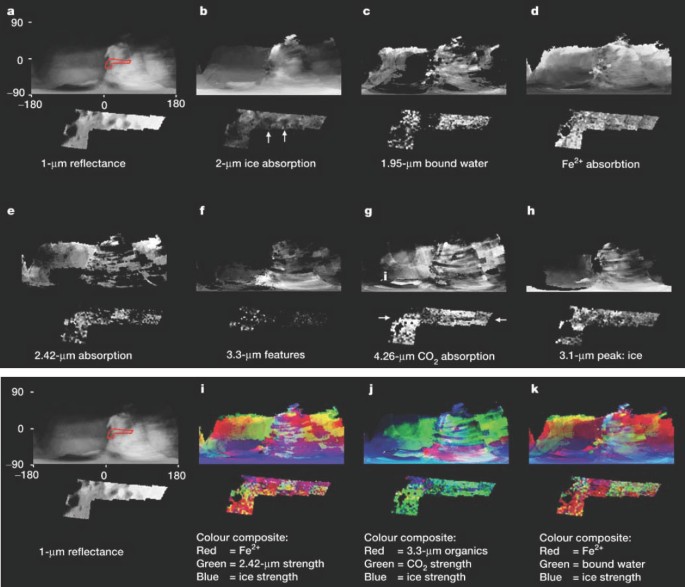
ABSTRACT The origin of Phoebe, which is the outermost large satellite of Saturn, is of particular interest because its inclined, retrograde orbit suggests that it was gravitationally
captured by Saturn, having accreted outside the region of the solar nebula in which Saturn formed1. By contrast, Saturn's regular satellites (with prograde, low-inclination, circular
orbits) probably accreted within the sub-nebula in which Saturn itself formed2. Here we report imaging spectroscopy of Phoebe resulting from the Cassini–Huygens spacecraft encounter on 11
June 2004. We mapped ferrous-iron-bearing minerals, bound water, trapped CO2, probable phyllosilicates, organics, nitriles and cyanide compounds. Detection of these compounds on Phoebe makes
it one of the most compositionally diverse objects yet observed in our Solar System. It is likely that Phoebe's surface contains primitive materials from the outer Solar System,
indicating a surface of cometary origin. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through
your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 51 print issues and online access $199.00 per year only $3.90 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant
access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions *
Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS SPACE WEATHERING RECORD AND PRISTINE STATE OF RYUGU SAMPLES FROM MICROMEGA SPECTRAL ANALYSIS Article 05
October 2023 CHANDRAYAAN-3 APXS ELEMENTAL ABUNDANCE MEASUREMENTS AT LUNAR HIGH LATITUDE Article 21 August 2024 A JWST/DISCO-TNOS PORTRAIT OF THE PRIMORDIAL SOLAR SYSTEM THROUGH ITS
TRANS-NEPTUNIAN OBJECTS Article 19 December 2024 REFERENCES * Pollack, J. B. et al. Gas drag in primordial circumplanetary envelopes: A mechanism for satellite capture. _Icarus_ 37, 587–611
(1979) Article ADS Google Scholar * Burns, J. A. in _Satellites_ (eds Burns, J. A. & Matthews, M. S.) 117–158 (Univ. Arizona Press, Tucson, 1986) Google Scholar * Brown, R. H. et al.
The Cassini Huygens Mission. _Space Sci. Rev._ (in the press) * Owen, T. C. et al. Detection of water ice on Saturn's satellite Phoebe. _Icarus_ 139, 379–382 (1999) Article ADS CAS
Google Scholar * Liou, J. C. & Malhotra, R. Depletion of the outer asteroid belt. _Science_ 275, 375–377 (1997) Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Levison, H. F. & Morbidelli, A.
The formation of the Kuiper belt by the outward transport of bodies during Neptune's migration. _Nature_ 426, 419–421 (2003) Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Brown, R. H.,
Cruikshank, D. P. & Pendleton, Y. J. Water ice on Kuiper Belt object 1996 TO66 . _Astrophys. J. Lett._ 519, 101–104 (1999) Article ADS Google Scholar * Barucci, M. A. et al. Analysis
of Trans-Neptunian and Centaur colours: continuous trend or grouping? _Astron. Astrophys._ 371, 1150–1154 (2001) Article ADS Google Scholar * Buratti, B. J., Hicks, M. D., Tryka, K. A.,
Sittig, M. S. & Newburn, R. L. High-resolution 0.33–0.92 µm spectra of Iapetus, Hyperion, Phoebe, Rhea, Dione, and D-type asteroids: How are they related? _Icarus_ 155, 375–381 (2002)
Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Jarvis, K. S., Vilas, F., Larson, S. M. & Gaffey, M. J. Are Hyperion and Phoebe linked to Iapetus? _Icarus_ 146, 125–132 (2000) Article ADS CAS
Google Scholar * McCord, T. B. et al. Non-water-ice constituents in the surface material of the icy Galilean satellites from Galileo Near-Infrared Mapping Spectrometer investigation. _J.
Geophys. Res._ 103, 8603–8626 (1998) Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Clark, R. N. et al. _The U.S. Geological Survey, Digital Spectral Library splib05_ (Open File Report 03-395, USGS,
Denver, 2003); 〈http://speclab.cr.usgs.gov/spectral-lib.html〉 Google Scholar * Hook, S. _ASTER Spectral Library_ (Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, 2004); 〈http://speclib.jpl.nasa.gov〉
Google Scholar * Buratti, B. J. et al. Iapetus: First data from the Cassini Visual Infrared Mapping Spectrometer. _Bull. Am. Astron. Soc._ 36, 1072 (2004) ADS Google Scholar * Soderblom,
L. A. et al. Observations of comet 19P/Borrelly by the Miniature Integrated Camera and Spectrometer aboard Deep Space 1. _Science_ 296, 1087–1091 (2002) Article ADS CAS Google Scholar *
Stein, S. E. NIST Standard Reference Database 35. _NIST Spectral Library_ (National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, Maryland, 2004);
〈http://www.nist.gov/srd/nist35.htm〉. * Gaffey, M. J. Forging an asteroid-meteorite link. _Science_ 260, 167–168 (1993) Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Cruikshank, D. P. et al. Search
for 3.4-µm C-H spectral bands on low albedo asteroids. _Icarus_ 156, 434–441 (2002) Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Brown, R. H. et al. Cassini's Visual and Infrared Mapping
Spectrometer (VIMS): Observations during approach and orbit insertion. _Astrophys. J. Lett._ (in the press) * Cruikshank, D. P. et al. Constraints on the composition of Trojan asteroid 624
Hektor. _Icarus_ 153, 348–360 (2001) Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Clark, R. N. et al. Imaging spectroscopy: Earth and planetary remote sensing with the USGS Tetracorder and expert
systems. _J. Geophys. Res._ 108, 5131, doi:10.1029/2002JE001847 (2003) Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This work was funded by the Cassini project. Authors from American
institutions were funded by NASA; authors from European institutions were funded by ESA. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * US Geological Survey, MS964, Federal Center, Box
25046, Colorado, 80225, Denver, USA Roger N. Clark, Todd M. Hoefen & John M. Curchin * Lunar and Planetary Laboratory and Stewart Observatory, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona,
85721, USA Robert H. Brown & J. Lunine * German Aerospace Center (DLR), Institute of Space Sensor Technology and Planetary Exploration, Rutherfordstrasse 2, D-12489, Berlin, Germany Ralf
Jaumann & K.-D. Matz * NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, California, 94035, USA Dale P. Cruikshank * Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena,
California, 91109, USA Robert M. Nelson, Bonnie J. Buratti, K. H. Baines & D. L. Matson * University of Hawaii at Manoa, HIGP/SOEST, 1680 East-West Road, Honolulu, Hawaii, 96822, USA
Thomas B. McCord * Istituto di Fisica dello Spazio Interplanetario, CNR, 00133, Rome, Italy G. Bellucci, F. Capaccioni, P. Cerroni, A. Coradini, V. Formisano & V. Mennella * Institut
d'Astrophysique Spatiale, Université de Paris-Sud, F-91405, Orsay Cedex, France J.-P. Bibring & Y. Langevin * Astronomy Department, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York, 14853, USA
P. D. Nicholson * Observatoire de Paris, 92195, Meudon, France B. Sicardy * Laboratoire de Planétologie et Géodynamique, UMR CNRS 6112, Université de Nantes, 44322, Nantes, France C. Sotin *
Planetary Science Institute NW, Corporate Center Pasadena, 255 S. Lake Avenue, Suite 300, Pasadena, California, 91101, USA Karl Hibbits * Department of Earth and Space Sciences, University
of Seattle, Washington, 8195-1310, USA Gary Hansen Authors * Roger N. Clark View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Robert H. Brown View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Ralf Jaumann View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Dale P.
Cruikshank View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Robert M. Nelson View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed
Google Scholar * Bonnie J. Buratti View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Thomas B. McCord View author publications You can also search for
this author inPubMed Google Scholar * J. Lunine View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * K. H. Baines View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * G. Bellucci View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * J.-P. Bibring View author publications You
can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * F. Capaccioni View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * P. Cerroni View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * A. Coradini View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * V. Formisano
View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Y. Langevin View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * D.
L. Matson View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * V. Mennella View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google
Scholar * P. D. Nicholson View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * B. Sicardy View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * C. Sotin View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Todd M. Hoefen View author publications You can also search for this
author inPubMed Google Scholar * John M. Curchin View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Gary Hansen View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Karl Hibbits View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * K.-D. Matz View author publications You
can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Roger N. Clark. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare that they have no
competing financial interests. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Clark, R., Brown, R., Jaumann, R. _et al._ Compositional maps of
Saturn's moon Phoebe from imaging spectroscopy. _Nature_ 435, 66–69 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03558 Download citation * Received: 21 December 2004 * Accepted: 11 March 2005
* Issue Date: 05 May 2005 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03558 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry,
a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative







