- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
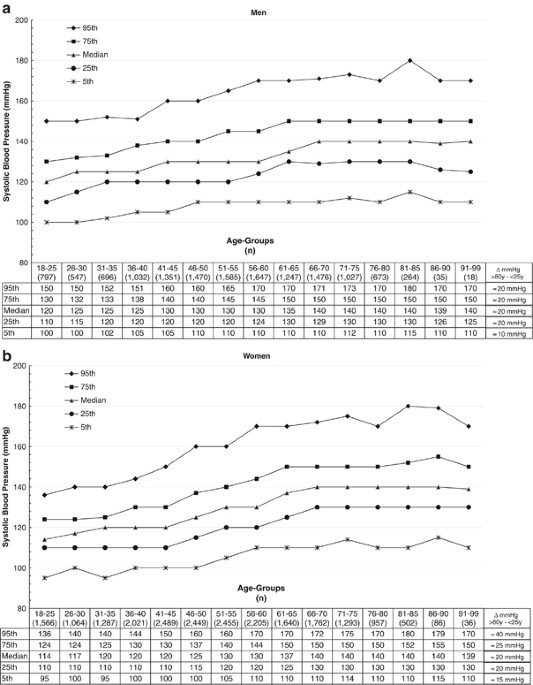
ABSTRACT The percentile distribution of blood pressure (BP) with regard to age, sex and cardiovascular risk factors is unknown. We aimed to provide epidemiological data for a comprehensive
description of the BP distribution across a wide age-range. We used data from the German Metabolic and Cardiovascular Risk Project (GEMCAS), a cross-sectional study with 35 683 participants
aged 18–99 years, conducted during October 2005 in 1511 randomly selected general practices in Germany. BP and waist circumference were measured, data on lifestyle, cardiovascular disease
(CVD) risk factors and medication assessed. In men, we found even in the lowest percentile (5th) a gradual increase of the systolic BP from the lowest to the highest age group of 10 mm Hg,
all other percentile groups an increase of 20 mm Hg. In women, this increase ranged from 15 mm Hg (5th percentile) to 40 mm Hg (95th percentile). In a subgroup of participants with no
antihypertensive usage (_n_=22 550) and no CVD/CVD risk factors (_n_=13 297), we still observed a distinct age-related increase of BP readings. Our study provides detailed information on the
population distribution of BP readings in both sexes and also among very old individuals. The results are useful in a public health context to plan gender- and age-specific prevention
strategies. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe
to this journal Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles $119.00 per year only $9.92 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full
article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs *
Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS PREVALENCE OF HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE AND CARDIOVASCULAR RISK FACTORS FROM A COMMUNITY SCREENING PROGRAMME IN THE MIDDLE-EAST; A
3-YEAR ANALYSIS OF DATA FROM THE MAY MEASUREMENT MONTH PROGRAMME (2017–2019) IN OMAN Article 06 October 2021 HIGH-NORMAL BLOOD PRESSURE AND RELATED CARDIOVASCULAR RISK FACTORS PREVALENCE IN
THE ROMANIAN ADULT POPULATION: INSIGHTS FROM THE SEPHAR III STUDY Article 25 September 2020 CLUSTERS OF RISK FACTORS IN METABOLIC SYNDROME AND THEIR INFLUENCE ON CENTRAL BLOOD PRESSURE IN A
GLOBAL STUDY Article Open access 24 August 2022 REFERENCES * Franklin SS, Larson MG, Khan SA, Wong ND, Leip EP, Kannel WB _et al_. Does the relation of blood pressure to coronary heart
disease risk change with aging? The Framingham Heart Study. _Circulation_ 2001; 103: 1245–1249. Article CAS Google Scholar * Acheson RM . Blood pressure in a national sample of U.S.
adults: percentile distribution by age, sex and race. _Int J Epidemiol_ 1973; 2: 293–301. Article CAS Google Scholar * Pobee JO, Larbi EB, Belcher DW, Wurapa FK, Dodu SR . Blood pressure
distribution in a rural Ghanaian population. _Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg_ 1977; 71: 66–72. Article CAS Google Scholar * Lim TO, Ding LM, Goh BL, Zaki M, Suleiman AB, Maimunah AH _et al_.
Distribution of blood pressure in a national sample of Malaysian adults. _Med J Malaysia_ 2000; 55: 90–107. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Azizi F, Ghanbarian A, Madjid M, Rahmani M .
Distribution of blood pressure and prevalence of hypertension in Tehran adult population: Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study (TLGS), 1999-2000. _J Hum Hypertens_ 2002; 16: 305–312. Article CAS
Google Scholar * Wright JD, Hughes JP, Ostchega Y, Yoon SS, Nwankwo T . Mean systolic and diastolic blood pressure in adults aged 18 and over in the United States, 2001–2008. _Natl Health
Stat Report_ 2011; 35: 1–22 24. Google Scholar * Moebus S, Hanisch J, Neuhaeuser M, Aidelsburger P, Wasem J, Jöckel KH . Assessing the prevalence of the Metabolic Syndrome according to
NCEP ATP III in Germany: feasibility and quality aspects of a two step approach in 1550 randomly selected primary health care practices. _GMS Ger Med Sci_ 2006; 4: Doc07. PubMed Google
Scholar * Hoffmann W, Latza U, Terschüren C . Leitlinien und Empfehlungen zur Sicherung von Guter Epidemiologischer Praxis (GEP) - überarbeitete Fassung nach Evaluation. _Gesundheitswesen_
2005; 67: 217–225. Article CAS Google Scholar * Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL Jr _et al_. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Joint National
Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure; National High Blood Pressure Education Program Coordinating Committee. The Seventh Report of the Joint
National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. _JAMA_ 2003; 289: 2560–2572. Article CAS Google Scholar * Thamm M .
Blutdruck in Deutschland- Zustandsbeschreibung und Trends. _Gesundheitswesen_ 1999; 61, Sonderheft 2 S90–S93. PubMed Google Scholar * Kohler E, Ziese T . _Telefonischer Gesundheitssurvey
des Robert Koch-Instituts zu chronischen Krankheiten und ihren Bedingungen_. Robert Koch-Institut: Berlin, Germany, 2004. Google Scholar * Stang A, Moebus S, Möhlenkamp S, Dragano N,
Schmermund A, Beck EM _et al_. Algorithms for converting random-zero to automated oscillometric blood pressure values, and vice versa. _Am J Epidemiol_ 2006; 164: 85–94. Article Google
Scholar * Coe TR, Houghton K . Comparison of the automated Dinamap blood pressure monitor with the mercury sphygmomanometer for detecting hypertension in the day case pre-assessment clinic.
_Ambul Surg_ 2002; 10: 9–15. Article Google Scholar * Wolf-Maier K, Cooper RS, Banegas JR, Giampaoli S, Hense HW, Joffres M _et al_. Hypertension prevalence and blood pressure levels in 6
European countries, Canada, and the United States. _JAMA_ 2003; 289: 2363–2369. Article Google Scholar * Franklin SS, Gustin W 4th, Wong ND, Larson MG, Weber MA, Kannel WB _et al_.
Hemodynamic patterns of age-related changes in blood pressure. The Framingham Heart Study. _Circulation_ 1997; 96: 308–315. Article CAS Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank the physicians and their personnel involved in the study for their contribution. We are similarly indebted to all the study participants for their kind cooperation in
examinations and interviews. The study was funded by an unrestricted educational research grant by Sanofi Aventis Deutschland GmbH, Berlin, Germany. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND
AFFILIATIONS * Institute for Medical Informatics, Biometry and Epidemiology, University Hospital of Essen, University of Duisburg-Essen, Essen, Germany C Balijepalli, C Lösch, K-H Jöckel
& S Moebus * Providence Health Care Research Institute, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada C Balijepalli & K H Humphries * Institut für Pharmakologie und
präventive Medizin, Mahlow, Germany P Bramlage * Department of Cardiology, University Hospital of Essen, Essen, Germany R Erbel Authors * C Balijepalli View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * C Lösch View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * P Bramlage View author publications You can
also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * R Erbel View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * K H Humphries View author publications
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * K-H Jöckel View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * S Moebus View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to S Moebus. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no
conflict of interest. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Balijepalli, C., Lösch, C., Bramlage, P. _et al._ Percentile distribution of blood
pressure readings in 35683 men and women aged 18 to 99 years. _J Hum Hypertens_ 28, 193–200 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2013.85 Download citation * Received: 29 April 2013 * Revised:
18 July 2013 * Accepted: 26 July 2013 * Published: 26 September 2013 * Issue Date: March 2014 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2013.85 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following
link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature
SharedIt content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS * blood pressure * age * percentiles * primary care * epidemiology * Germany


