- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT This systematic review aims to update current evidence on the efficacy and safety of photodynamic therapy (PDT) and anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) injections
for acute central serous chorioretinopathy (CSC). A comprehensive literature search was conducted in PubMed, EMBASE, and Cochrane Library. Studies comparing (1) PDT versus placebo, (2)
anti-VEGF versus placebo, and (3) PDT versus anti-VEGF were included and meta-analyzes were performed when appropriate. Ocular and systemic adverse effects were also summarized. Literature
search yielded six comparative studies, among which five were included for this review. Meta-analysis with three studies indicated that eyes treated with PDT achieved better best-corrected
visual acuity (BCVA) and central macular thickness (CMT) than the placebo group throughout a follow-up of 12 months. Meta-analysis with another two studies comparing anti-VEGF injections and
placebo showed that BCVA at first month was better in anti-VEGF group than in placebo group, though the differences of BCVA and CMT no longer existed at 3 and 6 months after injection.
There was no report directly comparing PDT and anti-VEGF for acute CSC. No severe complications was reported in included studies. In this review, current evidence suggested that early
treatment of acute CSC by PDT is valuable in improving visual acuity, reducing subretinal fluid, and maintaining long term effectiveness. Anti-VEGF injection could shorten the duration of
symptoms and accelerate visual improvement at early stage of disease. Direct comparison between these two treatment will be needed in the future. SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS
RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIALS IN CENTRAL SEROUS CHORIORETINOPATHY: A REVIEW Article 30 March 2023 EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF THE MINERALOCORTICOID RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST TREATMENT FOR CENTRAL SEROUS
CHORIORETINOPATHY: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND META-ANALYSIS Article 07 January 2021 REAL WORLD OUTCOMES OF PHOTODYNAMIC THERAPY FOR CHRONIC CENTRAL SEROUS CHORIORETINOPATHY Article Open access
26 December 2022 INTRODUCTION Central serous chorioretinopathy (CSC) is characterized by serous detachment of the neurosensory retina at the macula with or without pigment epithelial
detachment, which typically affects young and middle aged adults. The pathologenesis is believed to involve the hyperperfusion of choroid and impairment of retinal pigment epithelium
barrier. Patients may experience decreased vision, altered color vision, visual distorsion, or central scotoma. The natural history of CSC in most patients is self-limiting.1 The subretinal
fluid may disappear in a couple of months without any treatment, and the prognosis is often good. Spontaneous resolution, however, does not always happen within the first 3 months of
disease. Cases which do not resolve spontaneously might turn into chronic course of CSC. Gass _et al_2 demonstrated that 5% of patients may experience severe visual disturbances/impariment.
In the first year, the recurrent rate is ~30–50%.3 So treatment is needed in these chronic cases to prevent progressive pigment epithelial and photoreceptor damage and irreversible visual
impairment.2, 4, 5 Current strategies for treating chronic or recurrent CSC include fluorescein angiography guided laser photocoagulation, photodynamic therapy (PDT), and anti-vascular
endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) therapy.5, 6, 7, 8 Whether the condition warrants an early intervention within 3 months of onset remains controversial. Some studies suggested that some
patients might experience visual loss after spontaneous resolution and prompt treatment in acute CSC could result in better visual outcomes.9, 10, 11 Others indicated that early treatment
did not make significant difference in long-term visual acuity.4, 12, 13 Considering the self-limiting nature of CSC, treatment attempts for acute CSC should pay special attention on safety.
Laser photocoagulation targeting extrafoveal leaking point might induce paracentral scotoma, and thus less considered for acute CSC.14, 15 PDT and intravitreal anti-VEGF injection, which
are generally agreed on their safety profile, have been used in the treatment of acute CSC.16, 17 Several studies have demonstrated that PDT applied to the regions of documented choroidal
vascular hyperpermeability on ICGA is effective for the treatment of CSC by inducing local choroidal hypoperfusion.18, 19, 20, 21 Moreover, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) has been
implicated as the major factor responsible for increased vascular permeability.22, 23, 24 In acute CSC, the efficacy of PDT or anti-VEGF treatment has been observed by a few studies.10, 17,
25, 26 However, other studies13 made different conclusions that the efficacy of PDT and anti-VEGF for acute CSC is neither statistically nor clinically significant. This study aims to
systematically review and meta-analyze published studies on PDT and anti-VEGF therapy for acute CSC, and guide future clinical practice. METHODS SEARCH STRATEGY Three databases (PubMed,
EMBASE, and Cochrane Library) were last searched on September, 2014. In conducting the search in PubMed, EMBASE, three domains of terms were searched: (1) PDT or equivalents (eg, photodymic
therapy, verteporfin, and visudyne), (2) anti-VEGF or equivalents (eg, ranibizumab, bevacizumab, afflibercept, and conbercept), and (3) CSC or equivalents (eg, central sereous
chorioretinopathy). The results from each domain were then combined with OR. In Cochrane Library, CSC or equivalents was used in search. The details of search methodologies are illustrated
in Appendix. The selected paper had been written in English, and no restrictions were imposed on study design. All potentially related articles were retrieved and imported into EndNote
X7(Thomson Reuters, New York, NY, USA), where duplicate studies were manually removed. INCLUSION AND EXCLUSION CRITERIA Published comparative studies, whether randomized controlled trials
(RCTs) or non-RCT studies, were included if they compared (1) PDT versus placebo; (2) anti-VEGF versus placebo; or (3) PDT versus anti-VEGF in the treatment of acute CSC eyes without
previous intervention. The selected studies should include one or more of the following results at months 1, 3, 6, 12 or longer observation time point: best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA),
central macular thickness (CMT), and ocular or systemic adverse events. Two authors independently reviewed the titles and abstracts of retrieved articles, and determined whether they met
inclusion criteria. Full texts were read as necessary. Disagreement and inconsistencies were discussed and resolved by discussion and consensus. QUALITY ASSESSMENT Study quality was
evaluated and assessed using the tool described by Jadad scores (5-point). Jadad scores include the following criteria: randomization, double blinding, and description of withdraws and
dropouts. Moreover, the additional criteria are (1) the description of randomization method was appropriate, and (2) the description of double blinding method was appropriate. The studies
scored 1 point for each criterion met.27 STATISTICAL ANALYZES All RCTs and non-RCT studies with balanced baseline measurements were considered for meta-analysis. We performed all
meta-analyzes using the Review Manager (RevMan) software, version 5.3.3(Cochrane Collaboration, Oxford, UK). Data from the articles were combined using a fixed-effects and continuous
variable pattern. In the meta-analysis, the effect sizes of each study were presented as mean difference with 95% confidence intervals (CI). If the 95% CI of weighted mean difference crossed
zero, the pooled effect sizes were considered statistically insignificant. According to baseline characteristics and estimated statistical heterogeneity, I-square (I2) statistic was to
examine and evaluate the clinical statistical heterogeneity among studies (I2≤40, insignificant heterogeneity). Sensitivity analysis was assessed by sequentially omitting one study. Because
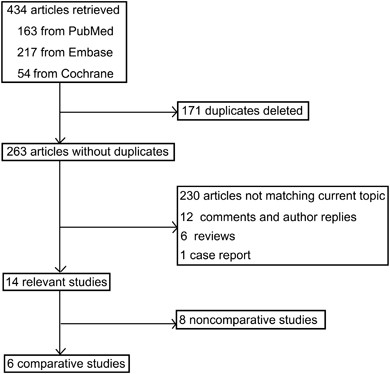
of the limited number studies, potential publication bias was not analyzed. RESULTS RESULTS OF LITERATURE SEARCH The literature search yielded 434 articles, 163 from PubMed, 217 from EMBASE,
and 54 from Cochrane Library. By removing 171 duplicated articles, 263 articles without duplicates were yielded. Then 230 ineligible articles, 12 comments and author replies, 6 reviews and
1 case report were excluded, producing 14 relevant study reports (Figure 1). After excluding eight non-comparative case series,10, 16, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33 the remaining six comparative
studies, including four RCTs 9, 11, 13, 34 and two non-RCTs,25, 26 were included for study (Table 1). STUDY CHARACTERISTICS Three comparative studies, including two RCTs and one non-RCT
study, compared PDT and placebo, and the other three, including two RCTs and one non-RCT study, compared anti-VEGF injections and placebo. There was no study directly comparing PDT and
anti-VEGF therapy. The characteristics of the included six study was displayed in Table 1. Six studies9, 11, 13, 25, 26, 34 differed in regions, sample sizes, and the proportion of patient
allocation in the treatment and control groups. In all three studies which compared PDT and placebo, PDT groups were treated with 50% of standard dosage of verteporfin. Among the three
studies comparing anti-VEGF and placebo, two RCTs9, 13 used standard injection dosage (1.25 mg bevacizumab or 0.5 mg ranibizumab), and in one non-RCT study by Aydin _et al_26 bevacizumab
(2.0 mg) was injected. Because of non-standard dosing, imbalanced baseline, and distinct data analyzing method, the study by Aydin _et al_ was excluded from further meta-analysis. COMPARISON
OF THE PHOTODYNAMIC THERAPY AND PLACEBO The three studies9, 11, 34 which compared functional and anatomic repairs between the PDT (50% dose of verteporfin) and placebo did not show
significant statistical or clinical heterogeneity. Meta-analysis demonstrated significant benefits of PDT through 12 months of observation. The weighted mean difference (95% CI) of BCVA
(logMAR) and CMT (_μ_m) between PDT and placebo group at month 1, 3, and 12 were −0.01 (−0.06, 0.03), −0.07 (−0.12, −0.02), −0.09 (−0.15, −0.03), and −119 (−175, −62), −121 (−182, −59), −72
(−111, −33), respectively (Figures 2 and 3). Sensitivity analysis indicated that no studies substantially influenced the final results. COMPARISON OF THE INTRAVITREAL ANTI-VEGF INJECTION AND
PLACEBO The 2 RCTs which compared anti-VEGF injections and placebo did not show significant statistical or clinical heterogeneity.9, 13 Meta-analysis revealed early (month 1) visual
benefits of anti-VEGF therapy, whereas the benefits tended to shrink quickly over time. The weighted mean difference (95% CI) of BCVA (logMAR) and CMT (μm) between anti-VEGF and placebo
group at months 1, 3, and 6 were −0.07 (−0.14, −0.01), 0.01 (−0.04, 0.06), 0.01 (−0.05, 0.07), and −49 (−108, 10), −8 (−68, 53), 0 (−70, 70), respectively (Figures 4 and 5). SAFETY Except
for mild subconjunctival hemorrhage at injection site, no severe ocular or systematic complication was reported to be associated with intravitreal anti-VEGF injections in either the included
or excluded studies. PDT was also considered to be safe and no adverse event was reported. DISCUSSION Based on the self-limiting nature of CSC, the generally agreed rule for CSC management
used to be that an at least 3-month period of observation should be given first to patients with acute episodes of CSC before considering treatment. Accumulating evidences are challenging
this notion. Our systemic review and meta-analysis revealed that early treatment of acute CSC with PDT is associated with better long term visual and anatomical outcomes. Anti-VEGF
injections might also help in accelerating visual recovery though significant difference was not observed in long term follow-up. This means that the patients will suffer blurred vision,
metamorphopsia, micropsia, dyschromatopsia, hypermetropization, and central scotoma, as well as loss of contrast sensitivity and increasing hyperopia until spontaneous resolution occurs. We
demonstrate that acute CSC may be treated in patients who often desire rapid rehabilitation of the disease and vision. We should consider the effectiveness of treatment to improve vision,
shortening the duration of symptoms, reducing recurrence, and even a more detailed evaluation of visual function such as contrast sensitivity, retinal sensitivity and so on. Although thermal
laser photocoagulation applied to extrafoveal leaking point has been shown to shorten the duration of symptoms, it is not without complications such as central scotoma, secondary choroidal
neovascularization (CNV), foveal leakage, and so on. Therefore, thermal laser photocoagulation can not be widely used to the treatment of CSC. It has been proved that standard-dose PDT is
useful and effective in the treatment of CSC. Nevertheless, potential side effects may occur after treatment, such as RPE atrophy, macular ischemia, even secondary CNV, and so on.
Restricting the dosage of PDT for CSC may minimize complications, rapidly reduce the choroidal hyperpermeability and prompt resolution of subretinal fluid. For its advantage, reducing the
dosage of PDT has been already applied for chronic CSC.20, 28, 35, 36, 37, 38 Currently, there are many research on the treatment of acute CSC, most studies are non-RCTs. Two RCTs and one
non-RCT comparative studies were included for the comparison between the PDT and observation groups. There was no significant difference in baseline between the treatment and observation
groups for the non-RCT study. According to meta-analysis, patients with acute CSC treated with half-dose PDT achieved significant difference in the improvement of BCVA and CMT recovery than
the observation group. Recently, anti-VEGF antibody has been used in CSC as an effective and safe treatment option.9 Bevacizumab, a recombinant humanized full-length monoclonal antibody of
VEGF, could penetrate the reretina and is transported into the photoreceptor outer segments, RPE, and choroid after intravitreal injection. Many studies have reported that intravitreal
bevacizumab was associated with visual acuity improvement and reduced neurosensory detachment without adverse events in patients with CSC. Ranibizumab may have potentially better retinal
penetration than bevacizumab because of its smaller molecular size and higher binding affinity for VEGF.9, 39 According to recent research, two RCTs reported intravitreal
bevacizumab/ranibizumab injection in the treatment of acute CSC. Meta-analysis of 6-month studies showed patients for acute CSC treated with injection gained significantly better BCVA than
the observation group at the 1-month follow-up. However, there are no significant difference in the BVCA or CMT recovery between the treatment and observation groups over time. The outcomes
may be related to the small number of cases, and the short follow-up period. More objective parameters should be needed to assess the visual functional changes, such as contrast sensitivity,
retinal sensitivity, and so on. In conclusion, early and prompt treatment should be advocated in acute CSC patients. The prefered therapy is PDT, which is likely to result in better
functional and anatomical outcomes in long term observation. Though anti-VEGF injections accelerated early restoration of vision and quick absorption of subretinal fluid, the benefits no
longer existed at month 3 and thereafter. Future studies should include large number of subjects with a long period of follow-up. The involvement of new functional index such as contrast
sensitivity, microperimetry and electrophysiological measurements might also help in redefining ‘acute CSC’, determining optimal treatment time point, and evaluating individual prognosis.
REFERENCES * Klein ML, Van Buskirk EM, Friedman E, Gragoudas E, Chandra S . Experience with nontreatment of central serous choroidopathy. _Arch Ophthalmol_ 1974; 91 (4): 247–250. Article
CAS Google Scholar * Gass JD . Pathogenesis of disciform detachment of the neuroepithelium. _Am J Ophthalmol_ 1967; 63 (Suppl): 1–139. Google Scholar * Levine R, Brucker AJ, Robinson F .
Long-term follow-up of idiopathic central serous chorioretinopathy by fluorescein angiography. _Ophthalmology_ 1989; 96 (6): 854–859. Article CAS Google Scholar * Wang M, Munch IC, Hasler
PW, Prunte C, Larsen M . Central serous chorioretinopathy. _Acta Ophthalmol_ 2008; 86 (2): 126–145. Article Google Scholar * Gemenetzi M, De Salvo G, Lotery AJ . Central serous
chorioretinopathy: an update on pathogenesis and treatment. _Eye (Lond)_ 2010; 24 (12): 1743–1756. Article CAS Google Scholar * Roisman L, Magalhaes FP, Lavinsky D, Moraes N, Hirai FE,
Cardillo JA _et al_. Micropulse diode laser treatment for chronic central serous chorioretinopathy: a randomized pilot trial. _Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging Retina_ 2013; 44 (5): 465–470.
Article Google Scholar * Nicolo M, Eandi CM, Alovisi C, Grignolo FM, Traverso CE, Musetti D _et al_. Half-fluence versus half-dose photodynamic therapy in chronic central serous
chorioretinopathy. _Am J Ophthalmol_ 2014; 157 (5): 1033–1037. Article Google Scholar * Inoue M, Kadonosono K, Watanabe Y, Kobayashi S, Yamane S, Arakawa A . Results of one-year follow-up
examinations after intravitreal bevacizumab administration for chronic central serous chorioretinopathy. _Ophthalmologica_ 2011; 225 (1): 37–40. Article Google Scholar * Kim M, Lee SC, Lee
SJ . Intravitreal ranibizumab for acute central serous chorioretinopathy. _Ophthalmologica_ 2013; 229 (3): 152–157. Article CAS Google Scholar * Seong HK, Bae JH, Kim ES, Han JR, Nam WH,
Kim HK . Intravitreal bevacizumab to treat acute central serous chorioretinopathy: short-term effect. _Ophthalmologica_ 2009; 223 (5): 343–347. Article CAS Google Scholar * Chan WM, Lai
TY, Lai RY, Liu DT, Lam DS . Half-dose verteporfin photodynamic therapy for acute central serous chorioretinopathy: one-year results of a randomized controlled trial. _Ophthalmology_ 2008;
115 (10): 1756–1765. Article Google Scholar * Chung YR, Seo EJ, Lew HM, Lee KH . Lack of positive effect of intravitreal bevacizumab in central serous chorioretinopathy: meta-analysis and
review. _Eye (Lond)_ 2013; 27 (12): 1339–1346. Article CAS Google Scholar * Lim JW, Ryu SJ, Shin MC . The effect of intravitreal bevacizumab in patients with acute central serous
chorioretinopathy. _Korean J Ophthalmol_ 2010; 24 (3): 155–158. Article Google Scholar * Burumcek E, Mudun A, Karacorlu S, Arslan MO . Laser photocoagulation for persistent central serous
retinopathy: results of long-term follow-up. _Ophthalmology_ 1997; 104 (4): 616–622. Article CAS Google Scholar * Ross A, Ross AH, Mohamed Q . Review and update of central serous
chorioretinopathy. _Curr Opin Ophthalmol_ 2011; 22 (3): 166–173. Article Google Scholar * Hagen S, Ansari-Shahrezaei S, Smretschnig E, Glittenberg C, Krebs I, Graf A _et al_. The effect of
photodynamic therapy on macular sensitivity in eyes with acute central serous chorioretinopathy. _Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol_ 2013; 251 (4): 1081–1089. Article CAS Google Scholar *
Park SU, Lee SJ, Kim M . Intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor versus observation in acute central serous chorioretinopathy: one-year results. _Korean J Ophthalmol_ 2014; 28
(4): 306–313. Article Google Scholar * Yannuzzi LA, Slakter JS, Gross NE, Spaide RF, Costa D, Huang SJ _et al_. Indocyanine green angiography-guided photodynamic therapy for treatment of
chronic central serous chorioretinopathy: a pilot study. _Retina_ 2003; 23 (3): 288–298. Article Google Scholar * Cardillo Piccolino F, Eandi CM, Ventre L, Rigault de la Longrais RC,
Grignolo FM . Photodynamic therapy for chronic central serous chorioretinopathy. _Retina_ 2003; 23 (6): 752–763. Article Google Scholar * Taban M, Boyer DS, Thomas EL, Taban M . Chronic
central serous chorioretinopathy: photodynamic therapy. _Am J Ophthalmol_ 2004; 137 (6): 1073–1080. Article Google Scholar * Kim KS, Lee WK . Photodynamic therapy with verteporfin for
avascular serous pigment epithelial detachment in elderly Koreans. _Retina_ 2010; 30 (1): 93–99. Article CAS Google Scholar * Prunte C, Flammer J . Choroidal capillary and venous
congestion in central serous chorioretinopathy. _Am J Ophthalmol_ 1996; 121 (1): 26–34. Article CAS Google Scholar * Stanga PE, Lim JI, Hamilton P . Indocyanine green angiography in
chorioretinal diseases: indications and interpretation: an evidence-based update. _Ophthalmology_ 2003; 110 (1): 15–21; quiz 22-13. Article Google Scholar * Tolentino MJ, McLeod DS,
Taomoto M, Otsuji T, Adamis AP, Lutty GA . Pathologic features of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced retinopathy in the nonhuman primate. _Am J Ophthalmol_ 2002; 133 (3): 373–385.
Article CAS Google Scholar * Kim KS, Lee WK, Lee SB . Half-dose photodynamic therapy targeting the leakage point on the fluorescein angiography in acute central serous chorioretinopathy:
a pilot study. _Am J Ophthalmol_ 2014; 157 2: 366–373.e361. Article Google Scholar * Aydin E . The efficacy of intravitreal bevacizumab for acute central serous chorioretinopathy. _J Ocul
Pharmacol Ther_ 2013; 29 (1): 10–13. Article CAS Google Scholar * Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ _et al_. Assessing the quality of reports of
randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? _Control Clin Trials_ 1996; 17 (1): 1–12. Article CAS Google Scholar * Ober MD, Yannuzzi LA, Do DV, Spaide RF, Bressler NM, Jampol LM
_et al_. Photodynamic therapy for focal retinal pigment epithelial leaks secondary to central serous chorioretinopathy. _Ophthalmology_ 2005; 112 (12): 2088–2094. Article Google Scholar *
Ratanasukon M, Thongthong K, Bhurayanontachai P, Jirarattanasopa P . Photoreceptor disruption in central serous chorioretinopathy treated by half-dose photodynamic therapy. _Clin Ophthalmol_
2013; 7: 87–92. Article Google Scholar * Dang Y, Sun X, Xu Y, Mu Y, Zhao M, Zhao J _et al_. Subfoveal choroidal thickness after photodynamic therapy in patients with acute idiopathic
central serous chorioretinopathy. _Ther Clin Risk Manag_ 2014; 10: 37–43. Article Google Scholar * Smretschnig E, Ansari-Shahrezaei S, Moussa S, Glittenberg C, Krebs I, Binder S .
Half-fluence photodynamic therapy in acute central serous chorioretinopathy. _Retina_ 2012; 32 (10): 2014–2019. Article CAS Google Scholar * Mehany SA, Shawkat AM, Sayed MF, Mourad KM .
Role of Avastin in management of central serous chorioretinopathy. _Saudi J Ophthalmol_ 2010; 24 (3): 69–75. Article Google Scholar * Zhao MW, Zhou P, Xiao HX, Lv YS, Li CA, Liu GD _et
al_. Photodynamic therapy for acute central serous chorioretinopathy: The safe effective lowest dose of verteporfin. _Retina_ 2009; 29 (8): 1155–1161. Article Google Scholar * Wu ZH, Lai
RY, Yip YW, Chan WM, Lam DS, Lai TY . Improvement in multifocal electroretinography after half-dose verteporfin photodynamic therapy for central serous chorioretinopathy: a randomized
placebo-controlled trial. _Retina_ 2011; 31 (7): 1378–1386. Article CAS Google Scholar * Battaglia Parodi M, Da Pozzo S, Ravalico G . Photodynamic therapy in chronic central serous
chorioretinopathy. _Retina_ 2003; 23 (2): 235–237. Article CAS Google Scholar * Canakis C, Livir-Rallatos C, Panayiotis Z, Livir-Rallatos G, Persidis E, Conway MD _et al_. Ocular
photodynamic therapy for serous macular detachment in the diffuse retinal pigment epitheliopathy variant of idiopathic central serous chorioretinopathy. _Am J Ophthalmol_ 2003; 136 (4):
750–752. Article Google Scholar * Chan WM, Lam DS, Lai TY, Tam BS, Liu DT, Chan CK . Choroidal vascular remodelling in central serous chorioretinopathy after indocyanine green guided
photodynamic therapy with verteporfin: a novel treatment at the primary disease level. _Br J Ophthalmol_ 2003; 87 (12): 1453–1458. Article Google Scholar * Colucciello M . Choroidal
neovascularization complicating photodynamic therapy for central serous retinopathy. _Retina_ 2006; 26 (2): 239–242. Article Google Scholar * Torres-Soriano ME, Garcia-Aguirre G, Kon-Jara
V, Ustariz-Gonzales O, Abraham-Marin M, Ober MD _et al_. A pilot study of intravitreal bevacizumab for the treatment of central serous chorioretinopathy (case reports). _Graefes Arch Clin
Exp Ophthalmol_ 2008; 246 (9): 1235–1239. Article CAS Google Scholar Download references AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Ophthalmology, Xi’an No.1 Hospital,
Xi’an, Shaanxi, China H Q Lu & T Zhang * Department of Ophthalmology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing, China E Q Wang & Y X Chen Authors * H Q Lu View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * E Q Wang View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * T Zhang View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Y X Chen View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR
Correspondence to Y X Chen. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no conflict of interest. APPENDIX APPENDIX RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS
ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Lu, H., Wang, E., Zhang, T. _et al._ Photodynamic therapy and anti-vascular endothelial growth factor for acute central serous chorioretinopathy: a systematic
review and meta-analysis. _Eye_ 30, 15–22 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2015.208 Download citation * Received: 28 April 2015 * Accepted: 03 September 2015 * Published: 30 October 2015
* Issue Date: January 2016 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2015.208 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative










:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(299x0:301x2)/amy-poehler-2-600x450-ab533a62ebbe404ebdd93ce088d6a06f.jpg)