- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT I/St and A/Sn mice are polar extremes in terms of several parameters defining sensitivity to _Mycobacterium tuberculosis_. TNF-α, mainly produced by activated macrophages, can
mediate both physiological and pathophysiological processes. Adequate TNF-α levels are essential for a forceful protective response to _M. tuberculosis_. We have functionally characterized a
nonsynonymous substitution, Arg8His, in the highly conserved cytoplasmic domain of the pro-TNF-α leader peptide from extremely _M. tuberculosis-_sensitive I/St mice. This was compared to
the common pro-TNF-α variant found in A/Sn mice. Using cDNA constructs, both variants were constitutively expressed in HEK293A cells. A significantly higher secretion level of Arg8His TNF-α
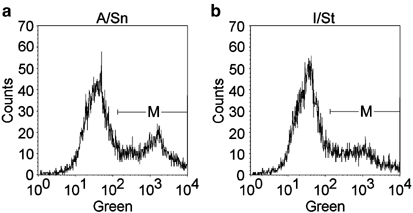
was shown using flow cytometry and ELISA analysis (_P_=0.0063), while intracellular levels were similar for both protein variants. An even TNF-α distribution throughout the cells was seen
using confocal microscopy. This suggests that the Arg8His substitution affects pro-TNF-α processing. The I/St mouse may serve as a model to further explore the function of the well-conserved
cytoplasmic region of TNF-α. However, other identified substitutions in the I/St promoter, introns and 3′UTR of _Tnf-_α, as well as the cellular environment _in vivo_ may affect the balance
between soluble and intracellular Arg8His TNF-α before and during _M. tuberculosis_ infection. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content,
access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles $119.00 per year only $19.83 per
issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL
ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS _MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS_ STRAIN WITH
DELETIONS IN _MENT3_ AND _MENT4_ IS ATTENUATED AND CONFERS PROTECTION IN MICE AND GUINEA PIGS Article Open access 27 June 2024 TOLLIP INHIBITS LIPID ACCUMULATION AND THE INTEGRATED STRESS
RESPONSE IN ALVEOLAR MACROPHAGES TO CONTROL _MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS_ INFECTION Article 25 March 2024 DEPLETION OF ESSENTIAL MYCOBACTERIAL GENE GLMM REDUCES PATHOGEN SURVIVAL AND INDUCES
HOST-PROTECTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSES AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS Article Open access 06 August 2024 ACCESSION CODES ACCESSIONS GENBANK/EMBL/DDBJ * Y00467 REFERENCES * Nikonenko BV, Apt AS, Moroz AM,
Averbakh MM . Genetic analysis of susceptibility of mice to H37Rv tuberculosis infection: sensitivity versus relative resistance. _Prog Leuk Biol_ 1985; 3: 291–298. Google Scholar *
Lavebratt C, Apt AS, Nikonenko BV, Schalling M, Schurr E . Severity of tuberculosis in mice is linked to distal chromosome 3 and proximal chromosome 9. _J Infect Dis_ 1999; 180: 150–155.
Article CAS Google Scholar * Nikonenko BV, Apt AS, Moroz AM, Averbakh MM . Comparative analysis of mycobacterial infections in susceptible I/St and resistant A/Sn mice. _Tuberc Lung Dis_
2000; 80: 15–25. Article CAS Google Scholar * Sanchez F, Radaeva TV, Nikonenko BV et al. Multigenic control of disease severity after virulent _Mycobacterium tuberculosis_ infection in
mice. _Infect Immun_ 2003; 71: 126–131. Article CAS Google Scholar * Dinarello CA . Proinflammatory cytokines. _Chest_ 2000; 118: 503–508. Article CAS Google Scholar * Vassalli P . The
pathophysiology of tumor necrosis factors. _Annu Rev lmmunol_ 1992; 10: 411–452. Article CAS Google Scholar * Sharma R, Anker SD . Cytokines, apoptosis and cachexia: the potential for
TNF antagonism. _Int J Cardiol_ 2002; 85: 161–171. Article Google Scholar * Ware CF, VanArsdale S, VanArsdale TL . Apoptosis mediated by the TNF-related cytokine and receptor families. _J
Cell Biochem_ 1996; 60: 47–55. Article CAS Google Scholar * Dinarello CA . Proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines as mediators in the pathogenesis of septic shock. _Chest_ 1997;
112 (Suppl): 321S–329S. Article CAS Google Scholar * Flynn JL . Immunology of tuberculosis and implications in vaccine development. _Tuberculosis_ 2004; 84: 93–101. Article Google
Scholar * Flynn JL, Goldstein MM, Chan J et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha is required in the protective immune response against _Mycobacterium tuberculosis_ in mice. _Immunity_ 1995; 2:
561–572. Article CAS Google Scholar * Bean AG, Roach DR, Briscoe H et al. Structural deficiencies in granuloma formation in TNF gene-targeted mice underlie the heightened susceptibility
to aerosol _Mycobacterium tuberculosis_ infection, which is not compensated for by lymphotoxin. _J Immunol_ 1999; 162: 3504–3511. CAS Google Scholar * Roach DR, Bean AG, Demangel C, France
MP, Briscoe H, Britton WJ . TNF regulates chemokine induction essential for cell recruitment, granuloma formation, and clearance of mycobacterial infection. _J Immunol_ 2002; 168:
4620–4627. Article CAS Google Scholar * Keane J, Gershon S, Wise RP et al. Tuberculosis associated with infliximab, a tumor necrosis factor alpha-neutralizing agent. _N Engl J Med_ 2001;
345: 1098–1104. Article CAS Google Scholar * Knight J . Polymorphisms in tumor necrosis factor and other cytokines as risks for infectious diseases and the septic syndrome. _Curr Infect
Dis Rep_ 2001; 3: 427–439. Article Google Scholar * Hajeer AH, Hutchinson IV . Influence of TNFalpha gene polymorphisms on TNFalpha production and disease. _Hum Immunol_ 2001; 62:
1191–1199. Article CAS Google Scholar * Tang P, Hung MC, Klostergaard J . Human pro-tumor necrosis factor is a homotrimer. _Biochemistry_ 1996; 35: 8216–8225. Article CAS Google Scholar
* Kriegler M, Perez C, DeFay K, Albert I, Lu SD . A novel form of TNF/Cachectin is a cell surface cytotoxic transmembrane protein: ramifications for the complex physiology of TNF. _Cell_
1988; 53: 45–53. Article CAS Google Scholar * Black RA, Rauch CT, Kozlosky CJ et al. A metalloproteinase disintegrin that releases tumour-necrosis factor-alpha from cells. _Nature_ 1997;
385: 729–733. Article CAS Google Scholar * Moss ML, Jin SL, Milla ME et al. Cloning of a disintegrin metalloproteinase that processes precursor tumour-necrosis factor-alpha. _Nature_
1997; 385: 733–736. Article CAS Google Scholar * Perez C, Albert I, DeFay K et al. A nonsecretable cell surface mutant of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) kills by cell-to-cell contact. _Cell_
1990; 63: 251–258. Article CAS Google Scholar * Decoster E, Vanhaesebroeck B, Vandenabeele P et al. Generation and biological characterization of membrane-bound, uncleavable murine tumor
necrosis factor. _J Biol Chem_ 1995; 270: 18473–18478. Article CAS Google Scholar * Grell M, Douni E, Wajant H et al. The transmembrane form of tumor necrosis factor is the prime
activating ligand of the 80 kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor. _Cell_ 1995; 83: 793–802. Article CAS Google Scholar * Utsumi T, Takeshige T, Tanaka K et al. Transmembrane TNF (pro-TNF)
is palmitoylated. _FEBS Lett_ 2001; 500: 1–6. Article CAS Google Scholar * Ruuls SR, Hoek RM, Ngo VN et al. Membrane-bound TNF supports secondary lymphoid organ structure but is
subservient to secreted TNF in driving autoimmune inflammation. _Immunity_ 2001; 15: 533–543. Article CAS Google Scholar * Majorov KB, Lyadova IV, Kondratieva TK et al. Different innate
ability of I/St and A/Sn mice to combat virulent _Mycobacterium tuberculosis_: phenotypes expressed in lung and extrapulmonary macrophages. _Infect Immun_ 2003; 71: 697–707. Article CAS
Google Scholar * Eruslanov EB, Majorov KB, Orlova MO et al. Lung cell responses to _M. tuberculosis_ in genetically susceptible and resistant mice following intratracheal challenge. _Clin
Exp Immunol_ 2004; 135: 19–28. Article CAS Google Scholar * Bastos KR, Marinho CR, Barboza R, Russo M, Alvarez JM, D’Imperio Lima MR . What kind of message does IL-12/IL-23 bring to
macrophages and dendritic cells? _Microbes Infect_ 2004; 6: 630–636. Article CAS Google Scholar * Xing Z, Zganiacz A, Santosuosso M . Role of IL-12 in macrophage activation during
intracellular infection: IL-12 and mycobacteria synergistically release TNF-alpha and nitric oxide from macrophages via IFN-gamma induction. _J Leukocyte Biol_ 2000; 68: 897–902. CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Bekker LG, Moreira AL, Bergtold A, Freeman S, Ryffel B, Kaplan G . Immunopathologic effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha in murine mycobacterial infection are dose
dependent. _Infect Immun_ 2000; 68: 6954–6961. Article CAS Google Scholar * Alexopoulou L, Pasparakis M, Kollias G . A murine transmembrane tumor necrosis factor (TNF) transgene induces
arthritis by cooperative p55/p75 TNF receptor signaling. _Eur J Immunol_ 1997; 27: 2588–2592. Article CAS Google Scholar * Tracey KJ, Fong Y, Hesse DG et al. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal
antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. _Nature_ 1987; 330: 662–664. Article CAS Google Scholar * Mohler KM, Sleath PR, Fitzner JN et al. Protection against a lethal
dose of endotoxin by an inhibitor of tumour necrosis factor processing. _Nature_ 1994; 370: 218–220. Article CAS Google Scholar * Mueller C, Corazza N, Trachsel-Loseth S et al.
Noncleavable transmembrane mouse tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFalpha) mediates effects distinct from those of wild-type TNFalpha _in vitro_ and _in vivo_. _J Biol Chem_ 1999; 274:
38112–38118. Article CAS Google Scholar * Zheng Y, Saftig P, Hartmann D, Blobel C . Evaluation of the contribution of different ADAMs to tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) shedding and of the
function of the TNFα ectodomain in ensuring selective stimulated shedding by the TNFα convertase (TACE/ADAM17). _J Biol Chem_ 2004; 279: 42898–42906. Article CAS Google Scholar * Gearing
AJ, Beckett P, Christodoulou M et al. Processing of tumour necrosis factor-alpha precursor by metalloproteinases. _Nature_ 1994; 370: 555–557. Article CAS Google Scholar * Solomon KA,
Covington MB, DeCicco CP, Newton RC . The fate of pro-TNF-alpha following inhibition of metalloprotease-dependent processing to soluble TNF-alpha in human monocytes. _J Immunol_ 1997; 159:
4524–4531. CAS Google Scholar * Glaser KB, Falduto M, Metzger R et al. Expression, release, and regulation of human TNF from stable transfectants of HEK-293 cells. _Inflamm Res_ 1997; 46
(Suppl. 2): S127. Article CAS Google Scholar * Solomon KA, Pesti N, Wu G, Newton RC . Cutting edge: a dominant negative form of TNF-α converting enzyme inhibits proTNF and TNFRII
secretion. _J Immunol_ 1999; 163: 4105–4108. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Reddy P, Slack JL, Davis R et al. Functional analysis of the domain structure of tumor necrosis factor-α
converting enzyme. _J Biol Chem_ 2000; 275: 14608–14614. Article CAS Google Scholar * Itai T, Tanaka M, Nagata S . Processing of tumor necrosis factor by the membrane-bound
TNF-α-converting enzyme, but not its truncated soluble form. _Eur J Biochem_ 2001; 268: 2074–2082. Article CAS Google Scholar * Utsumi T, Akimaru K, Kawabata Z et al. Human pro-tumor
necrosis factor: molecular determinants of membrane translocation, sorting, and maturation. _Mol Cell Biol_ 1995; 15: 6398–6405. Article CAS Google Scholar * Cseh K, Beutler B .
Alternative cleavage of the cachectin/tumor necrosis factor propeptide results in a larger, inactive form of secreted protein. _J Biol Chem_ 1989; 264: 16256–16260. CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Utsumi T, Levitan A, Hung MC, Klostergaard J . Effects of truncation of human pro-tumor necrosis factor transmembrane domain on cellular targeting. _J Biol Chem_ 1993; 268:
9511–9516. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Han J, Brown T, Beutler B . Endotoxin-responsive sequences control cachectin/tumor necrosis factor biosynthesis at the translational level. _J Exp
Med_ 1990; 171: 465–475. Article CAS Google Scholar * Han J, Beutler B . The essential role of the UA-rich sequence in endotoxin-induced cachectin/TNF synthesis. _Eur Cytokine Netw_ 1990;
1: 71–75. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Beutler B . Regulation of cachectin biosynthesis occurs at multiple levels. _Prog Clin Biol Res_ 1990; 349: 229–240. CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Hel Z, Skamene E, Radzioch D . Two distinct regions in the 3′ untranslated region of tumor necrosis factor alpha mRNA form complexes with macrophage proteins. _Mol Cell Biol_ 1996; 16:
5579–5590. Article CAS Google Scholar * Caput D, Beutler B, Hartog K, Thayer R, Brown-Shimer S, Cerami A . Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3′-untranslated region of
mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. _Biochemistry_ 1986; 83: 1670–1674. CAS Google Scholar * Han J, Huez G, Beutler B . Interactive effects of the tumor necrosis factor
promoter and 3′-untranslated regions. _J Immunol_ 1991; 146: 1843–1848. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Schug J, Overton GC . _Technical Report CBIL-TR-1997-1001-v0.0_. Computational Biology
and Informatics Laboratory School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Pennsylvania, 1997. Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This study was supported by grants from Swedish Medical
Research Council, Karolinska Institutet Foundation, Magnus Bergwall Foundation, and Swedish Heart and Lung Foundation. We thank Ricardo Giscombe for skilful assistance with the flow
cytometry experiments. AUTHOR INFORMATION Author notes * H Källström Present address: Department of Medical Biochemistry and Microbiology, The Biomedical Center, Uppsala University, Box 582,
751 23, Uppsala, Sweden AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Molecular Medicine, Karolinska Institutet, CMM, Karolinska Hospital, Stockholm, Sweden A K Kähler, A-S Persson, F Sánchez
& C Lavebratt * Department of Cell and Molecular Biology, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden H Källström * Laboratory for Immunogenetics, Central Institute for Tuberculosis of the
Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Moscow, Russia A S Apt * McGill Center for the Study of Host Resistance, Montreal General Hospital, Montreal, Quebec, Canada E Schurr Authors * A K
Kähler View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * A-S Persson View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
* F Sánchez View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * H Källström View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google
Scholar * A S Apt View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * E Schurr View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google
Scholar * C Lavebratt View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to C Lavebratt. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS
Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Kähler, A., Persson, AS., Sánchez, F. _et al._ A new coding mutation in the _Tnf_-α leader sequence in tuberculosis-sensitive
I/St mice causes higher secretion levels of soluble TNF-α. _Genes Immun_ 6, 620–627 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364249 Download citation * Received: 01 March 2005 * Revised: 13
June 2005 * Accepted: 13 June 2005 * Published: 14 July 2005 * Issue Date: 01 October 2005 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364249 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following
link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature
SharedIt content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS * TNF-α * tuberculosis * leader peptide * pro-TNF-α







