- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
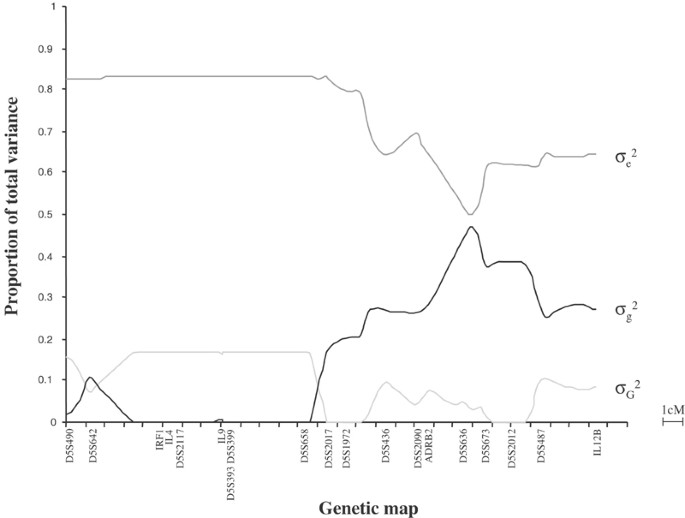
ABSTRACT We have previously mapped a locus controlling _Plasmodium falciparum_ blood infection levels (PFBI) to chromosome 5q31–q33. We genotyped 19 microsatellite markers on chromosome
5q31–q33 in a new sample of 44 pedigrees comprising 84 nuclear families and 292 individuals living in a _P. falciparum_ endemic area. Using a nonparametric multipoint variance-component
approach (by GENEHUNTER), we evidenced a peak of linkage close to D5S636 (_P_=0.0069), with a heritability of 0.46. Using a variance-component method for linkage-disequilibrium mapping of
quantitative traits (by QTDT) and the Bonferroni correction for multiple testing, we further detected allelic association in the presence of linkage between blood infection levels and D5S487
(_P_=6 × 10−5; _P__c_=0.0011), which is located on the distal part of the peak. These results confirm the importance of chromosome 5q31–q33 in the genetic control of PFBI levels. Access
through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles $119.00 per year only $19.83 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy
now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer
support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS MALARIA PROTECTION DUE TO SICKLE HAEMOGLOBIN DEPENDS ON PARASITE GENOTYPE Article Open access 09 December 2021 THE IMPACT OF
MALARIA-PROTECTIVE RED BLOOD CELL POLYMORPHISMS ON PARASITE BIOMASS IN CHILDREN WITH SEVERE _PLASMODIUM FALCIPARUM_ MALARIA Article Open access 08 June 2022 GENOMICS REVEALS HETEROGENEOUS
_PLASMODIUM FALCIPARUM_ TRANSMISSION AND SELECTION SIGNALS IN ZAMBIA Article Open access 06 April 2024 REFERENCES * Haldane JBS . The rate of mutation of human genes. _Proc. VIII Int Cong.
Genet. Hereditas_ 1949; 35: 267–273. Google Scholar * Hill AV . The immunogenetics of human infectious diseases. _Annu Rev Immunol_ 1998; 16: 593–617. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
* Kwiatkowski D . Genetic susceptibility to malaria getting complex. _Curr Opin Genet Dev_ 2000; 10: 320. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Abel L, Cot M, Mulder L, Carnevale P,
Feingold J . Segregation analysis detects a major gene controlling blood infection levels in human malaria. _Am J Hum Genet_ 1992; 50: 1308–1317. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
* Garcia A, Cot M, Chippaux JP _et al_. Genetic control of blood infection levels in human malaria: evidence for a complex genetic model. _Am J Trop Med Hyg_ 1998; 58: 480–488. Article
CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Rihet P, Abel L, Traore Y, Traore-Leroux T, Aucan C, Fumoux F . Human malaria: segregation analysis of blood infection levels in a suburban area and a rural
area in Burkina Faso. _Genet Epidemiol_ 1998; 15: 435–450. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Jepson A, Sisay JF, Banya W _et al_. Genetic linkage of mild malaria to the major
histocompatibility complex in Gambian children: study of affected sibling pairs. _BMJ_ 1997; 315: 96–97. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Kun JF, Mordmuller B, Lell B,
Lehman LG, Luckner D, Kremsner PG . Polymorphism in promoter region of inducible nitric oxide synthase gene and protection against malaria. _Lancet_ 1998; 351: 265–266. Article CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Aucan C, Traore Y, Fumoux F, Rihet P . Familial correlation of immunoglobulin G subclass responses to _Plasmodium falciparum_ antigens in Burkina Faso. _Infect Immun_
2001; 69: 996–1001. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Migot-Nabias F, Mombo LE, Luty AJ _et al_. Human genetic factors related to susceptibility to mild malaria in
Gabon. _Gene Immun_ 2000; 1: 435–441. Article CAS Google Scholar * Sjoberg K, Lepers JP, Raharimalala L _et al_. Genetic regulation of human anti-malarial antibodies in twins. _Proc Natl
Acad Sci U S A_ 1992; 89: 2101–2104. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Stirnadel HA, Beck HP, Alpers MP, Smith TA . Genetic analysis of IgG subclass responses against
RESA and MSP2 of _Plasmodium falciparum_ in adults in Papua New Guinea. _Epidemiol Infect_ 2000; 124: 153–162. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Rihet P, Traore Y, Abel
L, Aucan C, Traore-Leroux T, Fumoux F . Malaria in humans: _Plasmodium falciparum_ blood infection levels are linked to chromosome 5q31–q33. _Am J Hum Genet_ 1998; 63: 498–450. Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Traore Y, Rihet P, Traore-Leroux T _et al_. Analysis of the genetic factors controlling malarial infection in man. _Sante_ 1999; 9: 53–59. CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Kruglyak L, Daly MJ, Reeve DM, Lander ES . Parametric and nonparametric linkage analysis: a unified multipoint approach. _Am J Hum Genet_ 1996; 58: 1347–1363. CAS PubMed PubMed
Central Google Scholar * Garcia A, Marquet S, Bucheton B _et al_. Linkage analysis of blood _Plasmodium falciparum_ levels: interest of the 5q31–q33 chromosome region. _Am J Trop Med Hyg_
1998; 58: 705–709. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Marquet S, Abel L, Hillaire D _et al_. Genetic localization of a locus controlling the intensity of infection by _Schistosoma
mansoni_ on chromosome 5q31–q33. _Nat Genet_ 1996; 14: 181–184. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Muller-Myhsok B, Stelma FF, Guisse-Sow F _et al_. Further evidence suggesting the
presence of a locus, on human chromosome 5q31–q33, influencing the intensity of infection with _Schistosoma mansoni_. _Am J Hum Genet_ 1997; 61: 452–454. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central
Google Scholar * Meyers DA, Postma DS, Panhuysen CI _et al_. Evidence for a locus regulating total serum IgE levels mapping to chromosome 5. _Genomics_ 1994; 23: 464–470. Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Xu J, Postma DS, Howard TD _et al_. Major genes regulating total serum immunoglobulin E levels in families with asthma. _Am J Hum Genet_ 2000; 67: 1163–1173.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Vignal A, Gyapay G, Hazan J _et al_. A non-radioactive multiplex procedure for genotyping of microsatellite markers. In: Adolph, K.
(ed). _Methods in Molecular Genetics 1: Gene and Chromosome Analysis_. Academic Press: San Diego, 1993, pp 211–221. Google Scholar * Dib C, Faure S, Fizames C _et al_. A comprehensive
genetic map of the human genome based on 5,264 microsatellites. _Nature_ 1996; 380: 152–154. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Pratt SC, Daly MJ, Kruglyak L . Exact multipoint
quantitative-trait linkage analysis in pedigrees by variance components. _Am J Hum Genet_ 2000; 66: 1153–1157. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Lathrop GM, Lalouel JM,
Julier C, Ott J . Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 1984; 81: 3443–3446. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Abecasis GR,
Cardon LR, Cookson WO . A general test of association for quantitative traits in nuclear families. _Am J Hum Genet_ 2000; 66: 279–292. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Download
references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This research was supported by the French Ministry of Research and Technology, the Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (France), the Conseil Régional Provence
Alpes Côte d'Azur (France), and the Conseil Général des Bouches du Rhône (France). BK and CA were, respectively, supported by studentships from the Agence Universitaire de la
Francophonie and the Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale. LF is supported by a studentship from the French Ministry of Research and Technology. AUTHOR INFORMATION Author notes * L Flori and
B Kumulungui: Both authors equally contributed to this work. AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Université de la Méditerranée, Marseille, France L Flori, C Aucan, C Esnault, F Fumoux & P Rihet
* Université de Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso B Kumulungui & A S Traoré Authors * L Flori View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * B Kumulungui
View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * C Aucan View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * C
Esnault View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * A S Traoré View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
* F Fumoux View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * P Rihet View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google
Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to P Rihet. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Flori, L., Kumulungui, B., Aucan, C. _et al._
Linkage and association between _Plasmodium falciparum_ blood infection levels and chromosome 5q31–q33. _Genes Immun_ 4, 265–268 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6363960 Download
citation * Published: 22 May 2003 * Issue Date: 01 June 2003 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6363960 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read
this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
KEYWORDS * _Plasmodium falciparum_ * malaria * parasitemia * genetic linkage * variance components * quantitative transmission/disequilibrium test
