- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
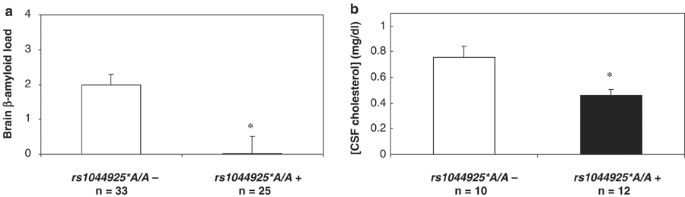
ABSTRACT A common polymorphism of the gene encoding acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase 1 (_SOAT1_), which is involved in the regulation of _β_-amyloid peptide generation, is
associated with low brain amyloid load (_P_=0.03) and with low cerebrospinal fluid levels of cholesterol (_P_=0.005). This polymorphism of _SOAT1_ is also associated with reduced risk for
Alzheimer's disease in ethnically distinct populations (_P_=0.0001, odds ratio: 0.6, 95% confidence interval 0.4–0.8). Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview
of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only
$21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during
checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS CHOLESTERYL ESTER
LEVELS ARE ELEVATED IN THE CAUDATE AND PUTAMEN OF HUNTINGTON’S DISEASE PATIENTS Article Open access 20 November 2020 ABNORMAL BRAIN CHOLESTEROL HOMEOSTASIS IN ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE—A TARGETED
METABOLOMIC AND TRANSCRIPTOMIC STUDY Article Open access 01 June 2021 CORTICAL THICKNESS IS DIFFERENTLY ASSOCIATED WITH ALDH2 RS671 POLYMORPHISM ACCORDING TO LEVEL OF AMYLOID DEPOSITION
Article Open access 30 September 2021 REFERENCES * Selkoe DJ . Alzheimer's disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. _Physiol Rev_ 2001; 81: 741–766. Article CAS Google Scholar * Simons
M, Keller P, De Strooper B, Beyreuther K, Dotti CG, Simons K . Cholesterol depletion inhibits the generation of beta-amyloid in hippocampal neurons. _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 1998; 95:
6460–6464. Article CAS Google Scholar * Fassbender K, Simons M, Bergmann C, Stroick M, Lutjohann D, Keller P _et al_. Simvastatin strongly reduces levels of Alzheimer's disease beta
-amyloid peptides Abeta 42 and Abeta 40 _in vitro_ and _in vivo_. _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 2001; 98: 5856–5861. Article CAS Google Scholar * Rudel LL, Lee RG, Cockman TL . Acyl coenzyme
A: cholesterol acyltransferase types 1 and 2: structure and function in atherosclerosis. _Curr Opin Lipidol_ 2001; 12: 121–127. Article CAS Google Scholar * Puglielli L, Konopka G,
Pack-Chung E, Ingano LA, Berezovska O, Hyman BT _et al_. Acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase modulates the generation of the amyloid beta-peptide. _Nat Cell Biol_ 2001; 3: 905–912.
Article CAS Google Scholar * Kehoe P, Wavrant-De Vrieze F, Crook R, Wu WS, Holmans P, Fenton I _et al_. A full genome scan for late ons_et al_zheimer's disease. _Hum Mol Genet_ 1999;
8: 237–245. Article CAS Google Scholar * Myers A, Wavrant De-Vrieze F, Holmans P, Hamshere M, Crook R, Compton D _et al_. Full genome screen for Alzheimer disease: Stage II analysis. _Am
J Med Genet_ 2002; 114: 235–244. Article Google Scholar * Sullivan PF, Eaves LJ, Kendler KS, Neale MC . Genetic case-control association studies in neuropsychiatry. _Arch Gen Psychiatry_
2001; 58: 1015–1024. Article CAS Google Scholar * McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM . Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the
NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. _Neurology_ 1984; 34: 939–944. Article CAS Google Scholar *
Thal DR, Rub U, Schultz C, Sassin I, Ghebremedhin E, Del Tredici K _et al_. Sequence of Abeta-protein deposition in the human medial temporal lobe. _J Neuropathol Exp Neurol_ 2000; 59:
733–748. Article CAS Google Scholar * Thal DR, Rüb U, Orantes M, Braak H . Phases of Aß-deposition in the human brain and its relevance for the development of AD. _Neurology_ 2002; 58:
1791–1800. Article Google Scholar * Braak H, Braak E Neuropathological staging of Alzheimer-related changes. _Acta Neuropathol_ 1991; 82: 239–259. * Dzeletovic S, Breuer O, Lund E,
Diczfalusy U . Determination of cholesterol oxidation products in human plasma by isotope dilution-mass spectrometry. _Anal Biochem_ 1995; 225: 73–80. Article CAS Google Scholar *
Demeester N, Castro G, Desrumaux C, De Geitere C, Fruchart JC, Santens P _et al_. Characterization and functional studies of lipoproteins, lipid transfer proteins, and lecithin: cholesterol
acyltransferase in CSF of normal individuals and patients with Alzheimer's disease. _J Lipid Res_ 2000; 41: 963–974. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Montine TJ, Montine KS, Swift LL .
Central nervous system lipoproteins in Alzheimer's disease. _Am J Pathol_ 1997; 151: 1571–1575. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Mulder M, Ravid R, Swaab DF, de Kloet ER,
Haasdijk ED, Julk J _et al_. Reduced levels of cholesterol, phospholipids, and fatty acids in cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer disease patients are not related to apolipoprotein E4.
_Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord_ 1998; 12: 198–203. Article CAS Google Scholar * Accad M, Smith SJ, Newland DL, Sanan DA, King Jr LE, Linton MF _et al_. Massive xanthomatosis and altered
composition of atherosclerotic lesions in hyperlipidemic mice lacking acyl CoA: cholesterol acyltransferase 1. _J Clin Invest_ 2000; 105: 711–719. Article CAS Google Scholar * Hixson JE,
Vernier DT . Restriction isotyping of human apolipoprotein E by gene amplification and cleavage with HhaI. _J Lipid Res_ 1990; 31: 545–548. CAS Google Scholar * Kokoris M, Dix K, Moynihan
K, Mathis J, Erwin B, Grass P _et al_. High-throughput SNP genotyping with the Masscode system. _Mol Diagn_ 2000; 5: 329–340. Article CAS Google Scholar * Terwilliger JD, Ott J . Linkage
disequilibrium between alleles at marker loci. In: Terwilliger JD and Ott J (eds). _Handbook of Human Genetic Linkage_. The Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, 1994, p. 189–198.
Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank Ms. Esmeralda Garcia, Ms Christin Wilde, Mrs Andrea Walther, and Ms Estelle Obrist for their patient care and sampling. The technical expertise
of Ms Anja Kerksiek is gratefully acknowledged. This work was supported in parts by grants of the Swiss Science National Foundation (32-65869.01) and the Roche Research Foundation (22-2001)
to AP, by the Bundesministerium für Bildung, Forschung, Wissenschaft und Technologie (01EC9402) to DL and KvB, by the National Center for Competence in Research (NCCR) ‘Neuronal Plasticity
and Repair’, and by the EU DIADEM program on Diagnosis of Dementia. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Division of Psychiatry Research, University of Zürich, Switzerland M A
Wollmer, J R Streffer, R M Nitsch, C Hock & A Papassotiropoulos * Third Department of Neurology, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece M Tsolaki * Department of Neuroscience,
Neuroimmunology Unit, IRCCS H. San Raffaele, Italy L M E Grimaldi * Department of Neuroscience, AUSL n.2, Caltanissetta, Italy L M E Grimaldi * Department of Clinical Pharmacology,
University of Bonn Medical Center, Germany D Lütjohann & K von Bergmann * Institute of Neuropathology, University of Bonn Medical Center, Germany D Thal Authors * M A Wollmer View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * J R Streffer View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * M Tsolaki View
author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * L M E Grimaldi View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * D
Lütjohann View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * D Thal View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar *
K von Bergmann View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * R M Nitsch View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google
Scholar * C Hock View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * A Papassotiropoulos View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to A Papassotiropoulos. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Wollmer, M.,
Streffer, J., Tsolaki, M. _et al._ Genetic association of acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase with cerebrospinal fluid cholesterol levels, brain amyloid load, and risk for
Alzheimer's disease. _Mol Psychiatry_ 8, 635–638 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001296 Download citation * Received: 26 June 2002 * Revised: 06 October 2002 * Accepted: 10
October 2002 * Published: 08 July 2003 * Issue Date: 01 June 2003 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001296 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to
read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing
initiative KEYWORDS * SNP * polymorphism * ACAT1 * SOAT1 * case–control study * dementia