- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT Human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) is the most frequent cause of dementia in adults under 40. We sought to use gene delivery to protect from HIV-1-related neuron loss. Because
HIV-1 envelope (Env) gp120 elicits oxidant stress and apoptosis in cultured neurons, we established reproducible parameters of Env-mediated neurotoxicity _in vivo_, then tested
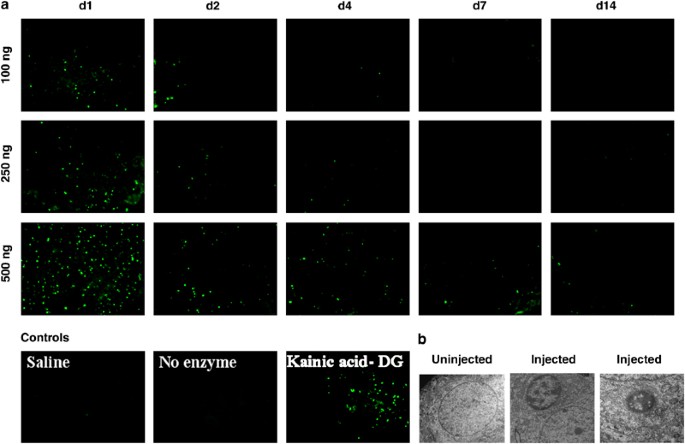
neuroprotection using gene delivery of antioxidant enzymes. We injected 100–500 ng μl−1gp120 stereotaxically into rat caudate–putamens (CP) and assayed brains for apoptosis by terminal
deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated biotinylated UTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) 6-h to 14-day post-injection. Peak apoptosis occurred 1 day after injection of 250 and 500 ng μl−1gp120.
TUNEL-positive cells mostly expressed neuronal markers (NeuroTrace), although some expressed CD68 and so were most likely microglial cells. Finally, we compared neuroprotection from
gp120-induced apoptosis provided by localized and generalized intra-central nervous system (CNS) gene delivery. Recombinant SV40 vectors carrying Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase (SOD1) or
glutathione peroxidase (GPx1) were injected into the CP, where gp120 was administered 4–24 weeks later. Alternatively, we inoculated the vector into the lateral ventricle (LV), with or
without prior intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration of mannitol. Intracerebral injection of SV(SOD1) or SV(GPx1) significantly protected neurons from gp120-induced apoptosis throughout the
24-week study. Intraventricular vector administration protected from gp120 neurotoxicity comparably, particularly if preceded by mannitol i.p. Thus, HIV-1 gp120 is neurotoxic _in vivo_, and
intracerebral or intra-ventricular administration of rSV40 vectors carrying antioxidant enzymes is neuroprotective. These findings suggest the potential utility of both localized and
widespread gene delivery in treating neuroAIDS and other CNS diseases characterized by excessive oxidative stress. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of
subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 6 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only
$43.17 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS CURCUMIN ENHANCES
ELVITEGRAVIR CONCENTRATION AND ALLEVIATES OXIDATIVE STRESS AND INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE Article Open access 14 November 2023 AAV VECTORS TRIGGER DNA DAMAGE RESPONSE-DEPENDENT PRO-INFLAMMATORY
SIGNALLING IN HUMAN IPSC-DERIVED CNS MODELS AND MOUSE BRAIN Article Open access 18 April 2025 ITACONATE PROTECTS FERROPTOTIC NEURONS BY ALKYLATING GPX4 POST STROKE Article 08 May 2024
REFERENCES * Mattson MP, Haughey NJ, Nath A . Cell death in HIV dementia. _Cell Death Diff_ 2005; 12: 893–904. Article CAS Google Scholar * Major EO, Rausch D, Marra C, Clifford D .
HIV-associated dementia. _Science_ 2000; 288: 440–442. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * McArthur JC, Hoover DR, Bacellar H, Miller EN, Cohen BA, Becker JT _et al_. Dementia in AIDS
patients: incidence and risk factors. Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study. _Neurology_ 1993; 43: 2245–2252. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Koutsilieri E, Sopper S, Scheller C, ter Meulen
V, Riederer P . Parkinsonism in HIV dementia. _J Neural Transm_ 2002; 109: 767–775. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Ellis RJ, Deutsch R, Heaton RK, Marcotte TD, McCutchan JA, Nelson
JA _et al_. Cognitive impairment is an independent risk factor for death in HIV infection. San Diego HIV Neurobehavioral Research Center Group. _Arch Neurol_ 1997; 54: 416–424. Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Ances BM, Ellis RJ . Dementia and neurocognitive disorders due to HIV-1 infection. _Semin Neurol_ 2007; 27: 86–92. Article PubMed Google Scholar * Nath A,
Sacktor N . Influence of highly active antiretroviral therapy on persistence of HIV in the central nervous system. _Curr Opin Neurol_ 2006; 19: 358–361. Article PubMed Google Scholar *
Ranki A, Nyberg M, Ovod V, Haltia M, Elovaara I, Raininko R _et al_. Abundant expression of HIV Nef and Rev proteins in brain astrocytes _in vivo_ is associated with dementia. _AIDS_ 1995;
9: 1001–1008. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * van de Bovenkamp M, Nottet HS, Pereira CF . Interactions of human immunodeficiency virus-1 proteins with neurons: possible role in the
development of human immunodeficiency virus-1 associated dementia. _Eur J Clin Invest_ 2002; 32: 619–627. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Cicala C, Arthos J, Rubbert A, Selig S,
Wildt K, Cohen OJ _et al_. HIV-1 envelope induces activation of caspase-3 and cleavage of focal adhesion kinase in primary human CD4(+) T cells. _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 2000; 97: 1178–1183.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Twu C, Liu NQ, Popik W, Bukrinsky M, Sayre J, Roberts J _et al_. Cardiomyocytes undergo apoptosis in human immunodeficiency virus
cardiomyopathy through mitochondrion- and death receptor-controlled pathways. _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 2002; 99: 14386–14391. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Garden
GA, Guo W, Jayadev S, Tun C, Balcaitis S, Choi J _et al_. HIV associated neurodegeneration requires p53 in neurons and microglia. _FASEB J_ 2004; 18: 1141–1143. Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Xu Y, Kulkosky J, Acheampong E, Nunnari G, Sullivan J, Pomerantz RJ . HIV-1-mediated apoptosis of neuronal cells: proximal molecular mechanisms of HIV-1-induced encephalopathy.
_Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 2004; 101: 7070–7075. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Meucci O, Fatatis A, Simen AA, Bushell TJ, Gray PW, Miller RJ . Chemokines regulate
hippocampal neuronal signaling and gp120 neurotoxicity. _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 1998; 95: 14500–14505. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Regulier EG, Reiss K, Khalili
K, Amini S, Zagury JF, Katsikis PD _et al_. T-cell and neuronal apoptosis in HIV infection: implications for therapeutic intervention. _Int Rev Immunol_ 2004; 23: 25–59. Article CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Kruman I, Nath A, Mattson MP . HIV-1 protein Tat induces apoptosis of hippocampal neurons by a mechanism involving caspase activation, calcium overload, and oxidative
stress. _Exp Neurol_ 1998; 154: 276–288. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kaul M, Lipton SA . Chemokines and activated macrophages in HIV gp120-induced neuronal apoptosis. _Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA_ 1999; 96: 8212–8216. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Lipton SA, Choi YB, Pan ZH, Lei SZ, Chen HS, Sucher NJ _et al_. A redox-based mechanism for the
neuroprotective and neurodestructive effects of nitric oxide and related nitroso-compounds. _Nature_ 1993; 364: 626–632. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Dreyer EB, Kaiser PK,
Offermann JT, Lipton SA . HIV-1 coat protein neurotoxicity prevented by calcium channel antagonists. _Science_ 1990; 248: 364–367. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lipton SA, Sucher
NJ, Kaiser PK, Dreyer EB . Synergistic effects of HIV coat protein and NMDA receptor-mediated neurotoxicity. _Neuron_ 1991; 7: 111–118. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Agrawal L,
Louboutin JP, Reyes BAS, van Bockstaele EJ, Strayer DS . Antioxidant enzyme gene delivery to protect from HIV-1 gp120-induced neuronal apoptosis. _Gene Therapy_ 2006; 13: 1645–1656. Article
CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Dexter DT, Carter CJ, Wells FR, Javoy-Agid F, Agid Y, Lees A _et al_. Basal lipid perxidation in substantia nigra is increased in Parkinson's disease.
_J Neurochem_ 1987; 52: 381–389. Article Google Scholar * Rosen DR, Siddique T, Patterson D, Figlewicz DA, Sapp P, Hentati A _et al_. Mutations in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase are associated
with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. _Nature_ 1993; 362: 59–62. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Beal MF . Aging, energy, and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases.
_Ann Neurol_ 1995; 38: 357–366. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Smith MA, Perry G . Free radical damage, iron, and Alzheimer's disease. _J Neurol Sci_ 1995; 134: 92–94. Article
PubMed Google Scholar * Smith MA, Sayre LM, Monnier VM, Perry G . Radical ageing in Alzheimer's disease. _Trends Neurosci_ 1995; 18: 172–176. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Cao W, Carney JM, Duchon A, Floyd RA, Chevion M . Oxygen free radicals involvement in ischemia and reperfusion of the brain injury to brain. _Neurosci Lett_ 1998; 88: 233–238. Article
Google Scholar * Montoliu C, Valles S, Renau-Piqueras J, Guerri C . Ethanol-induced oxygen radical formation and lipid peroxidation in rat brain: effect of chronic alcohol consumption. _J
Neurochem_ 1994; 63: 1855–1862. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Smith CD, Carney JM, Starke-Reed PE, Oliver CN, Stadtman ER, Floyd RA _et al_. Excess brain protein oxidation and
enzyme dysfunction in normal aging and in Alzheimer's disease. _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 1991; 88: 10540–10543. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Mollace V, Nottet
HS, Clayette P, Turco MC, Muscoli C, Salvemini D _et al_. Oxidative stress and neuroAIDS: triggers, modulators and novel antioxidants. _Trends Neurosci_ 2001; 24: 411–416. Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Turchan J, Pocernich CB, Gairola C, Chauhan A, Schifitto G, Butterfield DA _et al_. Oxidative stress in HIV demented patients and protection _ex vivo_ with novel
antioxidants. _Neurology_ 2003; 60: 307–314. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Agrawal L, Louboutin JP, Strayer DS . Preventing HIV-1 Tat-induced apoptosis using antioxidant enzymes:
mechanistic and therapeutic implications. _Virology_ 2007; 363: 462–472. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Cutler RG, Haughey NJ, Tammara A, McArthur JC, Nath A, Reid R _et al_.
Dysregulation of sphingolipids and sterol metabolism by ApoE4 in HIV dementia. _Neurology_ 2004; 63: 626–630. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kruman I, Bruce-Keller AJ, Bredesen D,
Waeg G, Mattson MP . Evidence that 4-hydroxynonenal mediates oxidative stress-induced neuronal apoptosis. _J Neurosci_ 1997; 17: 5089–5100. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google
Scholar * Bruce-Keller AJ, Li YJ, Lovell MA, Kraemer PJ, Gary DS, Brown RR _et al_. 4-Hydroxynonenal, a product of lipid peroxidation, damages cholinergic neurons and impairs visuospatial
memory in rats. _J Neuropathol Exp Neurol_ 1998; 57: 257–267. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Ridet JL, Bensadoun JC, Deglon N, Aebischer P, Zurn AD . Lentivirus-mediated expression
of glutathione peroxidase: neuroprotection in murine models of Parkinson's disease. _Neurobiol Dis_ 2006; 21: 29–34. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hoehn B, Yenari MA, Sapolsky
RM, Steinberg GK . Glutathione peroxidase overexpression inhibits cytochrome _c_ release and proapoptotic mediators to protect neurons from experimental stroke. _Stroke_ 2003; 34:
2489–2494. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Watanabe Y, Chu Y, Andresen JJ, Nakane H, Faraci FM, Heistad DD . Gene transfer of extracellular superoxide dismutase reduces cerebral
vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. _Stroke_ 2003; 34: 434–440. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Betz AL, Shakui P, Davidson BL . Gene transfer to rodent brain with recombinant
adenoviral vectors: effects of infusion parameters, infectious titer, and virus concentration on transduction volume. _Exp Neurol_ 1998; 150: 136–142. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Cao H, Koehler DR, Hu J . Adenoviral vectors for gene replacement therapy. _Viral Immunol_ 2004; 17: 327–333. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kaplitt MG, Leone P, Samulski RJ, Xiao
X, Pfaff DW, O'Malley KL _et al_. Long-term gene expression and phenotypic correction using adeno-associated virus vectors in the mammalian brain. _Nat Genet_ 1994; 8: 148–154. Article
CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Davidson BL, Stein CS, Heth JA, Martins I, Kotin RM, Derksen TA _et al_. Recombinant adeno-associated virus type 2, 4, and 5 vectors: transduction of variant
cell types and regions in the mammalian central nervous system. _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 2000; 97: 3428–3432. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Fu H, Muenzer J,
Samulski RJ, Breese G, Sifford J, Zeng X _et al_. Self-complementary adeno-associated virus serotype 2 vector: global distribution and broad dispersion of AAV-mediated transgene expression
in mouse brain. _Mol Ther_ 2003; 6: 911–917. Article Google Scholar * Burger C, Gorbatyuk OS, Velardo MJ, Peden CS, Williams P, Zolotukhin S _et al_. Recombinant AAV viral vectors
pesudotyped with viral capsids from serotypes 1, 2, and 5 display differential efficiency and cell tropism after delivery to different regions of the central nervous system. _Mol Ther_ 2004;
10: 302–317. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Naldini L, Blomer U, Gage FH, Trono D, Verma IM . Efficient transfer, integration, and sustained long-term expression of the transgene
in adult rat brains injected with a lentiviral vector. _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 1996; 93: 11382–11388. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Blomer U, Naldini L, Kafri T,
Trono D, Verma IM, Gage FH . Highly efficient and sustained gene transfer in adult neurons with a lentivirus vector. _J Virol_ 1997; 71: 6641–6649. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google
Scholar * Strayer DS, Milano J . SV40 mediates stable gene transfer _in vivo_. _Gene Therapy_ 1996; 3: 581–587. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Sauter BV, Parashar B, Chowdhury NR, Kadakol
A, Ilan Y, Singh H _et al_. A replication-deficient rSV40 mediates liver-directed gene transfer and a long-term amelioration of jaundice in gunn rats. _Gastroenterology_ 2000; 119:
1348–1357. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Duan YY, Wu J, Zhu JL, Liu SL, Ozaki I, Strayer DS _et al_. Gene therapy for human alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency in an animal model using
SV40-derived vectors. _Gastroenterology_ 2004; 127: 1222–1232. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Mandel RJ, Rendahl KG, Spratt SK, Snyder RO, Cohen LK, Leff SE . Characterization of
intrastriatal recombinant adeno-associated virus-mediated gene transfer of human tyrosine hydroxylase and human GTP-cyclohydrolase I in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. _J Neurosci_
1998; 18: 4271–4284. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Louboutin JP, Reyes BAS, Agrawal L, van Bockstaele EJ, Strayer DS . Strategies for CNS-directed gene delivery:
_in vivo_ gene transfer to the brain using SV40-derived vectors. _Gene Therapy_ 2007; 14: 939–949. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Cordelier P, Van Bockstaele E, Calarota SA, Strayer
DS . Inhibiting AIDS in the central nervous system: gene delivery to protect neurons from HIV. _Mol Ther_ 2003; 7: 801–810. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Cordelier P, Morse B,
Strayer DS . Targeting CCR5 with siRNAs: using recombinant SV40-derived vectors to protect macrophages and microglia from R5-tropic HIV. _Oligonucleotides_ 2003; 13: 281–294. Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Anderson DW, Cordelier P, Strayer DS, Schneider JS . Viral gene delivery of GAD antisense genes to basal ganglia output neurons promoters behavioral recovery in a
rat Parkinson model. _Movement Dis_ 2002; 17: S58. Article Google Scholar * Ghodsi A, Stein C, Derksen T, Martins I, Anderson RD, Davidson BL . Systemic hyperosmolarity improves
beta-glucuronidase distribution and pathology in murine MPS VII brain following intraventricular gene transfer. _Exp Neurol_ 1999; 160: 109–116. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Mastakov MY, Baer K, Xu R, Fitzsimons H, During MJ . Combined injection of rAAV with mannitol enhances gene expression in the rat brain. _Mol Ther_ 2001; 3: 225–232. Article CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Bourgoin C, Emiliani C, Kremer EJ, Gelot A, Tancini B, Gravel RA _et al_. Widespread distribution of beta-hexosaminidase activity in the brain of a Sandhoff mouse model
after coinjection of adenoviral vector and mannitol. _Gene Therapy_ 2003; 10: 1841–1849. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Burger C, Nguyen FN, Deng J, Mandel RJ . Systemic
mannitol-induced hyperosmolarity amplifies rAAV2-mediated striatal transduction to a greater extent than local co-infusion. _Mol Ther_ 2005; 11: 327–331. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
* Doran SE, Ren XD, Betz AL, Pagel MA, Neuwelt EA, Roessler BJ _et al_. Gene expression from recombinant viral vectors in the central nervous system after blood–brain barrier disruption.
_Neurosurgery_ 1995; 36: 965–970. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * McKee HJ, Strayer DS . Immune responses against SIV envelope glycoprotein, using recombinant SV40 as a vaccine
delivery vector. _Vaccine_ 2002; 20: 3613–3625. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Solbrig MV, Koob GF, Parsons LH, Kadota T, Horscroft N, Briese T _et al_. Neurotrophic factor
expression after CNS viral injury produces enhanced sensitivity to psychostimulants: potential mechanisms for addiction vulnerability. _J Neurosci_ 2000; 20: RC104 (1–6). * Strayer DS . Gene
therapy using SV40-derived vectors: what does the future hold? _J Cell Physiol_ 1999; 181: 375–384. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Strayer DS, Kondo R, Milano J, Duan LX . Use of
SV40-based vectors to transduce foreign genes to normal human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. _Gene Therapy_ 1997; 4: 219–225. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Strayer DS, Lamothe
M, Wei D, Milano J, Kondo R . Generation of recombinant SV40 vectors for gene transfer. SV40 protocols. In: Raptis L (ed). _Methods in Molecular Biology_, vol. 165. Humana Press: Totowa,
NJ, USA, 2001, pp 103–117. Google Scholar * Strayer DS, Mitchell C, Geverd D, Nichols CN . Papoviruses SV40. In: Friedmann T, Rossi JR (eds). _DNA Delivery/Gene Transfer Manual_. Cold
Spring Harbor Press: New York, 2007, pp 273–287. Google Scholar * Paxinos G, Watson C . _The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates_, 2nd edn. Academic Press: New York, 1986. Google Scholar
* Rouger K, Louboutin JP, Villanova M, Cherel Y, Fardeau M . X-linked vacuolated myopathy: TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma expression in muscle fibers with MHC class I on sarcolemma. _Am J Pathol_
2001; 158: 355–359. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank Mr David Knowlton for technical assistance. We are also grateful to Dr
Pierre Cordelier for important scientific discussions, suggestions and advice. This work was supported by NIH Grants MH69122, MH70287 and AI48244. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND
AFFILIATIONS * Department of Pathology, Anatomy and Cell Biology, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA, USA J-P Louboutin, L Agrawal & D S Strayer * Department of Neurosurgery,
Farber Institute for Neurosciences, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA, USA B A S Reyes & E J Van Bockstaele Authors * J-P Louboutin View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * L Agrawal View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * B A S Reyes View author publications You can
also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * E J Van Bockstaele View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * D S Strayer View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to J-P Louboutin. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS
ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Louboutin, JP., Agrawal, L., Reyes, B. _et al._ Protecting neurons from HIV-1 gp120-induced oxidant stress using both localized intracerebral and generalized
intraventricular administration of antioxidant enzymes delivered by SV40-derived vectors. _Gene Ther_ 14, 1650–1661 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3303030 Download citation *
Received: 16 April 2007 * Revised: 23 July 2007 * Accepted: 23 July 2007 * Published: 04 October 2007 * Issue Date: December 2007 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3303030 SHARE THIS
ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS * Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase * glutathione peroxidase * neuroAIDS