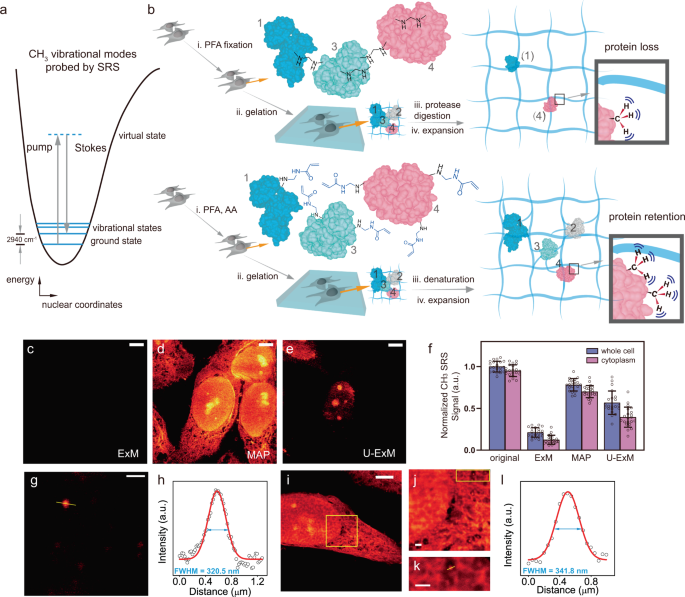
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT AN important aspect of the stomatal mechanism in green plants is the transport of solutes into and out of guard cells in response to stimuli such as illumination1. The effect of
abscisic acid (ABA) in causing stomata to close has been ascribed to ABA-promoted solute leakage from guard cells2. The experiments reported here show that leakage alone is insufficient to
explain stomatal closure caused by ABA. The involvement of live epidermal cells, acting as recipients of solutes from guard cells, is necessary, as Penny and Bowling have suggested,
especially when considering intact leaves3. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access
through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 51 print issues and online access $199.00 per year only $3.90 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink *
Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional
subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS ABA SIGNALLING AND METABOLISM ARE NOT ESSENTIAL FOR DARK-INDUCED STOMATAL CLOSURE BUT AFFECT
RESPONSE SPEED Article Open access 11 March 2021 HYDROGEN PEROXIDE IS REQUIRED FOR LIGHT-INDUCED STOMATAL OPENING ACROSS DIFFERENT PLANT SPECIES Article Open access 14 June 2024 LIGHT
PREVENTS PATHOGEN-INDUCED AQUEOUS MICROENVIRONMENTS VIA POTENTIATION OF SALICYLIC ACID SIGNALING Article Open access 09 February 2023 REFERENCES * Zeiger, E., Moody, W., Hepler, P. &
Varela, F. _Nature_ 270, 270–271 (1977). Article ADS Google Scholar * Dittrich, P. & Raschke, K. _Planta_ 134, 77–81 (1977). Article CAS Google Scholar * Penny, M. G. &
Bowling, D. J. F. _Planta_ 119, 17–25 (1974). Article CAS Google Scholar * Itai, C., Weyers, J. D. B., Hillman, J. R., Meidner, H. & Willmer, C. _Nature_ 271, 652–653 (1978). Article
ADS CAS Google Scholar * Glinka, Z. _Physiol. Pl._ 24, 476–479 (1971). Article Google Scholar * Edwards, M., Meidner, H. & Sheriff, D. W. _J. exp. Bot._ 27, 163–171 (1976).
Article Google Scholar * Squire, G. R. & Mansfield, T. A. _New Phytol._ 71, 1033–1043 (1972). Article Google Scholar Download references AUTHOR INFORMATION Author notes * C. ITAI
Present address: Department of Biology, Ben Gurion, University of the Negev, Israel AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Biology, University of Stirling, UK C. ITAI & HANS MEIDNER
Authors * C. ITAI View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * HANS MEIDNER View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed
Google Scholar RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE ITAI, C., MEIDNER, H. Effect of abscisic acid on solute transport in epidermal tissue.
_Nature_ 271, 653–654 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1038/271653a0 Download citation * Received: 16 September 1977 * Accepted: 19 December 1977 * Issue Date: 16 February 1978 * DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1038/271653a0 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently
available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative