- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
Access through your institution Buy or subscribe Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with MLL gene rearrangements (MLLmut) is often associated with M5 or M4 FAB subtypes, is frequent in infants and
in patients with secondary leukemia following treatment with DNA topoisomerase-II inhibitors.1 MLLmut are predictive of a poor clinical outcome in AML, even if the outcome of patients with
t(9;11) is more favorable than that with other MLLmut. The MLL gene (11q23) is involved in about 60 different translocations and about 30 partner genes have been identified. The most common
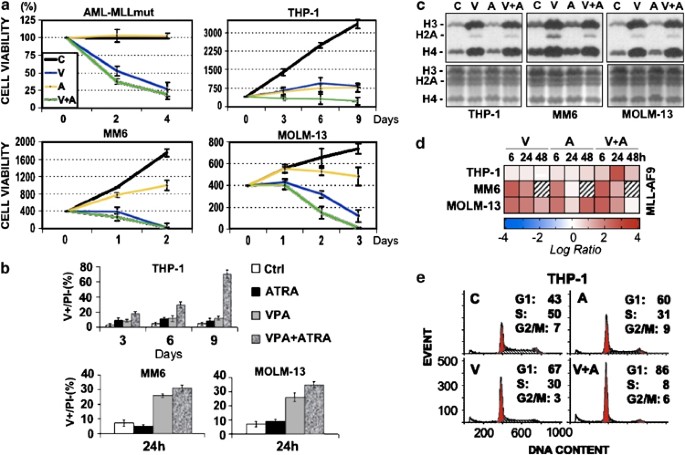
translocation in AML is t(9;11)(p22;q23) giving rise to MLL-AF9.1 The HDAC inhibitor (HDACi) valproic acid (VPA) induces tumor-selective apoptosis through activation of the death receptor
pathway AML with PML-RAR-alpha or AML1-ETO.2 This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices
may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support
REFERENCES * Daser A, Rabbitts TH . The versatile mixed leukaemia gene MLL and its many associations in leukaemogenesis. _Semin Cancer Biol_ 2005; 15: 175–188. Article CAS Google Scholar
* Insinga A, Monestiroli S, Ronzoni S, Gelmetti V, Marchesi F, Viale A _et al_. Inhibitors of histone deacetylases induce tumor-selective apoptosis through activation of the death receptor
pathway. _Nat Med_ 2005; 11: 71–76. Article CAS Google Scholar * Bennin DA, Don AS, Brake T, McKenzie JL, Rosenbaum H, Ortiz L _et al_. Cyclin G2 associates with protein phosphatase 2A
catalytic and regulatory B′ subunits in active complexes and induces nuclear aberrations and a G1/S phase cell cycle arrest. _J Biol Chem_ 2002; 277: 27449–27467. Article CAS Google
Scholar * Trus MR, Yang L, Suarez Saiz F, Bordeleau L, Jurisica I, Minden MD . The histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid alters sensitivity towards all trans retinoic acid in acute
myeloblastic leukemia cells. _Leukemia_ 2005; 19: 1161–1168. Article CAS Google Scholar * Kawagoe H, Kawagoe R, Sano K . Targeted down-regulation of MLL-AF9 with antisense
oligodeoxyribonucleotide reduces the expression of the HOXA7 and -A10 genes and induces apoptosis in a human leukemia cell line, THP-1. _Leukemia_ 2001; 15: 1743–1749. Article CAS Google
Scholar * Pession A, Martino V, Tonelli R, Beltramini C, Locatelli F, Biserni G _et al_. MLL-AF9 oncogene expression affects cell growth but not terminal differentiation and is
downregulated during monocyte-macrophage maturation in AML-M5 THP-1 cells. _Oncogene_ 2003; 22: 8671–8676. Article CAS Google Scholar * Akashi M, Osawa Y, Koeffler HP, Hachiya M . p21WAF1
expression by an activator of protein kinase C is regulated mainly at the post-transcriptional level in cells lacking p53: important role of RNA stabilization. _Biochem J_ 1999; 337 (Part
3): 607–616. Article CAS Google Scholar * Wiederschain D, Kawai H, Shilatifard A, Yuan ZM . Multiple MLL fusion proteins suppress p53-mediated response to DNA damage. _J Biol Chem_ 2005;
280: 24315–24321. Article CAS Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This work was supported by grants from AIRC (to AP and regional grant), MURST/FISR, and by the University
of Bologna. RS, RF and MF were supported by AGEOP. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Pediatrics, University of Bologna, Bologna, Italy R Tonelli, R Sartini, R
Fronza, F Freccero, M Franzoni & A Pession * Department of Physics, University of Bologna, Bologna, Italy D Dongiovanni & R Campanini * Department of Experimental Oncology, European
Institute of Oncology, Milan, Italy M Ballarini & S Minucci * Division of Medical Genetics, S. Orsola Hospital, Bologna, Italy S Ferrari * Servizio di Genetica Medica, IRCCS-Ospedale
CSS, San Giovanni Rotondo, Italy M D'apolito * Biotech Biotechnologies Laboratory s.r.l., Parma, Italy G Di Cola * Department of Biochemistry, University of Bologna, Bologna, Italy G
Capranico & A Khobta * Department of Pediatrics, University of Modena, Modena, Italy P Paolucci * Department of Biomolecular Sciences and Biotechnology, University of Milan, Milan, Italy
S Minucci Authors * R Tonelli View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * R Sartini View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * R Fronza View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * F Freccero View author publications You can also search for this
author inPubMed Google Scholar * M Franzoni View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * D Dongiovanni View author publications You can also search
for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * M Ballarini View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * S Ferrari View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * M D'apolito View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * G Di Cola View author publications
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * G Capranico View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * A Khobta View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * R Campanini View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * P Paolucci View
author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * S Minucci View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * A Pession
View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to A Pession. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION Supplementary Information
accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website (http://www.nature.com/leu) SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (XLS 2232 KB) SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (XLS 337 KB)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (XLS 187 KB) SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL (DOC 982 KB) RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Tonelli, R., Sartini, R.,
Fronza, R. _et al._ G1 cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis by histone deacetylase inhibition in MLL-AF9 acute myeloid leukemia cells is p21 dependent and MLL-AF9 independent. _Leukemia_ 20,
1307–1310 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404221 Download citation * Published: 13 April 2006 * Issue Date: 01 July 2006 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404221 SHARE THIS
ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative