- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT PTK787/ZK 222584 (PTK/ZK) is an oral angiogenesis inhibitor targeting vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor tyrosine kinases, including VEGFR-1/Flt-1, VEGFR-2/KDR,
VEGFR-3/Flt-4, the platelet-derived growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase and the c-kit protein tyrosine kinase. The objective of this Phase I study was to evaluate the safety,
tolerability, biologic activity and pharmacologic profile of PTK/ZK administered orally, twice daily, on a continuous dosing schedule in patients with primary refractory or relapsed acute
myeloid leukemia (AML), secondary AML, poor-prognosis _de novo_ AML or advanced myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). Acute myeloid leukemia patients for whom PTK/ZK monotherapy was ineffective
could receive PTK/ZK combined with standard induction chemotherapy. Sixty-three patients received PTK/ZK at doses of 500–1000 mg orally b.i.d. Safety and pharmacokinetic data were collected.
Responses were evaluated according to standard bone marrow and peripheral blood criteria. At 1000 mg b.i.d., dose-limiting toxicities of lethargy, hypertension, nausea, emesis and anorexia
were observed. Other adverse events related to PTK/ZK were dizziness, weakness, fatigue, diarrhea and pruritus; these were generally mild and reversible. Pharmacokinetic data showed that
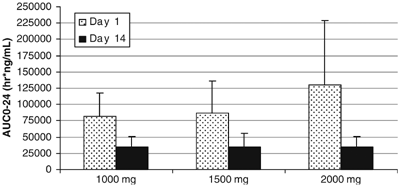
steady state was reached by day 14, there was no accumulation with repeat dosing and there was no significant increase in exposure at steady state beyond the maximum tolerated dose (MTD).
Complete remission was observed in five of 17 AML patients treated with PTK/ZK combined with chemotherapy.In conclusion, the MTD of PTK/ZK is 750 mg orally b.i.d. The drug is generally well
tolerated and can be given in combination with chemotherapy for patients with MDS and AML. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access
via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy
this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: *
Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS FIRST-IN-HUMAN, DOSE-ESCALATION, PHASE 1 STUDY OF
ANTI-ANGIOPOIETIN-2 LY3127804 AS MONOTHERAPY AND IN COMBINATION WITH RAMUCIRUMAB IN PATIENTS WITH ADVANCED SOLID TUMOURS Article Open access 03 August 2020 ENDOGLIN INHIBITOR TRC105 WITH OR
WITHOUT BEVACIZUMAB FOR BEVACIZUMAB-REFRACTORY GLIOBLASTOMA (ENDOT): A MULTICENTER PHASE II TRIAL Article Open access 08 September 2023 PHASE 1 DOSE-ESCALATION STUDY EVALUATING THE SAFETY,
PHARMACOKINETICS, AND CLINICAL ACTIVITY OF OBI-3424 IN PATIENTS WITH ADVANCED OR METASTATIC SOLID TUMORS Article Open access 12 May 2023 REFERENCES * Folkman J . Angiogenesis in cancer,
vascular, rheumatoid and other diseases. _Nat Med_ 1995; 1: 27–31. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Weinstat-Saslow D, Steeg PS . Angiogenesis and colonization in the tumor metastatic process:
basic and applied advances. _FASEB J_ 1994; 8: 401–407. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Liotta LA, Steep PS, Stetler-Stevenson WG . Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: an imbalance
of negative and positive regulation. _Cell_ 1991; 64: 327–336. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Padro T, Ruiz S, Bieker R, Burger H, Steins M, Kienast J _et al_. Increased
angiogenesis in the bone marrow of patients with acute myeloid leukemia. _Blood_ 2000; 96: 2637–2644. Google Scholar * Hussong JW, Rodgers GM, Shami PJ . Evidence of increased angiogenesis
in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. _Blood_ 2000; 95: 309–313. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Aguayo A, Kantarjian H, Manshouri T, Gidel C, Estey E, Thomas D _et al_. Angiogenesis in
acute and chronic leukemias and myelodysplastic syndromes. _Blood_ 2000; 96: 2240–2245. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * De Bont ED, Rosati S, Jacobs S, Kamps WA, Vellenga E . Increased bone
marrow vascularization in patients with acute myeloid leukemia: a possible role for vascular endothelial growth factor. _Br J Haematol_ 2001; 113: 296–304. Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Dvorak HF, Detmar M, Clafey KP . Vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) – an important mediator of angiogenesis in malignancy and inflammation. _Int
Arch Allergy Immunol_ 1995; 107: 233–235. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Ferrara N . The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in pathological angiogenesis. _Breast Cancer Res
Treat_ 1995; 36: 127–137. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Zhang HT, Craft P, Scott PAE . Enhancement of tumor growth and vascular density by transfection of vascular endothelial cell
growth factor in MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cells. _J Nat Cancer Inst_ 1995; 87: 213–219. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Shalaby F, Rossant J, Yamaguchi TP, Gertsenstein M, Wu
XF, Breitman ML _et al_. Failure of blood-island formation and vasculogenesis in FLK-1 deficient mice. _Nature_ 1995; 376: 62–66. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Carmeliet P,
Ferreira V, Breier G, Pollefeyt S, Kieckens L, Gertsenstein M _et al_. Abnormal blood vessel development and lethality in embryos lacking a single VEGF allele. _Nature_ 1996; 380: 435–439.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Bellamy WT, Richter L, Frutiger Y, Grogan TM . Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in hematopoietic malignancies.
_Cancer Res_ 1999; 59: 728–733. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Pruneri G, Bertolini F, Soligo D, Carboni N, Cortelezzi A, Ferrucci PF _et al_. Angiogenesis in myelodysplastic syndromes. _Br
J Cancer_ 1999; 81: 1398–1401. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Fiedler W, Graeven U, Ergun S, Verago S, Kilic N, Stockschlader M _et al_. Vascular endothelial growth
factor, a possible paracrine growth factor in human acute myeloid leukemia. _Blood_ 1997; 89: 1870–1875. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Bellamy WT, Richter L, Sirjani D, Roxas C,
Glinsmann-Gibson B, Frutiger Y _et al_. Vascular endothelial cell growth factor is an autocrine promoter of abnormal localized immature myeloid precursors and leukemia progenitor formation
in myelodysplastic syndromes. _Blood_ 2001; 97: 1427–1434. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Dias S, Hattori K, Zhu Z, Heissig B, Choy M, Lane W _et al_. Autocrine stimulation of
VEGFR-2 activates human leukemic cell growth and migration. _J Clin Invest_ 2000; 106: 511–521. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Dias S, Hattori K, Heissig B, Zhu Z,
Wu Y, Witte L _et al_. Inhibition of both paracrine and autocrine VEGF/VEGFR-2 signaling pathways is essential to induce long-term remission of xenotransplanted human leukemias. _Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA_ 2001; 98: 10857–10862. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Aguayo A, Estey E, Kantarjian H, Mansouri T, Gidel C, Keating M _et al_. Cellular vascular
endothelial growth factor is a predictor of outcome in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. _Blood_ 1999; 94: 3717–3721. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Wood JM, Bold G, Buchdunger E, Cozens
R, Ferrari S, Frei J _et al_. PTK787/ZK 222584, a novel and potent inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases, impairs vascular endothelial growth
factor-induced responses and tumor growth after oral administration. _Cancer Res_ 2000; 60: 2178–2189. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Drevs J, Muller-Driver R, Wittig C, Fuxius S, Esser N,
Hugenschmidt H _et al_. PTK787/ZK 222584, a specific vascular endothelial growth factor-receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, affects the anatomy of the tumor vascular bed and the functional
vascular properties as detected by dynamic enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. _Cancer Res_ 2002; 92: 4015–4122. Google Scholar * Morgan B, Thomas AL, Devs J, Hennig J, Buchert M, Jivan A
_et al_. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging as a biomarker for the pharmacological response of PTK787/ZK 222584, an inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor
tyrosine kinases, in patients with advanced colorectal cancer and liver metastases: results from two phase I studies. _J Clin Oncol_ 2003; 21: 3955–3964. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
* Cheson BD, Bennett JM, Kantarjian H, Pinto A, Schiffer CA, Nimer SD _et al_. Report of the international working group to standardize response criteria for myelodysplastic syndromes.
_Blood_ 2000; 96: 3671–3674. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Thomas AL, Morgan B, Horsfield MA, Higginson A, Kay A, Lee L _et al_. Phase I study of the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics,
and pharmacodynamics of PTK787/ZK 222584 administered twice daily in patients with advanced cancer. _J Clin Oncol_ 2005; 23: 4162–4171. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Gasparini G,
Longo R, Fanelli M, Teicher BA . Combination of antiangiogenic therapy with other anticancer therapies: results, challenges and open questions. _J Clin Oncol_ 2005; 23: 1295–1311. Article
CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Mesters RM, Padro T, Bieker R, Steins M, Kreuter M, Goner M . Stable remission after administration of the receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor SU5416 in a
patient with refractory acute myeloid leukemia. _Blood_ 2001; 98: 241–243. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Karp JE, Gojo I, Pili R, Gocke CD, Greer J, Guo C . Targeting vascular
endothelial growth factor for relapsed and refractory adult acute myelogenous leukemias: therapy with sequential 1-beta-d-arabinofuranosylcytosine, mitoxantrone, and bevacizumab. _Clin
Cancer Res_ 2004; 10: 3577–3585. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Download references AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Leukemia Program, Weill Medical College of Cornell
University/The New York Presbyterian Hospital, New York, NY, USA G J Roboz, R Carlin, M W Schuster & E J Feldman * MD Anderson Cancer Center, The University of Texas, Houston, TX, USA F
J Giles & J E Cortes * Arizona Cancer Center, Tucson, AZ, USA A F List * Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp., East Hanover, NJ, USA M Kowalski, S Bilic, E Masson & M Rosamilia * Schering
AG, Berlin, Germany D Laurent Authors * G J Roboz View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * F J Giles View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * A F List View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * J E Cortes View author publications You can
also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * R Carlin View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * M Kowalski View author publications You
can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * S Bilic View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * E Masson View author publications You
can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * M Rosamilia View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * M W Schuster View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * D Laurent View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * E J Feldman View
author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to G J Roboz. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS
ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Roboz, G., Giles, F., List, A. _et al._ Phase 1 study of PTK787/ZK 222584, a small molecule tyrosine kinase receptor inhibitor, for the treatment of acute myeloid
leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. _Leukemia_ 20, 952–957 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404213 Download citation * Received: 15 November 2005 * Revised: 24 January 2006 *
Accepted: 02 February 2006 * Published: 13 April 2006 * Issue Date: 01 June 2006 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404213 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with
will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt
content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS * myelodysplastic syndrome * VEGF







