- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
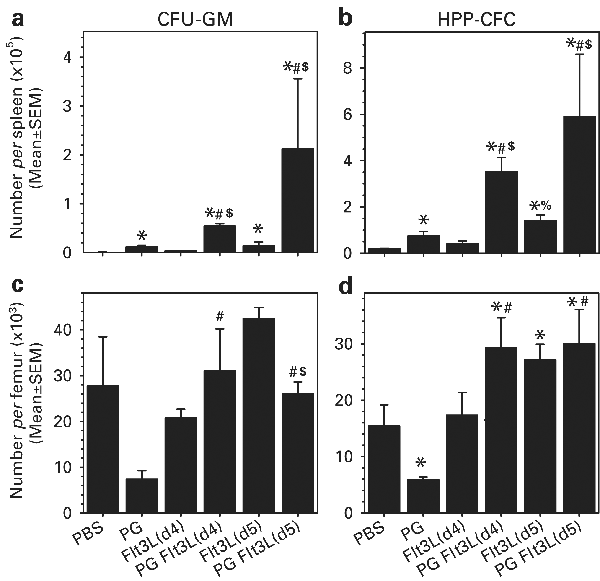
SUMMARY: Fms-like tyrosine kinase (Flt3L) is a potent stimulator of hematopoietic progenitor cell (HPC) expansion and mobilization; however, this requires 7–10 days of administration. We
investigated whether sustained delivery of Flt3L using a poloxamer-based matrix (PG) could accelerate and/or improve the hematopoietic activity of Flt3L in mice. A single injection of
PG-Flt3L stimulated significantly more rapid and greater HPC mobilization to the spleen and peripheral blood than the daily injection of Flt3L formulated in saline. Pharmacokinetic analysis
demonstrated that the formulation of Flt3L in PG prolonged its elimination (_Tβ_) half-life (2.3-fold) and increased its bioavailability (>two fold) and the time to maximum serum
concentration (_T_max) (2.7-fold). Further, coadministration of G-CSF and PG-Flt3L allowed lower doses of Flt3L to be active, with significantly greater hematopoietic and mobilization
activity, compared to the same total dose of G-CSF, Flt3L or G-CSF and Flt3L formulated in saline. These data demonstrate that formulation of Flt3L in PG significantly accelerates and
increases HPC expansion and mobilization. The observation of increased bioactivity by PG-Flt3L in rodents suggests the potential for improved clinical efficacy of Flt3L by reducing the time
required for HPC mobilization. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your
institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access
to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read
our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS LIPID NANOPARTICLE-MEDIATED MRNA DELIVERY TO CD34+ CELLS IN RHESUS MONKEYS Article 22 November 2024 A BISPECIFIC
NANOSYSTEM ACTIVATES ENDOGENOUS NATURAL KILLER CELLS IN THE BONE MARROW FOR HAEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES THERAPY Article 23 July 2024 EXTENSION OF HUMAN GCSF SERUM HALF-LIFE BY THE FUSION OF
ALBUMIN BINDING DOMAIN Article Open access 13 January 2022 REFERENCES * Brasel K, McKenna HJ, Morrissey P et al. Hematologic effects of Flt3 ligand _in vivo_ in mice. _Blood_ 1996; 88:
2004–2012. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Robinson S, Mosley RL, Parajuli P et al. Comparison of the hematopoietic activity of Flt-3 ligand and granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating
factor acting alone or in combination. _J Hematother Stem Cell Res_ 2000; 9: 711–720. Article CAS Google Scholar * Moghimi SM, Hunter AC . Poloxamers and poloxamines in nanoparticle
engineering and experimental medicine. _Trends Biotechnol_ 2000; 18: 412–420. Article CAS Google Scholar * Morikawa K, Okada F, Hosokawa M, Kobayashi H . Enhancement of therapeutic
effects of recombinant interleukin 2 on a transplantable rat fibrosarcoma by the use of a sustained release vehicle, Pluronic Gel. _Cancer Res_ 1987; 47: 37–41. CAS PubMed Google Scholar
* Johnston TP, Miller SC . Inulin disposition following intramuscular administration of an inulin/Poloxamer gel matrix. _J Parenter Sci Technol_ 1989; 43: 279–286. CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Johnston TP, Punjabi MA, Froelich CJ . Sustained delivery of interleukin-2 from a Poloxamer 407 gel matrix following intraperitoneal injection in mice. _Pharm Res_ 1992; 9:
425–434. Article CAS Google Scholar * Pec EA, Wout ZG, Johnston TP . Biological activity of urease formulated in Poloxamer 407 after intraperitoneal injection in the rat. _J Pharm Sci_
1992; 81: 626–630. Article CAS Google Scholar * Lu GW, Jun HW, Dzimianski MT et al. Pharmacokinetic studies of methotrexate in plasma and synovial fluid following i.v. bolus and topical
routes of administration in dogs. _Pharm Res_ 1995; 12: 1474–1477. Article CAS Google Scholar * Paavola A, Yliruusi J, Kajimoto Y et al. Controlled release of lidocaine from injectable
gels and efficacy in rat sciatic nerve block. _Pharm Res_ 1995; 12: 1997–2002. Article CAS Google Scholar * Paavola A, Yliruusi J, Rosenberg P . Controlled release and dura mater
permeability of lidocaine and ibuprofen from injectable Poloxamer-based gels. _J Control Release_ 1998; 52: 169–178. Article CAS Google Scholar * Paavola A, Tarkkila P, Xu M et al.
Controlled release gel of ibuprofen and lidocaine in epidural use–analgesia and systemic absorption in pigs. _Pharm Res_ 1998; 15: 482–487. Article CAS Google Scholar * Veyries ML,
Couarraze G, Geiger S et al. Controlled release of vancomycin from Poloxamer 407 gels. _Int J Pharm_ 1999; 192: 183–193. Article CAS Google Scholar * Barichello JM, Morishita M, Takayama
K, Nagai T . Absorption of insuzlin from Pluronic F-127 gels following subcutaneous administration in rats. _Int J Pharm_ 1999; 184:189–198. Article CAS Google Scholar * Barichello JM,
Morishita M, Takayama K et al. Enhanced rectal absorption of insulin-loaded Pluronic F-127 gels containing unsaturated fatty acids. _Int J Pharm_ 1999; 183: 125–132. Article CAS Google
Scholar * Ryu JM, Chung SJ, Lee MH et al. Increased bioavailability of propranolol in rats by retaining thermally gelling liquid suppositories in the rectum. _J Control Release_ 1999; 59:
163–172. Article CAS Google Scholar * Paavola A, Kilpelainen I, Yliruusi J, Rosenberg P . Controlled release injectable liposomal gel of ibuprofen for epidural analgesia. _Int J Pharm_
2000; 199: 85–93. Article CAS Google Scholar * Juhasz J, Lenaerts V, Raymond P, Ong H . Diffusion of rat atrial natriuretic factor in thermoreversible poloxamer gels. _Biomaterials_ 1989;
10: 265–268. Article CAS Google Scholar * Fults KA, Johnston TP . Sustained-release of urease from a Poloxamer gel matrix. _J Parenter Sci Technol_ 1990; 44: 58–65. CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Chi SC, Jun HW . Release rates of ketoprofen from Poloxamer gels in a membraneless diffusion cell. _J Pharm Sci_ 1991; 80: 280–283. Article CAS Google Scholar * Wang PL,
Johnston TP . Enhanced stability of two model proteins in an agitated solution environment using Poloxamer 407. _J Parenter Sci Technol_ 1993; 47: 183–189. CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Bhardwaj R, Blanchard J . Controlled-release delivery system for the alpha-MSH analog Melanotan-I using Poloxamer 407. _J Pharm Sci_ 1996; 85: 915–919. Article CAS Google Scholar *
Stratton LP, Dong A, Manning MC, Carpenter JF . Drug delivery matrix containing native protein precipitates suspended in a Poloxamer gel. _J Pharm Sci_ 1997; 86:1006–1010. Article CAS
Google Scholar * Moore T, Croy S, Mallapragada S, Pandit N . Experimental investigation and mathematical modeling of Pluronic F127 gel dissolution: drug release in stirred systems. _J
Control Release_ 2000; 67: 191–202. Article CAS Google Scholar * Anderson BC, Pandit NK, Mallapragada SK . Understanding drug release from poly(ethylene oxide)-b-poly(propylene
oxide)-b-poly(ethylene oxide) gels. _J Control Release_ 2001; 70: 157–167. Article CAS Google Scholar * Desai SD, Blanchard J . Evaluation of Pluronic F127-based sustained-release ocular
delivery systems for pilocarpine using the albino rabbit eye model. _J Pharm Sci_ 1998; 87: 1190–1195. Article CAS Google Scholar * Desai SD, Blanchard J . _In vitro_ evaluation of
Pluronic F127-based controlled-release ocular delivery systems for pilocarpine. _J Pharm Sci_ 1998; 87: 226–230. Article CAS Google Scholar * Brasel K, McKenna HJ, Charrier K et al. Flt3
ligand synergizes with granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor or granulocyte colony-stimulating factor to mobilize hematopoietic progenitor cells into the peripheral blood of mice.
_Blood_ 1997; 90: 3781–3788. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Egger SF, Brown GS, Kelsey LS et al. E. Studies on optimal dose and administration schedule of a hematopoietic stimulatory
beta-(14)-linked mannan. _Int J Immunopharmacol_ 1996; 18: 113–126. Article CAS Google Scholar * Bol S, van den Engh G, Visser J . A technique for staining haemopoietic colonies in agar
cultures. _Exp Hematol_ 1977; 5: 551–553. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Katakam M, Banga AK . Use of poloxamer polymers to stabilize recombinant human growth hormone against various
processing stresses. _Pharm Dev Technol_ 1997; 2: 43–149. Article Google Scholar * Illum L, Davis SS . Targeting of colloidal particles to the bone marrow. _Life Sci_ 1987; 40: 1553–1560.
Article CAS Google Scholar * Papayannopoulou T, Nakamoto B, Andrews RG et al. _In vivo_ effects of Flt3/Flk2 ligand on mobilization of hematopoietic progenitors in primates and potent
synergistic enhancement with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. _Blood_ 1997; 90: 620–629. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Molineux G, McCrea C, Yan XQ et al. Flt-3 Ligand synergizes with
granulocyte colony-stimulating factor to increase neutrophil numbers and to mobilize peripheral blood stem cells with long-term repopulating potential. _Blood_ 1997; 89: 3998–4004. CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Sudo Y, Shimazaki C, Ashihara E et al. Synergistic effect of FLT-3 ligand on the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-induced mobilization of hematopoietic stem
cells and progenitor cells into blood in mice. _Blood_ 1997; 89: 3186–3191. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Pless M, Wodnar-Filipowicz A, John L et al. Synergy of growth factors during
mobilization of peripheral blood precursor cells with recombinant human Flt3-ligand and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in rabbits. _Exp Hematol_ 1999; 27: 155–161. Article CAS
Google Scholar * Schmolka IR . Artificial Skin. I. Preparation and properties of Pluronic F-127 gels for treatment of burns. _J Biomed Mater Res_ 1972; 6: 571–582. Article CAS Google
Scholar * Nalbandian RM, Henry RL, Balko KW et al. Pluronic F-127 gel preparation as an artificial skin in the treatment of third-degree burns in pigs. _J Biomed Mater Res_ 1987; 21:
1135–1148. Article CAS Google Scholar * Paustian PW, McPherson JC, Haase RR et al. Intravenous Pluronic F-127 in early burn wound treatment in rats. _Burns_ 1993; 19: 187–191. Article
CAS Google Scholar * Pfrimmer W, Joyce RA, Turner AR, Boggs DR . Kinetics of the development of methylcellulose-induced hepatic hematopoiesis in adult mice. _Blood_ 1978; 51: 611–622. CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Bernabei PA, Di Lollo S, Saccardi R et al. Endogenous splenic colonies and megakaryopoiesis in methylcellulose treated irradiated mice. _Experientia_ 1985; 41:
97–99. Article CAS Google Scholar * Stang HD, Boggs DR . Effect of methylcellulose injection on murine hematopoiesis. _Am J Physiol_ 1977; 233: H234–H239. CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Johnston E, Crawford J, Blackwell S et al. Randomized, dose-escalation study of SD/01 compared with daily Filgrastim in patients receiving chemotherapy. _J Clin Oncol_ 2000; 18: 2522–2528.
Article CAS Google Scholar * Molineux G, Kinstler O, Briddell B et al. A new form of Filgrastim with sustained duration _in vivo_ and enhanced ability to mobilize PBPC in both mice and
humans. _Exp Hematol_ 1999; 27: 1724–1734. Article CAS Google Scholar * de Haan G, Ausema A, Wilkens M et al. Efficient mobilization of haematopoietic progenitors after a single injection
of pegylated recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in mouse strains with distinct marrow-cell pool sizes. _Br J Haematol_ 2000; 110: 638–646. Article CAS Google Scholar
* Bowen S, Tare N, Inoue T et al. Relationship between molecular mass and duration of activity of polyethylene glycol conjugated granulocyte colony-stimulating factor mutein. _Exp Hematol_
1999; 27: 425–432. Article CAS Google Scholar * Eliason JF, Greway A, Tare N et al. Extended activity in Cynomolgus monkeys of a granulocyte colony- stimulating factor mutein conjugated
with high molecular weight polyethylene glycol. _Stem Cells_ 2000; 18: 40–45. Article CAS Google Scholar * van der Auwera P, Platzer E, Xu ZX et al. Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
of single doses of subcutaneous pegylated human G-CSF mutant (Ro 25-8315) in healthy volunteers: comparison with single and multiple daily doses of Filgrastim. _Am J Hematol_ 2001; 66:
245–251. Article CAS Google Scholar * Lebsack ME, McKenna HJ, Hoek JA et al. Safety of FLT3 ligand in healthy volunteers. _Blood_ 1997; 90 (Suppl. 1): 170a (abstr. 751). Google Scholar
Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The authors gratefully acknowledge the gift of Flt3L from Immunex Corp. and the assistance of Lisa Chudomelka, Tina Winekauf and Richard Murcek in the
preparation of this manuscript. GJR and JMB are employees of RxKinetix, Inc. and JET is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board of RxKinetix, Inc. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND
AFFILIATIONS * Department of Pathology and Microbiology, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, Nebraska S N Robinson, J M Chavez, V M Pisarev, R L Mosley & J E Talmadge *
RxKinetix, Inc., Louisville, CO, USA G J Rosenthal & J M Blonder Authors * S N Robinson View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * J M Chavez
View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * V M Pisarev View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * R L
Mosley View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * G J Rosenthal View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google
Scholar * J M Blonder View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * J E Talmadge View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Robinson, S., Chavez, J., Pisarev, V. _et al._ Delivery of Flt3 ligand (Flt3L)
using a poloxamer-based formulation increases biological activity in mice. _Bone Marrow Transplant_ 31, 361–369 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1703816 Download citation * Received:
05 February 2002 * Accepted: 30 September 2002 * Published: 12 March 2003 * Issue Date: 01 March 2003 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1703816 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the
following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer
Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS * Flt3 ligand (Flt3L) * Sustained delivery * Poloxamer-based matrix * Hematopoiesis * Mobilization




![[withdrawn] category 1 licence application (part 2)](https://www.gov.uk/assets/static/govuk-opengraph-image-03837e1cec82f217cf32514635a13c879b8c400ae3b1c207c5744411658c7635.png)

