- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT We undertook a case–control study to examine the possible associations of the _TP53_ variants Arg>Pro at codon 72 and _p53PIN3_, a 16 bp insertion/duplication in intron 3, with
the risk of colorectal cancer (CRC). The _p53PIN3_ A2 allele (16 bp duplication) was associated with an increased risk (OR 1.55, 95% CI 1.10−2.18, _P_=0.012), of the same order of magnitude
as that observed in previous studies for other types of cancer. The Pro72 allele was weakly associated with CRC (OR=1.34, 95% CI 0.98−1.84, _P_=0.066). The possible functional role of
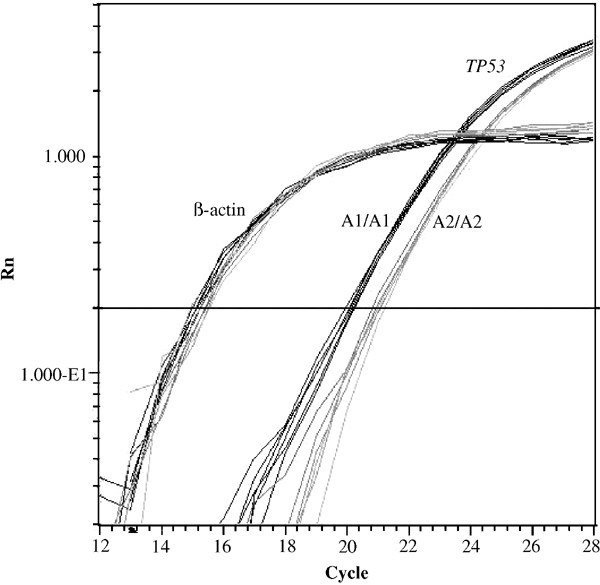
_p53PIN3_ was investigated by examining the _TP53_ mRNA transcripts in 15 lymphoblastoid cell lines with different genotypes. The possibility that the insertion/deletion could lead to
alternatively spliced mRNAs was excluded. However, we found reduced levels of _TP53_ mRNA associated with the A2 allele. In conclusion, the epidemiological study suggests a role for
_p53PIN3_ in tumorigenesis, supported by the _in vitro_ characterization of this variant. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access
via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 50 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $5.18 per issue Learn more Buy
this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: *
Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS SOLVING THE ENIGMA OF POLD1 P.V295M AS A POTENTIAL CAUSE OF
INCREASED CANCER RISK Article 20 July 2021 ROLE OF _POLE_ AND _POLD1_ IN FAMILIAL CANCER Article Open access 14 August 2020 GERMLINE VARIANT AFFECTING P53Β ISOFORMS PREDISPOSES TO FAMILIAL
CANCER Article Open access 18 September 2024 REFERENCES * Brunak S, Engelbrecht J and Knudsen S . (1991). _J. Mol. Biol._, 220, 49–65. * Cox DG and Canzian F . (2001). _Bioinformatics_, 17,
738–739. * Dumont P, Leu JI, Della Pietra AC, George DL and Murphy M . (2003). _Nat. Genet._, 33, 357–365. * Excoffier L and Slatkin M . (1995). _Mol. Biol. Evol._, 12, 921–927. * Hebsgaard
SM, Korning PG, Tolstrup N, Engelbrecht J, Rouze P and Brunak S . (1996). _Nucleic Acids Res._, 24, 3439–3452. * Landi S, Moreno V, Gioia-Patricola L, Guino E, Navarro M, de Oca J, Capella G
and Canzian F . (2003). _Cancer Res._, 63, 3560–3566. * Lazar V, Hazard F, Bertin F, Janin N, Bellet D and Bressac B . (1993). _Oncogene_, 8, 1703–1705. * Powell BL, van Staveren IL,
Roosken P, Grieu F, Berns EM and Iacopetta B . (2002). _Carcinogenesis_, 23, 311–315. * Rogan PK, Faux BM and Schneider TD . (1998). _Hum. Mutat._, 12, 153–171. * Runnebaum IB, Tong XW,
Konig R, Zhao H, Korner K, Atkinson EN, Kreienberg R, Kieback DG, Hong Z and Zhao H . (1995). _Lancet_, 345, 994. * Storey A, Thomas M, Kalita A, Harwood C, Gardiol D, Mantovani F, Breuer J,
Leigh IM, Matlashewski G and Banks L . (1998). _Nature_, 393, 229–234. * Tõnisson N, Zernant J, Kurg A, Pavel H, Slavin G, Roomere H, Meiel A, Hainaut P and Metspalu A . (2002). _Proc.
Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_, 99, 5503–5508. * Wang-Gohrke S, Becher H, Kreienberg R, Runnebaum IB and Chang-Claude J . (2002). _Pharmacogenetics_, 12, 269–272. * Wang-Gohrke S, Weikel W, Risch H,
Vesprini D, Abrahamson J, Lerman C, Godwin A, Moslehi R, Olipade O, Brunet JS, Stickeler E, Kieback DG, Kreienberg R, Weber B, Narod SA and Runnebaum IB . (1999). _Br. J. Cancer_, 81,
179–183. * Weston A, Pan CF, Ksieski HB, Wallenstein S, Berkowitz GS, Tartter PI, Bleiweiss IJ, Brower ST, Senie RT and Wolff MS . (1997). _Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev._, 6, 105–112. *
Wu X, Zhao H, Amos CI, Shete S, Makan N, Hong WK, Kadlubar FF and Spitz MR . (2002). _J. Natl. Cancer Inst._, 94, 681–690. Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Federica Gemignani is a
recipient of a fellowship from the International Association for the Study on Lung Cancer (IASLC), part of the Cancer Research Foundation of America (CRFA). Stefano Landi is a recipient of a
Marie Curie fellowship (HPMFCT-2000-00483) from the European Commission. S Gutièrrez-Enriquez and N Moullan are recipients of Special Training Awards from the International Agency for
Research on Cancer. This work was partially funded by grants from the Maraton of TV3 48/95, Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias FIS 96/0797, FIS 00/0027, FIS 01/1264 and SAF 00/81, and
Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer #7478. AUTHOR INFORMATION Author notes * Federica Gemignani, Victor Moreno and Stefano Landi: These authors contributed equally to the manuscript.
AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), 150, Cours Albert Thomas, Lyon, 69372, France Federica Gemignani, Stefano Landi, Norman Moullan, Amélie
Chabrier, Sara Gutiérrez-Enríquez, Janet Hall & Federico Canzian * Dipartimento di Scienze dell'Uomo e Ambiente, University of Pisa, 56100, Italy Federica Gemignani & Stefano
Landi * Institut Catala d'Oncologia, Hospitalet, Barcelona, Spain Victor Moreno, Elisabeth Guino & Gabriel Capella * Institut de Recerca Oncologica, Hospitalet, Barcelona, Spain
Miguel Angel Peinado Authors * Federica Gemignani View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Victor Moreno View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Stefano Landi View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Norman Moullan View author publications
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Amélie Chabrier View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Sara Gutiérrez-Enríquez
View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Janet Hall View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar *
Elisabeth Guino View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Miguel Angel Peinado View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * Gabriel Capella View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Federico Canzian View author publications You can also search
for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Federico Canzian. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE
Gemignani, F., Moreno, V., Landi, S. _et al._ A _TP53_ polymorphism is associated with increased risk of colorectal cancer and with reduced levels of _TP53_ mRNA. _Oncogene_ 23, 1954–1956
(2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207305 Download citation * Received: 18 June 2003 * Revised: 21 July 2003 * Accepted: 22 October 2003 * Published: 01 December 2003 * Issue Date: 11
March 2004 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207305 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable
link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS * _TP53_ * colorectal cancer * polymorphism *
mRNA levels







