- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
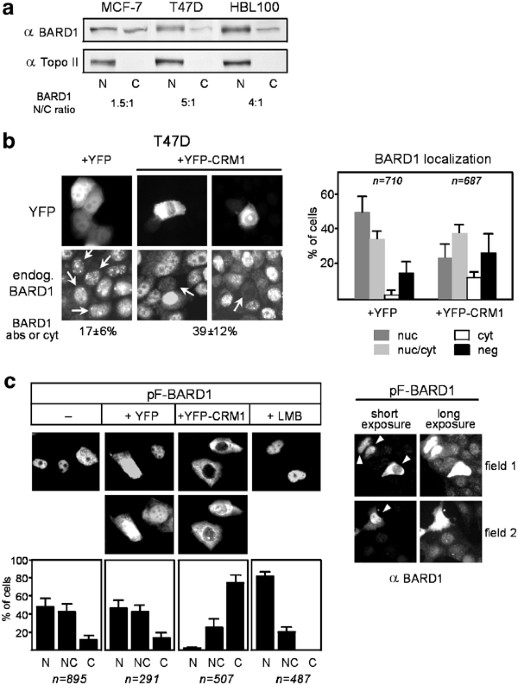
ABSTRACT The breast cancer-associated protein, BARD1, colocalizes with BRCA1 in nuclear foci in the S phase and after DNA damage, and the two proteins form a stable heterodimer implicated in
DNA repair, protein ubiquitination, and control of mRNA processing. BARD1 has a BRCA1-independent proapoptotic activity; however, little is known about its regulation. Here, we show that
BARD1 localization and apoptotic activity are regulated by nuclear–cytoplasmic shuttling. We identified a functional CRM1-dependent nuclear export sequence (NES) near the N-terminal RING
domain of BARD1. The NES forms part of the BRCA1 dimerization domain, and coexpression of BRCA1 resulted in masking of the NES and nuclear retention of BARD1. In transient expression assays,
BARD1 apoptotic activity was stimulated by nuclear export, and both apoptotic function and nuclear export were markedly reduced by BRCA1. Similar findings were obtained for endogenous
BARD1. Silencing BRCA1 expression by siRNA, or disrupting the endogenous BARD1/BRCA1 interaction by peptide competition caused a reduction in BARD1 nuclear localization and foci formation,
and increased the level of cytoplasmic BARD1 correlating with increased apoptosis. Our findings suggest that BRCA1/BARD1 heterodimer formation is important for optimal nuclear targeting of
BARD1 and its role in DNA repair and cell survival. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS
Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 50 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $5.18 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on
SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about
institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS SYSTEMATIC INVESTIGATION OF BRCA1-A, -B, AND -C COMPLEXES AND THEIR FUNCTIONS IN
DNA DAMAGE RESPONSE AND DNA REPAIR Article 27 July 2024 P50 MONO-UBIQUITINATION AND INTERACTION WITH BARD1 REGULATES CELL CYCLE PROGRESSION AND MAINTAINS GENOME STABILITY Article Open
access 06 October 2020 THE RANBP2/RANGAP1-SUMO COMPLEX GATES Β-ARRESTIN2 NUCLEAR ENTRY TO REGULATE THE MDM2-P53 SIGNALING AXIS Article 01 March 2021 REFERENCES * Baer R and Ludwig T .
(2002). _Curr. Opin. Gen. Dev._, 12, 86–91. * Bogerd HP, Fridell RA, Benson RE, Hua J and Cullen BR . (1996). _Mol. Cell. Biol._, 16, 4207–4214. * Brzovic PS, Meza JE, King MC and Klevit RE
. (2001b). _J. Biol. Chem._, 276, 41399–41406. * Brzovic PS, Rajagopal P, Hoyt DW, King MC and Klevit RE . (2001a). _Nat. Struct. Biol._, 8, 833–837. * Chen A, Kleiman FE, Manley JL, Ouchi T
and Pan ZQ . (2002). _J. Biol. Chem._, 277, 22085–22092. * Chiba N and Parvin JD . (2001). _J. Biol. Chem._, 276, 38549–38554. * Chiba N and Parvin JD . (2002). _Cancer Res._, 62,
4222–4228. * Fabbro M, Rodriguez JA, Baer R and Henderson BR . (2002). _J. Biol. Chem._, 277, 21315–21324. * Ghimenti CE, Sensi E, Presciuttini S, Brunetti IM, Conte P, Bevilacqua G and
Caligo MA . (2002). _Genes Chrom. Cancer_, 33, 235–242. * Hashizume R, Fukuda M, Maeda I, Nishikawa H, Oyake D, Yabuki Y, Ogata H and Ohta T . (2001). _J. Biol. Chem._, 276, 14537–14540. *
Henderson BR and Eleftheriou A . (2000). _Exp. Cell Res._, 256, 1–12. * Irminger-Finger I, Leung W-C, Li J, Dubois-Dauphin M, Harb J, Feki A, Jefford CE, Sorlano JV, Jaconi M, Montesano R
and Krause K-H . (2001). _Mol. Cell_, 8, 1255–1266. * Irminger-Finger I, Soriano JV, Vaudan G, Montesano R and Sappino AP . (1998). _J. Cell. Biol._, 143, 1329–1339. * Jin Y, Xu XL, Yang
M-CW, Wei F, Ayi T-C, Bowcock AM and Baer R . (1997). _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_, 94, 12075–12080. * Joukov V, Chen J, Fox EA, Green JBA and Livingston DM . (2001). _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.
USA_, 90, 12078–12083. * Kleiman FE and Manley JL . (1999). _Science_, 285, 1576–1579. * Kleiman FE and Manley JL . (2001). _Cell_, 104, 743–753. * Lorick KL, Jensen JP, Fang S, Ong AM and
Hatakeyama S . (1999). _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_, 96, 11354–11369. * McCarthy EE, Celebi JT, Baer R and Ludwig T . (2003). _Mol. Cell. Biol._, 23, 5056–5063. * Miki Y, Swensen J,
Shattuck-Eidens D, Futreal PA, Ahrshman K, Tavigian S, Liu Q, Cochran C, Bennett LM, Ding W, Bell R, Rosenthal J, Hussey C, Tran T, McClure M, Frye C, Hattier T, Phelps R, Haugen-Strano A,
Katcher H, Yakumo K, Gholami Z, Shaffer D, Stone S, Bayer S, Wray C, Bogden R, Dayananth P, Ward J, Tonin P, Narod S, Bristow PK, Norris FH, Helvering L, Morrison P, Rosteck P, Lai M,
Barrett JC, Lewis C, Neuhausen S, Cannon-Albright L, Goldgar D, Wiseman R, Kamb A and Skolnick MHA . (1994). _Science_, 266, 66–71. * Rodriguez JA and Henderson BR . (2000). _J. Biol.
Chem._, 275, 38589–38596. * Ruffner H, Joazeiro CAP, Hemmati D, Hunter T and Verma IM . (2001). _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_, 98, 5134–5139. * Scully R, Chen J, Ochs RL, Keegan K, Hoekstra
M, Feunteun J and Livingston DM . (1997). _Cell_, 90, 425–435. * Spahn L, Petermann R, Siligan C, Schmid JA, Aryee DNT and Kovar H . (2002). _Cancer Res._, 62, 4583–4587. * Sui G, Soohoo C,
Affar EB, Gay F, Shi Y, Forrester WC and Shi Y . (2002). _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_, 99, 5515–5520. * Thai TH, Du F, Tsan JT, Jin Y, Phung A, Spillman MA, Massa HF, Muller CY, Ashfaq R,
Mathis J, Miller DS, Trask BJ, Baer R and Bowcock AM . (1998). _Hum. Mol. Genet._, 7, 195–202. * Wu LC, Wang ZW, Tsan JT, Spillman MA, Phung A, Xu XL, Yang MC, Hwang LY, Bowcock AM and Baer
R . (1996). _Nat. Genet_, 14, 430–440. * Xu X, Qiao W, Linke SP, Cao L, Li WM, Furth PA, Harris CC and Deng CX . (2001). _Nat. Genet._, 28, 266–271. Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We
thank J Holt and R Baer for supplying cDNAs and antibodies. We are grateful to R Kefford and T Cunningham for support at the Westmead Millennium Institute. This work was partly supported by
a grant from the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) of Australia. BRH was supported by an NHMRC Senior Research Fellowship. SS was supported by an Erwin Schroedinger
post-doctoral fellowship from the FWF of Austria. AUTHOR INFORMATION Author notes * José Antonio Rodriguez Present address: Department of Medical Oncology, Academic Hospital, Vrije
Universiteit Amsterdam, 1081HV, Amsterdam, The Netherlands * José Antonio Rodriguez and Stefan Schüchner: These two authors contributed equally to this work AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS *
Westmead Institute for Cancer Research, University of Sydney, Westmead Millennium Institute at Westmead Hospital, PO Box 412, Darcy Road, Westmead, 2145, NSW, Australia José Antonio
Rodriguez, Stefan Schüchner, Wendy W Y Au, Megan Fabbro & Beric R Henderson Authors * José Antonio Rodriguez View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google
Scholar * Stefan Schüchner View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Wendy W Y Au View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * Megan Fabbro View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Beric R Henderson View author publications You can also search
for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Beric R Henderson. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE
Rodriguez, J., Schüchner, S., Au, W. _et al._ Nuclear–cytoplasmic shuttling of BARD1 contributes to its proapoptotic activity and is regulated by dimerization with BRCA1. _Oncogene_ 23,
1809–1820 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207302 Download citation * Received: 20 August 2003 * Revised: 17 October 2003 * Accepted: 21 October 2003 * Published: 01 December 2003 *
Issue Date: 11 March 2004 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207302 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS * BARD1 * BRCA1 * nuclear
export * cancer * apoptosis







