- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT Progesterone (P4) has been implicated as a protective factor for epithelial ovarian cancers, yet little is known about its mechanism of action. We previously reported that
pregnancy-equivalent doses of P4 inhibited the growth of normal and malignant human ovarian surface epithelial (HOSE) cells. Here, we investigated how P4-induced cell death in two
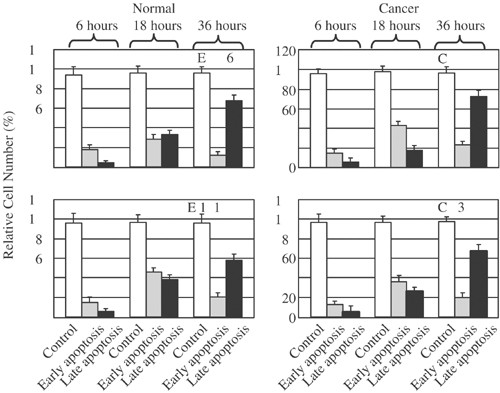
immortalized normal (HOSE 642, HOSE 12-12) and two malignant (OVCA 429, OVCA 432) HOSE cell lines. The exposure of HOSE or OVCA cell cultures to 10−6 M P4 induced time-dependent increases in
early and late apoptotic cells and activation of caspase-8 and -3, but not that of caspase-9. A general caspase inhibitor Z-VAD effectively blocked the P4-induced cell death in a
dose-dependent manner. Comparable levels of Fas mRNA and protein were expressed in HOSE and OVCA cell lines, and these levels were unaffected by P4. In contrast, levels of FasL mRNA and
protein were higher in OVCA cells than in HOSE cells. Interestingly, the hormone enhanced levels of FasL mRNA and protein in HOSE cells, but lowered their levels in OVCA cells. The exposure
of HOSE or OVCA cells to an activating anti-Fas antibody induced cell loss, whereas treatment of cells with a blocking anti-FasL antibody reduced the P4-induced cell loss. Cotreatment of
cells with the activating anti-Fas antibody and P4 produced additive effects on cell loss. These results reveal for the first time that P4 induces apoptosis in HOSE and OVCA cells via
activation of a caspase-8-initiated Fas/FasL signaling pathway. They also demonstrate differential P4-regulation of FasL expression between HOSE and OVCA cells. Access through your
institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 50 print
issues and online access $259.00 per year only $5.18 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to
local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT
BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS GAIN-OF-FUNCTION P53R175H BLOCKS APOPTOSIS IN A PRECURSOR MODEL OF OVARIAN HIGH-GRADE SEROUS CARCINOMA Article Open access 14 July 2023 ANTI-MÜLLERIAN HORMONE (AMH)
AUTOCRINE SIGNALING PROMOTES SURVIVAL AND PROLIFERATION OF OVARIAN CANCER CELLS Article Open access 26 January 2021 PAX8 PLAYS AN ESSENTIAL ANTIAPOPTOTIC ROLE IN UTERINE SEROUS PAPILLARY
CANCER Article 09 July 2021 REFERENCES * Adami HO, Hsieh CC, Lambe M, Trichopoulos D, Leon D, Persson I, Ekbom A and Janson PO . (1994). _Lancet_, 344, 1250–1254. * Adami HO, Lambe M,
Persson I, Ekbom A, Hsieh CC and Trichopoulos D . (1995). _Lancet_, 345, 789. * Akhmedkhanov A, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A and Toniolo P . (2001). _Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci._, 943, 296–315. * Alnemri
ES, Livingston DJ, Nicholson DW, Salvesen G, Thornberry NA, Wong WW and Yuan J . (1996). _Cell_, 87, 171. * Ashkenazi A and Dixit VM . (1998). _Science_, 281, 1305–1308. * Bast Jr RC, Feeney
M, Lazarus H, Nadler LM, Colvin RB and Knapp RC . (1981). _J. Clin. Invest._, 68, 1331–1337. * Bennett MW, O'Connell J, Houston A, Kelly J, O'Sullivan GC, Collins JK and Shanahan
F . (2001). _J. Clin. Pathol._, 54, 598–604. * Bennett MW, O'Connell J, O'Sullivan GC, Brady C, Roche D, Collins JK and Shanahan F . (1998). _J. Immunol._, 160, 5669–5675. * Bu SZ,
Yin DL, Ren XH, Jiang LZ, Wu ZJ, Gao QR and Pei G . (1997). _Cancer_, 79, 1944–1950. * Cramer DW, Hutchison B, Welch WR, Scully RE and Ryan KJ . (1983). _J. Natl. Can. Inst._, 71, 711–716.
* Cramer DW and Welch WR . (1993). _J. Natl. Cancer Inst._, 71, 717–721. * Das H, Koizumi T, Sugimoto T, Chakraborty S, Ichimura T, Hasegawa K and Nishimura R . (2000). _Br. J. Cancer_, 82,
1682–1688. * Earnshaw WC, Martins LM and Kaufmann SH . (1999). _Annu. Rev. Biochem._, 68, 383–424. * Ghahremani M, Foghi A and Dorrington JH . (1998). _Gynecol. Oncol._, 70, 275–281. *
Gratas C, Tohma Y, Barnas C, Taniere P, Hainaut P and Ohgaki H . (1998). _Cancer Res._, 58, 2057–2062. * Griffith TS and Ferguson TA . (1997). _Immunol. Today_, 18, 240–244. * Hayakawa A, Wu
J, Kawamoto Y, Zhou YW, Tanuma S, Nakashima I and Suzuki H . (2002). _Apoptosis_, 7, 107–113. * Hu Z and Deng X . (2000). _Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi_, 35, 423–426. * Keane MM, Ettenberg
SA, Lowrey GA, Russell EK and Lipkowitz S . (1996). _Cancer Res._, 56, 4791–4798. * Lambe M, Wuu J, Rossing MA and Hsieh CC . (1999). _Lancet_, 353, 1941. * Lepple-Wienhues A, Belka C, Laun
T, Jekle A, Walter B, Wieland U, Welz M, Heil L, Kun J, Busch G, Weller M, Bamberg M, Gulbins E and Lang F . (1999). _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_, 96, 13795–13800. * Milner AE, Palmer DH,
Hodgkin EA, Eliopoulos AG, Knox PG, Poole CJ, Kerr DJ and Young LS . (2002). _Cell Death Differ._, 9, 287–300. * Moller P, Koretz K, Leithauser F, Bruderlein S, Henne C, Quentmeier A and
Krammer PH . (1994). _Int. J. Cancer_, 57, 371–377. * Munakata S, Enomoto T, Tsujimoto M, Otsuki Y, Miwa H, Kanno H and Aozasa K . (2000). _Br. J. Cancer_, 84, 1446–1452. * Murdoch WJ and
McDonnel AC . (2002). _Reproduction_, 123, 743–750. * Nagata S . (1994). _Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London B. Biol. Sci._, 345, 281–287. * O'Connell J, Houston A, Bennett MW,
O'Sullivan GC and Shanahan F . (2001). _Nat. Med._, 7, 271–274. * O'Connell J, O'Sullivan GC, Collins JK and Shanahan F . (1996). _J. Exp. Med._, 184, 1075–1082. * Pinkoski MJ
and Green DR . (2000). _Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev._, 10, 114–119. * Reimer T, Herrnring C, Koczan D, Richter D, Gerber B, Kabelitz D, Friese K and Thiesen HJ . (2000). _Cancer Res._, 60,
822–828. * Riman T, Persson I and Nilsson S . (1998). _Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.)_, 49, 695–707. * Rodriguez GC, Nagarsheth NP, Lee KL, Bentley RC, Walmer DK, Cline M, Whitaker RS, Isner P,
Berchuck A, Dodge RK and Hughes CL . (2002). _J. Natl. Cancer Inst._, 94, 50–60. * Sampalo A, Navas G, Medina F, Segundo C, Camara C and Brieva JA . (2000). _Blood_, 96, 3168–3174. * Sapi E,
Brown WD, Aschkenazi S, Lim C, Munoz A, Kacinski BM, Rutherford T and Mor G . (2002). _J. Soc. Gynecol. Invest._, 9, 243–250. * Selam B, Kayisli UA, Mulayim N and Arici A . (2001). _Biol.
Reprod._, 65, 979–985. * Song K, Chen Y, Goke R, Wilmen A, Seidel C, Goke A and Hilliard B . (2000). _J. Exp. Med._, 191, 1095–1104. * Song J, Rutherford T, Naftolin F, Brown S and Mor G .
(2002). _Mol. Hum. Reprod._, 8, 447–455. * Strand S, Hofmann WJ, Hug H, Muller M, Otto G, Strand D, Mariani SM, Stremmel W, Krammer PH and Galle PR . (1996). _Nat. Med._, 2, 1361–1366. *
Suda T, Takahashi T, Golstein P and Nagata S . (1993). _Cell_, 75, 1169–1178. * Syed V, Ulinski G, Mok SC, Yiu GK and Ho SM . (2001). _Cancer Res._, 61, 6768–6776. * Syed V, Ulinski G, Mok
SC and Ho SM . (2002). _J. Natl. Cancer Inst._, 94, 617–629. * Tsao SW, Mok SC, Fey E G, Fletcher J A, Muto MG, Knapp RC and Berkowitz RS . (1995). _Exp. Cell Res._, 218, 499–507. *
Ungefroren H, Voss M, Jansen M, Roeder C, Henne-Bruns D, Kremer B and Kalthoff H . (1998). _Cancer Res._, 58, 1741–1749. * van Haaften-Day C, Russell P, Davies S, King NJ and Tattersall MH .
(2003). _Hum. Pathol._, 34, 74–79. * Wang S, Pudney J, Song J, Mor G, Schwartz PE and Zheng W . (2003). _Gynecol. Oncol._, 88, 108–117. * Wajant H . (2002). _Science_, 296, 1635–1636. *
Yonehara S, Ishii A and Yonehara M . (1989). _J. Exp. Med._, 169, 1747–1756. * Yu S, Lee M, Shin S and Park J . (2001). _J. Cell Biochem._, 82, 445–451. * Zimmermann KC, Bonzon C and Green
DR . (2001). _Pharmacol. Ther._, 92, 57–70. * Zou H, Li Y, Liu X and Wang X . (1999). _J. Biol. Chem._, 274, 11549–11556. Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This study was supported by an
Army Ovarian Cancer Research Program Grant DAMD17-99-1-9563 (to S-M Ho) and NIH Grants CA091250 (to V Syed) and CA94221 (to S-M Ho). This publication was made possible by Grant Number 5 P30
DK32520 from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases'. We thank Dr Samuel C Mok of Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, for his
generous gifts of HOSE and OVCA cell lines and editorial staff of Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, for editorial help. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of
Surgery, University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, USA Viqar Syed & Shuk-Mei Ho * Department of Cell Biology and Physiology, University of Massachusetts Medical School,
Worcester, MA, USA Shuk-Mei Ho Authors * Viqar Syed View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Shuk-Mei Ho View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Shuk-Mei Ho. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Syed,
V., Ho, SM. Progesterone-induced apoptosis in immortalized normal and malignant human ovarian surface epithelial cells involves enhanced expression of FasL. _Oncogene_ 22, 6883–6890 (2003).
https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206828 Download citation * Received: 14 February 2003 * Revised: 13 May 2003 * Accepted: 30 May 2003 * Published: 09 October 2003 * Issue Date: 09 October
2003 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206828 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link
is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS * caspases * Fas * Fas ligand * caspase-8 *
hormonal carcinogenesis * ovarian neoplasm