- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
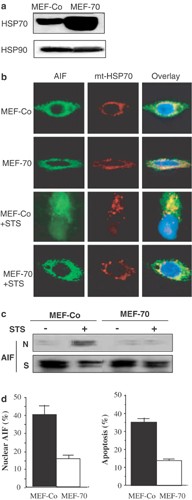
ABSTRACT Heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) can inhibit apoptosis by neutralizing and interacting with apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF), a mitochondrial flavoprotein that translocates upon
apoptosis induction to the nucleus, via the cytosol. Here, we show that only members of the HSP70 family interact with AIF. Systematic deletion mapping revealed the existence of three
distinct functional regions in the AIF protein: (1) a region between amino acids 150 and 228 that binds HSP70, (2) a domain between residues 367 and 459 that includes a nuclear localization
sequence (NLS) and (3) a C-terminal domain beyond residue 567 required for its chromatin-condensing activity. Deletion of the 150–268 domain completely abolished HSP70 binding and
facilitated the nuclear import of AIF, resulting in a gain-of-function phenotype with enhanced AIF-mediated chromatin condensation as compared to wild-type AIF. This gain-of-function
phenotype was observed in wild-type control cells (which express low but significant levels of HSP70), yet was lost when AIFΔ150–268 was introduced into HSP70 knockout cells, underscoring
the functional importance of the AIF–HSP70 interaction. Altogether, our data demonstrate that AIF inhibition by HSP70 involves cytosolic retention of AIF. Moreover, it appears that
endogenous HSP70 protein levels are sufficiently elevated to modulate the lethal action of AIF. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content,
access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 50 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $5.18 per issue Learn
more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS
OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS HSP90 MEDIATES THE CONNECTION OF MULTIPLE
PROGRAMMED CELL DEATH IN DISEASES Article Open access 05 November 2022 DELE1 OLIGOMERIZATION PROMOTES INTEGRATED STRESS RESPONSE ACTIVATION Article 07 August 2023 REGULATORY INTER-DOMAIN
INTERACTIONS INFLUENCE HSP70 RECRUITMENT TO THE DNAJB8 CHAPERONE Article Open access 11 February 2021 REFERENCES * Beckmann RP, Mizzen LE and Welch WJ . (1990). _Science_, 248, 850–854. *
Beere HM, Wolf BB, Cain K, Mosser DD, Mahboubi A, Kuwana T, Tailor P, Morimoto RI, Cohen GM and Green DR . (2000). _Nat. Cell. Biol._, 2, 469–475. * Castedo M, Ferri KF, Blanco J, Roumier T,
Larochette N, Barretina J, Amendola A, Nardacci R, Metivier D, Este JA, Piacentini M and Kroemer G . (2001). _J. Exp. Med._, 194, 1097–1110. * Courchesne PL, Jones MD, Robinson JH, Spahr
CS, McCracken S, Bentley DL, Luethy R and Patterson SD . (1998). _Electrophoresis_, 19, 956–967. * Daugas E, Susin SA, Zamzami N, Ferri KF, Irinopoulou T, Larochette N, Prevost MC, Leber B,
Andrews D, Penninger J and Kroemer G . (2000). _FASEB J._, 14, 729–739. * Ferri KF, Jacotot E, Blanco J, Este JA, Zamzami N, Susin SA, Xie Z, Brothers G, Reed JC, Penninger JM and Kroemer G
. (2000). _J. Exp. Med._, 192, 1081–1092. * Ferri KF and Kroemer G . (2001). _Nat. Cell. Biol._, 3, E255–E263. * Garrido C, Bruey JM, Fromentin A, Hammann A, Arrigo AP and Solary E . (1999).
_FASEB J._, 13, 2061–2070. * Garrido C, Gurbuxani S, Ravagnan L and Kroemer G . (2001). _Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun._, 286, 433–442. * Gurbuxani S, Bruey JM, Fromentin A, Larmonier N,
Parcellier A, Jaattela M, Martin F, Solary E and Garrido C . (2001). _Oncogene_, 20, 7478–7485. * Hu Y, Benedict MA, Ding L and Nunez G . (1999). _EMBO J._, 18, 3586–3595. * Jaattela M .
(1995). _Int. J. Cancer_, 60, 689–693. * Jacobson MD, Weil M and Raff MC . (1997). _Cell_, 88, 347–354. * Joza N, Susin SA, Daugas E, Stanford WL, Cho SK, Li CY, Sasaki T, Elia AJ, Cheng HY,
Ravagnan L, Ferri KF, Zamzami N, Wakeham A, Hakem R, Yoshida H, Kong YY, Mak TW, Zuniga-Pflucker JC, Kroemer G and Penninger JM . (2001). _Nature_, 410, 549–554. * Kroemer G and Reed JC .
(2000). _Nat. Med._, 6, 513–519. * Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES and Wang X . (1997). _Cell_, 91, 479–489. * Loeffler M, Daugas E, Susin SA, Zamzami N,
Metivier D, Nieminen AL, Brothers G, Penninger JM and Kroemer G . (2001). _FASEB J._, 15, 758–767. * Marzo I, Brenner C, Zamzami N, Susin SA, Beutner G, Brdiczka D, Remy R, Xie ZH, Reed JC
and Kroemer G . (1998). _J. Exp. Med._, 187, 1261–1271. * Miramar MD, Costantini P, Ravagnan L, Saraiva LM, Haouzi D, Brothers G, Penninger JM, Peleato ML, Kroemer G and Susin SA . (2001).
_J. Biol. Chem._, 276, 16391–16398. * Munster PN, Basso A, Solit D, Norton L and Rosen N . (2001). _Clin. Cancer Res._, 7, 2228–2236. * Murakami H, Pain D and Blobel G . (1988). _J. Cell.
Biol._, 107, 2051–2057. * Nylandsted J, Rohde M, Brand K, Bastholm L, Elling F and Jaattela M . (2000). _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_, 97, 7871–7876. * Ravagnan L, Gurbuxani S, Susin SA,
Maisse C, Daugas E, Zamzami N, Mak T, Jaattela M, Penninger JM, Garrido C and Kroemer G . (2001). _Nat. Cell. Biol._, 3, 839–843. * Seo JS, Park YM, Kim JI, Shim EH, Kim CW, Jang JJ, Kim SH
and Lee WH . (1996). _Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun._, 218, 582–587. * Shi Y and Thomas JO . (1992). _Mol. Cell. Biol._, 12, 2186–2192. * Solary E, Droin N, Bettaieb A, Corcos L,
Dimanche-Boitrel MT and Garrido C . (2000). _Leukemia_, 14, 1833–1849. * Susin SA, Lorenzo HK, Zamzami N, Marzo I, Snow BE, Brothers GM, Mangion J, Jacotot E, Costantini P, Loeffler M,
Larochette N, Goodlett DR, Aebersold R, Siderovski DP, Penninger JM and Kroemer G . (1999). _Nature_, 397, 441–446. * Volloch VZ and Sherman MY . (1999). _Oncogene_, 18, 3648–3651. * Wang X,
Yang C, Chai J, Shi Y and Xue D . (2002). _Science_, 298, 1587–1592. * Ye H, Cande C, Stephanou NC, Jiang S, Gurbuxani S, Larochette N, Daugas E, Garrido C, Kroemer G and Wu H . (2002).
_Nat. Struct. Biol._, 9, 680–684. Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank Clayton R Hunt (Department of Radiation Oncology, Washington University School Of Medicine, St Louis, MO
63108, USA), David J Dix (National Health and Environmental Effects Research Laboratory, US Environmental Protection Agency, NC 27711, USA) and Marja Jäättelä (Danish Cancer Society,
DK-2100, Copenhagen, Denmark) for the MEF HSP70.1, HSP70.3-deficient cells. This work was supported by the Institut National pour la Santé et la Recherche Medicale (INSERM), the Comité
Départemental de la Nièvre de la Ligue National contre le Cancer, the Association pour la Recherche contre le Cancer (ARC # 9567 and 5204), the Conseil Régional de Bourgogne (to CG), Ligue
Nationale contre le Cancer and the European Commission (QLG1-CT-1999-00739) (to GK). SG was supported by a Poste vert from the INSERM, AP by a fellowship from the Ministère de
l'Education Nationale and CC by a fellowship from ARC. AUTHOR INFORMATION Author notes * Sandeep Gurbuxani and Elise Schmitt: SG and ES contributed equally to this paper * Guido Kroemer
and Carmen Garrido: CG and GK share senior co-authorship AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * INSERM U-517, Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy, 7 Boulevard Jeanne d'Arc, Dijon, 21033, France
Sandeep Gurbuxani, Elise Schmitt, Arnaud Parcellier, Arlette Hammann & Carmen Garrido * CNRS UMR 1599, Institute Gustave Roussy, Villejuif, 94805, France Celine Cande, Eric Daugas,
Ilektra Kouranti & Guido Kroemer * Amgen Inc., Mammalian Genomics, Amgen Center, Thousand Oaks, 91320, CA, USA Chris Spahr * Department of Biochemistry, University of Cambridge, Tennis
Court Road, Cambridge, UK Alena Pance Authors * Sandeep Gurbuxani View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Elise Schmitt View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Celine Cande View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Arnaud
Parcellier View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Arlette Hammann View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google
Scholar * Eric Daugas View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Ilektra Kouranti View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * Chris Spahr View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Alena Pance View author publications You can also search for this
author inPubMed Google Scholar * Guido Kroemer View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Carmen Garrido View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Carmen Garrido. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE
Gurbuxani, S., Schmitt, E., Cande, C. _et al._ Heat shock protein 70 binding inhibits the nuclear import of apoptosis-inducing factor. _Oncogene_ 22, 6669–6678 (2003).
https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206794 Download citation * Received: 31 March 2003 * Revised: 19 May 2003 * Accepted: 19 May 2003 * Published: 02 October 2003 * Issue Date: 02 October 2003 *
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206794 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not
currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS * HSP70 * AIF * apoptosis * nuclear import








