- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Leptin (LEP) is an endocrine hormone that participates in many metabolic pathways, including those associated with the central regulation of energy homeostasis.
OBJECTIVE: We examined the associations between polymorphisms in the LEP and leptin receptor (LEPR) genes and resting metabolic rate (RMR) and respiratory quotient (RQ) in the Quebec Family
Study. METHODS AND SUBJECTS: Three polymorphisms in LEPR (K109R, Q223R and K656N) and one in LEP (19A>G) were genotyped in 678 subjects. RMR, RQ at rest and RQ while sitting, standing and
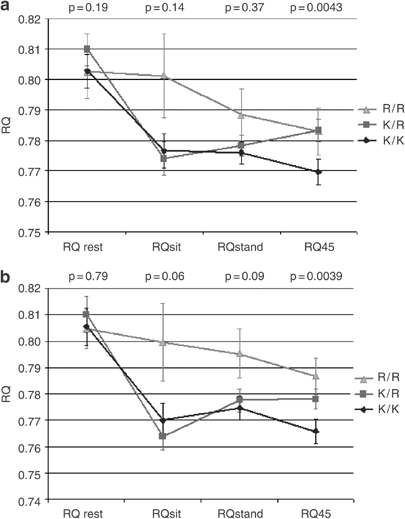
walking at 4.5 km/h (RQ45) were adjusted for age, sex, fat mass and fat-free mass. RESULTS: RQ45 was associated with the LEPR-K109R (_P_=0.004) and Q223R (_P_=0.03) polymorphisms, and RMR
showed association with the LEPR-K656N polymorphism (_P_=0.006). For the LEP-19A>G polymorphism, no significant associations were observed. However, LEP-A19A homozygotes who were carriers
of the LEPR N656 allele had a significantly lower RQ45 compared to other genotype combinations (_P_ for interaction=0.003). CONCLUSION: These findings suggest that DNA sequence variation in
the LEPR gene contributes to human variation in RMR and in the relative rates of substrate oxidation during low-intensity exercise in steady state but not in a resting state. Access through
your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12
print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be
subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR
CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS THE EFFECT OF PREDNISOLONE INGESTION AND ACUTE EXERCISE ON LIPOCALIN-2 AND ITS VARIANTS IN YOUNG MEN: A PILOT RANDOMISED CROSSOVER STUDY Article Open access 06
February 2025 CAUSAL ASSOCIATIONS BETWEEN CARDIORESPIRATORY FITNESS AND TYPE 2 DIABETES Article Open access 03 July 2023 ASSOCIATION BETWEEN _PTPN1_ POLYMORPHISMS AND OBESITY-RELATED
PHENOTYPES IN EUROPEAN ADOLESCENTS: INFLUENCE OF PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Article 11 November 2022 REFERENCES * Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M, Leopold L, Friedman JM . Positional cloning
of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. _Nature_ 1994; 372: 425–432. Article CAS Google Scholar * Margetic S, Gazzola C, Pegg GG, Hill RA . Leptin: a review of its peripheral
actions and interactions. _Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord_ 2002; 26: 1407–1433. Article CAS Google Scholar * Pelleymounter MA, Cullen MJ, Baker MB, Hecht R, Winters D, Boone T et al.
Effects of the obese gene product on body weight regulation in _ob/ob_ mice. _Science_ 1995; 269: 540–543. Article CAS Google Scholar * Halaas JL, Gajiwala KS, Maffei M, Cohen SL, Chait
BT, Rabinowitz D et al. Weight-reducing effects of the plasma protein encoded by the obese gene. _Science_ 1995; 269: 543–546. Article CAS Google Scholar * Hwa JJ, Fawzi AB, Graziano MP,
Ghibaudi L, Williams P, Van Heek M et al. Leptin increases energy expenditure and selectively promotes fat metabolism in _ob/ob_ mice. _Am J Physiol_ 1997; 272: R1204–R1209. CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Montague CT, Farooqi IF, Whitehead JP, Soos MA, Rau H, Wareham NJ et al. Congenital leptin deficiency is associated with severe early-onset obesity in humans. _Nature_
1995; 387: 903–908. Article Google Scholar * Farooqi IS, Keogh JM, Kamath S, Jones S, Gibson WT, Trussell R et al. Partial leptin deficiency and human adiposity. _Nature_ 2001; 414: 34–35.
Article CAS Google Scholar * Strobel A, Issad T, Camoin L, Ozata M, Strosberg AD . A leptin missense mutation associated with hypogonadism and morbid obesity. _Nat Genet_ 1998; 18:
213–215. Article CAS Google Scholar * Farooqi IS, Matarese G, Lord GM, Keogh JM, Lawrence E, Agwu C et al. Beneficial effects of leptin on obesity, T cell hyporesponsiveness, and
neuroendocrine/metabolic dysfunction of human congenital leptin deficiency. _J Clin Invest_ 2002; 110: 1093–1103. Article CAS Google Scholar * Salbe AD, Nicolson M, Ravussin E . Total
energy expenditure and the level of physical activity correlate with plasma leptin concentrations in five-year-old children. _J Clin Invest_ 1997; 99: 592–595. Article CAS Google Scholar
* Wauters M, Considine RV, Chagnon M, Mertens I, Rankinen T, Bouchard C et al. Leptin levels, leptin receptor gene polymorphisms, and energy metabolism in women. _Obes Res_ 2002; 10:
394–400. Article CAS Google Scholar * Rosenbaum M, Murphy EM, Heymsfield SB, Matthews DE, Leibel RL . Low dose leptin administration reverses effects of sustained weight-reduction on
energy expenditure and circulating concentrations of thyroid hormones. _J Clin Endocrinol Metab_ 2002; 87: 2391. Article CAS Google Scholar * Kennedy A, Gettys TW, Watson P, Wallace P,
Ganaway E, Pan Q et al. The metabolic significance of leptin in humans: gender-based differences in relationship to adiposity, insulin sensitivity, and energy expenditure. _J Clin Endocrinol
Metab_ 1997; 82: 1293–1300. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Filozof CM, Murua C, Sanchez MP, Brailovsky C, Perman M, Gonzalez CD et al. Low plasma leptin concentration and low rates of fat
oxidation in weight-stable post-obese subjects. _Obes Res_ 2000; 8: 205–210. Article CAS Google Scholar * Niskanen LK, Haffner SM, Karhunen LJ, Turpeinen AK, Miettinen R, Uusitupa MIJ .
Serum leptin in relation to resting energy expenditure and fuel metabolism in obese subjects. _Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord_ 1997; 21: 309–313. Article CAS Google Scholar * Toth MJ,
Sites CK, Poehlman ET . Hormonal and physiological correlates of energy expenditure and substrate oxidation in middle-aged, premenopausal women. _J Clin Endocrinol Metab_ 1999; 84:
2771–2775. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Verdich C, Toubro S, Buemann B, Holst JJ, Bulow J, Simonsen L et al. Leptin levels are associated with fat oxidation and dietary-induced weight loss
in obesity. _Obes Res_ 2001; 9: 452–461. Article CAS Google Scholar * Snyder EE, Walts B, Perusse L, Chagnon YC, Weisnagel SJ, Rankinen T et al. The human obesity gene map: the 2003
update. _Obes Res_ 2004; 12: 369–439. Article CAS Google Scholar * Lee GH, Proenca R, Montez JM, Carroll KM, Darvishzadeh JG, Lee JI et al. Abnormal splicing of the leptin receptor in
diabetic mice. _Nature_ 1996; 379: 632–635. Article CAS Google Scholar * Tartaglia LA, Dembski M, Weng X, Deng N, Culpepper J, Devos R et al. Identification and expression cloning of a
leptin receptor, OB-R. _Cell_ 1995; 83: 1263–1271. Article CAS Google Scholar * Phillips MS, Liu Q, Hammond HA, Dugan V, Hey PJ, Caskey CJ et al. Leptin receptor missense mutation in the
fatty Zucker rat. _Nat Genet_ 1996; 13: 18–19. Article CAS Google Scholar * Takaya K, Ogawa Y, Isse N, Okazaki T, Satoh N, Masuzaki H et al. Molecular cloning of rat leptin receptor
isoform complementary DNAs – identification of a missense mutation in Zucker fatty (fa/fa) rats. _Biochem Biophys Res Commun_ 1996; 225: 75–83. Article CAS Google Scholar * Takaya K,
Ogawa Y, Hiraoka J, Hosoda K, Yamori Y, Nakao K et al. Nonsense mutation of leptin receptor in the obese spontaneously hypertensive Koletsky rat. _Nat Genet_ 1996; 14: 130–131. Article CAS
Google Scholar * Wu-Peng XS, Chua SC, Okada N, Liu SM, Nicholson M, Leibel RL . Phenotype of the obese Koletsky (f) rat due to Tyr763Stop mutation in the extracellular domain of the
leptin receptor (Lepr): evidence for deficient plasma-to-CSF transport of leptin in both the Zucker and Koletsky obese rat. _Diabetes_ 1997; 46: 513–518. Article CAS Google Scholar *
Stefan N, Vozarova B, Del Parigi A, Ossowski V, Thompson DB, Hanson RL et al. The Gln223Arg polymorphism of the leptin receptor in Pima Indians: influence on energy expenditure, physical
activity and lipid metabolism. _Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord_ 2002; 26: 1629–1632. Article CAS Google Scholar * Norman RA, Tataranni PA, Pratley R, Thompson DB, Hanson RL, Prochazka M et
al. Autosomal genomic scan for loci linked to obesity and energy metabolism in Pima Indians. _Am J Hum Genet_ 1998; 62: 659–668. Article CAS Google Scholar * Bouchard C . Genetic
epidemiology, association, and sib-pair linkage: results from the Québec Family Study. In: Bray GA, Ryan DH (eds). _Molecular and Genetic Aspects of Obesity_, vol. 5, Pennington Center
Nutrition Series. Louisiana State University Press: Baton Rouge, LA, 1996, pp. 470–481. Google Scholar * Deriaz O, Dionne F, Perusse L, Tremblay A, Vohl MC, Cote G et al. DNA variation in
the genes of the Na,K-adenosine triphosphatase and its relation with resting metabolic rate, respiratory quotient, and body fat. _J Clin Invest_ 1994; 93: 838–843. Article CAS Google
Scholar * Siri WE . Body composition from fluid spaces and density, analysis of methods. In: Brozek J, Henschel A (eds). _Techniques for Measuring Body Composition_. National Academy of
Sciences: Washington, DC, 1961, pp. 223–244. Google Scholar * Himes JH, Bochard C . Do the new metropolitan life insurance weight–height tables correctly assess body frame and body fat
relationships? _Am J Public Health_ 1985; 75: 1076–1079. Article CAS Google Scholar * Behnke AR, Wilmore JH . _Evaluation and Regulation of Body Build and Composition_. Prentice-Hall:
Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1974. Google Scholar * Meneely GR, Kaltreider NL . The volume of the lung determined by helium dilution: description of the method and comparison with other
procedures. _J Clin Invest_ 1949; 28: 129–139. Article CAS Google Scholar * Chung WK, Power-Kehoe L, Chua M, Chu F, Aronne L, Huma Z et al. Exonic and intronic sequence variation in the
human leptin receptor gene (LEPR). _Diabetes_ 1997; 46: 1509–1511. Article CAS Google Scholar * Hager J, Clement K . A polymorphism in the 5′ untranslated region of the human ob gene is
associated with low leptin levels. _Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord_ 1998; 22: 200–205. Article CAS Google Scholar * Abecasis GR, Cookson WOC . GOLD – Graphical Overview of Linkage
Disequilibrium. _Bioinformatics_ 2000; 16: 182–183. Article CAS Google Scholar * Excoffier L, Slatkin M . Maximum-likelihood estimation of molecular haplotype frequencies in a diploid
population. _Mol Biol Evol_ 1995; 12: 921–927. CAS Google Scholar * White M . A heteroskedasticity-consistent covariance matrix estimator and a direct test for heteroskedasticity.
_Econometrica_ 1980; 48: 817–838. Article Google Scholar * Huber PJ . The behavior of maximum likelihood estimates under nonstandard conditions. _Proceedings of the Fifth Berkeley
Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability_, vol. 1. University of California Press: Berkeley, CA 1967, pp. 221–223. * Abecasis GR, Cherny SS, Cookson WO, Cardon LR . Merlin –
rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. _Nat Genet_ 2002; 30: 97–101. Article CAS Google Scholar * Karvonen MK, Pesonen U, Heinonen P, Laakso M, Rissanen A,
Naukkarinen H et al. Identification of new sequence variants in the leptin gene. _J Clin Endocrinol Metab_ 1998; 83: 3239–3242. Article CAS Google Scholar * Thompson DB, Ravussin E,
Bennett PH, Bogardus C . Structure and sequence variation at the human leptin receptor gene in lean and obese Pima Indians. _Hum Mol Genet_ 1997; 6: 675–679. Article CAS Google Scholar *
Lemonnier D, Suquet JP, Aubert R, De Gasquet P, Pequignot E . Metabolism of the mouse made obese by a high-fat diet. _Diabete Metab_ 1975; 1: 77–85. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Chagnon
YC, Wilmore JH, Borecki I, Gagnon J, Perusse L, Chagnon M et al. Associations between the leptin receptor gene and adiposity in middle-aged Caucasian males from the HERITAGE Family Study. _J
Clin Endocrinol Metab_ 2000; 85: 29–34. CAS Google Scholar * Yiannakouris N, Yannakoulia M, Melistas L, Chan JL, Klimis-Zacas D, Mantzoros CS . The Q223R polymorphism of the leptin
receptor gene is significantly associated with obesity and predicts a small percentage of body weight and body composition variability. _J Clin Endocrinol Metab_ 2001; 86: 4434–4439. Article
CAS Google Scholar * Mattevi VS, Zembrzuski VM, Hutz MH . Association analysis of genes involved in the leptin-signaling pathway with obesity in Brazil. _Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord_
2002; 26: 1179–1185. Article CAS Google Scholar * Quinton ND, Lee AJ, Ross RJM, Eastell R, Blakemore AIF . A single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the leptin receptor is associated with
BMI, fat mass and leptin levels in postmenopausal Caucasian women. _Hum Genet_ 2001; 108: 233–236. Article CAS Google Scholar * Wauters M, Mertens I, Chagnon M, Rankinen T, Considine RV,
Chagnon YC et al. Polymorphisms in the leptin receptor gene, body composition and fat distribution in overweight and obese women. _Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord_ 2001; 25: 714–720. Article
CAS Google Scholar * Lucantoni R, Ponti E, Berselli ME, Savia G, Minocci A, Calo G et al. The A19G polymorphism in the 5′ untranslated region of the human obese gene does not affect
leptin levels in severely obese patients. _J Clin Endocrinol Metab_ 2000; 85: 3589–3591. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Jiang Y, Wilk JB, Borecki I, Williamson S, DeStefano AL, Xu G et al.
Common variants in the 5′ region of the leptin gene are associated with body mass index in men from the national heart, lung, and blood institute family heart study. _Am J Hum Genet_ 2004;
75: 220–230. Article CAS Google Scholar * Snitker S, Tataranni PA, Ravussin E . Respiratory quotient is inversely associated with muscle sympathetic nerve activity. _J Clin Endocrinol
Metab_ 1998; 83: 3977–3979. Article CAS Google Scholar * Forbes S, Bui S, Robinson BR, Hochgeschwender U, Brennan MB . Integrated control of appetite and fat metabolism by the
leptin–proopiomelanocortin pathway. _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 2001; 98: 4233–4237. Article CAS Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The Québec Family Study was supported by
multiple grants from the Medical Research Council of Canada and the Canadian Institutes for Health Research (PG-11811, MT-13960 and GR-15187). R Loos is supported by a postdoctoral
fellowship from the American Heart Association; Southeast affiliate (no. 0325355B). C Bouchard is partially supported by the George A Bray Chair in Nutrition. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND
AFFILIATIONS * Human Genomics Laboratory, Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Baton Rouge, LA, USA R J F Loos, T Rankinen & C Bouchard * Department of Psychiatry, Genetic Psychiatry,
Laval University Robert-Giffard Research Center, Beauport, Québec, Canada Y Chagnon * Department of Social and Preventive Medicine, Physical Activity Sciences Laboratory, Laval University,
Ste-Foy, Québec, Canada A Tremblay & L Pérusse Authors * R J F Loos View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * T Rankinen View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Y Chagnon View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * A Tremblay View
author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * L Pérusse View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * C Bouchard
View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to C Bouchard. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT
THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Loos, R., Rankinen, T., Chagnon, Y. _et al._ Polymorphisms in the leptin and leptin receptor genes in relation to resting metabolic rate and respiratory
quotient in the Québec Family Study. _Int J Obes_ 30, 183–190 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803127 Download citation * Received: 15 December 2004 * Revised: 22 August 2005 *
Accepted: 29 August 2005 * Published: 11 October 2005 * Issue Date: 01 January 2006 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803127 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with
will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt
content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS * leptin * leptin receptor * resting metabolic rate * respiratory quotient