- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: To characterize and compare three obesity-prone inbred strains, AKR/J, DBA/2J and C57BL/6J, to three control strains, C3H/HeJ, BALB/cByJ and C57L/J, selected based on
their normal eating patterns and moderate weight gain on high-calorie diets. METHODS AND PROCEDURES: These six strains were examined at 5 weeks of age while still of normal body weight, and
they were maintained for 1 day or 3 weeks on different feeding paradigms with macronutrient diets. Measurements were taken of macronutrient intake, body weight and body fat accrual,
circulating hormones and metabolites, and the hypothalamic peptide, galanin. RESULTS: The three control strains each selected a balanced diet with 50% carbohydrate and 15–25% fat when given
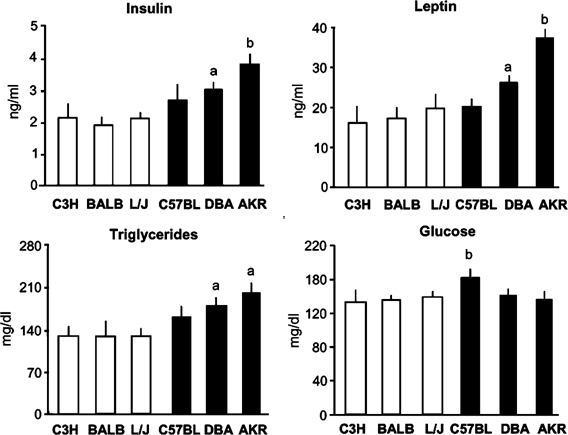
a choice of macronutrients, and they had similar, normal range of scores for the measures of body weight, adiposity, the hormones, insulin and leptin, and the metabolites, glucose and
triglycerides. When compared to this control baseline, the obesity-prone strains with similar total caloric intake to controls selected a diet with significantly more fat (30–40%) and less
carbohydrate (<40%). They also had greater adiposity, with the largest differences detected for the AKR/J and DBA/2J strains. These two obesity-prone strains compared to control strains
had elevated levels of insulin and leptin. They also had higher triglyceride levels and increased expression and levels of galanin in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. A very
different pattern was detected in the obesity-prone C57BL/6J strain, which exhibited a stronger preference for protein as well as fat, normal levels of insulin, leptin and triglycerides,
hyperglycemia relative to all other strains, and a small increase in galanin. CONCLUSION: These comparisons to control strains revealed a distinct phenotype in the two obesity-prone strains,
AKR/J and DBA/2J, which is very similar to that described in obesity-prone, outbred rats. They also identified a clearly different phenotype in the obesity-prone C57BL/6J strain. Access
through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices
may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support
SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS THE METABOLIC CONSEQUENCES OF ‘YO-YO’ DIETING ARE MARKEDLY INFLUENCED BY GENETIC DIVERSITY Article Open access 03 July 2024 C57BL/6J SUBSTRAIN
DIFFERENCES IN RESPONSE TO HIGH-FAT DIET INTERVENTION Article Open access 20 August 2020 HOUSING-TEMPERATURE REVEALS ENERGY INTAKE COUNTER-BALANCES ENERGY EXPENDITURE IN NORMAL-WEIGHT, BUT
NOT DIET-INDUCED OBESE, MALE MICE Article Open access 10 September 2022 REFERENCES * West DB, Boozer CN, Moody DL, Atkinson RL . Dietary obesity in nine inbred mouse strains. _Am J Physiol_
1992; 262: R1025–R1032. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * West DB, Waguespack J, McCollister S . Dietary obesity in the mouse: interaction of strain with diet composition. _Am J Physiol_ 1995;
268: R658–R665. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Smith BK, Andrews PK, West DB . Macronutrient diet selection in thirteen mouse strains. _Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol_ 2000; 278:
R797–R805. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Surwit RS, Feinglos MN, Rodin J, Sutherland A, Petro AE, Opara EC et al. Differential effects of fat and sucrose on the development of
obesity and diabetes in C57BL/6J and A/J mice. _Metabolism_ 1995; 44: 645–651. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Watson PM, Commins SP, Beiler RJ, Hatcher HC, Gettys TW . Differential
regulation of leptin expression and function in A/J vs C57BL/6J mice during diet-induced obesity. _Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab_ 2000; 279: E356–E365. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
* Tortoriello DV, McMinn J, Chua SC . Dietary-induced obesity and hypothalamic infertility in female DBA/2J mice. _Endocrinology_ 2004; 145: 1238–1247. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
* Wortley KE, Chang GQ, Davydova Z, Leibowitz SF . Peptides that regulate food intake: orexin gene expression is increased during states of hypertriglyceridemia. _Am J Physiol Regul Integr
Comp Physiol_ 2003; 284: R1454–R1465. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Smith BK, Andrews PK, York DA, West DB . Divergence in proportional fat intake in AKR/J and SWR/J mice endures
across diet paradigms. _Am J Physiol_ 1999; 3: R776–R785. Google Scholar * Smith BK, West DB, York DA . Carbohydrate versus fat intake: differing patterns of macronutrient selection in two
inbred mouse strains. _Am J Physiol_ 1997; 272: R357–R362. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Eberhart GP, West DB, Boozer CN, Atkinson RL . Insulin sensitivity of adipocytes from
inbred mouse strains resistant or sensitive to diet-induced obesity. _Am J Physiol_ 1994; 266: R1423–R1428. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Surwit RS, Petro AE, Parekh P, Collins S . Low
plasma leptin in response to dietary fat in diabetes- and obesity-prone mice. _Diabetes_ 1997; 46: 1516–1520. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lee SK, Opara EC, Surwit RS, Feinglos
MN, Akwari OE . Defective glucose-stimulated insulin release from perifused islets of C57BL/6J mice. _Pancreas_ 1995; 11: 206–211. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Parekh PI, Petro
AE, Tiller JM, Feinglos MN, Surwit RS . Reversal of diet-induced obesity and diabetes in C57BL/6J mice. _Metabolism: Clin Exp_ 1998; 47: 1089–1096. Article CAS Google Scholar * Collins S,
Daniel KW, Petro AE, Surwit RS . Strain-specific response to beta 3-adrenergic receptor agonist treatment of diet-induced obesity in mice. _Endocrinology_ 1997; 138: 405–413. Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Rossmeisl M, Rim JS, Koza RA, Kozak LP . Variation in type 2 diabetes – related traits in mouse strains susceptible to diet-induced obesity. _Diabetes_ 2003; 52:
1958–1966. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kaku K, Province M, Permutt MA . Genetic analysis of obesity-induced diabetes associated with a limited capacity to synthesize insulin in
C57BL/KS mice: evidence for polygenic control. _Diabetologia_ 1989; 32: 636–643. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Leibowitz SF, Akabayashi A, Wang J . Obesity on a high-fat diet: role of
hypothalamic galanin in neurons of the anterior paraventricular nucleus projecting to the median eminence. _J Neurosci_ 1998; 18: 2709–2719. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google
Scholar * Leibowitz SF, Wortley KE . Hypothalamic control of energy balance: different peptides, different functions. _Peptides_ 2004; 25: 473–504. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ . _The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates_. Academic Press: San Diego, CA, 2001. Google Scholar * Chang GQ, Karatayev O, Davydova Z, Leibowitz SF . Circulating
triglycerides impact on orexigenic peptides and neuronal activity in hypothalamus. _Endocrinology_ 2004; 145: 3904–3912. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Surwit RS, Kuhn CM, Cochrane
C, McCubbin JA, Feinglos MN . Diet-induced type II diabetes in C57BL/6J mice. _Diabetes_ 1988; 37: 1163–1167. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Giacco R, Clemente G, Busiello L,
Lasorella G, Rivieccio AM, Rivellese AA et al. Insulin sensitivity is increased and fat oxidation after a high-fat meal is reduced in normal-weight healthy men with strong familial
predisposition to overweight. _Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord_ 2003; 27: 790–796. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Levin BE . Arcuate NPY neurons and energy homeostasis in diet-induced
obese and resistant rats. _Am J Physiol_ 1999; 276: R382–R387. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Raben A, Astrup A . Leptin is influenced both by predisposition to obesity and diet
composition. _Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord_ 2000; 24: 450–459. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Ahren B, Scheurink AJ . Marked hyperleptinemia after high-fat diet associated with
severe glucose intolerance in mice. _Eur J Endocrinol_ 1998; 139: 461–467. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Huang XF, Han M, South T, Storlien L . Altered levels of POMC, AgRP and
MC4-R mRNA expression in the hypothalamus and other parts of the limbic system of mice prone or resistant to chronic high-energy diet-induced obesity. _Brain Res_ 2003; 992: 9–19. Article
CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Wang H, Storlien LH, Huang XF . Effects of dietary fat types on body fatness, leptin, and ARC leptin receptor, NPY, and AgRP mRNA expression. _Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab_ 2002; 282: E1352–E1359. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lin S, Storlien LH, Huang X . Leptin receptor, NPY, POMC mRNA expression in the diet-induced obese mouse
brain. _Brain Res_ 2000; 875: 89–95. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Ziotopoulou M, Mantzoros CS, Hileman SM, Flier JS . Differential expression of hypothalamic neuropeptides in the
early phase of diet-induced obesity in mice. _Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab_ 2000; 279: E838–E845. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Bergen HT, Mizuno T, Taylor J, Mobbs CV .
Resistance to diet-induced obesity is associated with increased proopiomelanocortin mRNA and decreased neuropeptide Y mRNA in the hypothalamus. _Brain Res_ 1999; 851: 198–203. Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Takahashi N, Patel HR, Qi Y, Dushay J, Ahima RS . Divergent effects of leptin in mice susceptible or resistant to obesity. _Horm Metab Res_ 2002; 34: 691–697.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Leibowitz SF, Dourmashkin JT, Chang GQ, Hill JO, Gayles EC, Fried SK et al. Acute high-fat diet paradigms link galanin to triglycerides and their
transport and metabolism in muscle. _Brain Res_ 2004; 1008: 168–178. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Dube MG, Kalra SP, Kalra PS . Hypothalamic galanin is up-regulated during
hyperphagia and increased body weight gain induced by disruption of signaling in the ventromedial nucleus. _Peptides_ 2000; 21: 519–526. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Mercer JG,
Lawrence CB, Atkinson T . Regulation of galanin gene expression in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus of the obese Zucker rat by manipulation of dietary macronutrients. _Brain Res Mol
Brain Res_ 1996; 43: 202–208. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Pedrazzi P, Cattaneo L, Valeriani L, Boschi S, Cocchi D, Zoli M . Hypothalamic neuropeptide Y and galanin in overweight
rats fed a cafeteria diet. _Peptides_ 1998; 19: 157–165. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Beck B, Burlet A, Nicolas JP, Burlet C . Galanin in the hypothalamus of fed and fasted lean
and obese Zucker rats. _Brain Res_ 1993; 623: 124–130. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kyrkouli SE, Stanley BG, Leibowitz SF . Galanin: stimulation of feeding induced by medial
hypothalamic injection of this novel peptide. _Eur J Pharmacol_ 1986; 122: 159–160. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Koegler FH, York DA, Bray GA . The effects on feeding of galanin
and M40 when injected into the nucleus of the solitary tract, the lateral parabrachial nucleus, and the third ventricle. _Physiol Behav_ 1999; 67: 259–267. Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Lin L, York DA, Bray GA . Comparison of Osborne-Mendel and S5B/PL strains of rat: central effects of galanin, NPY, beta-casomorphin and CRH on intake of high-fat and low-fat
diets. _Obes Res_ 1996; 4: 117–124. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hohmann JG, Krasnow SM, Teklemichael DN, Clifton DK, Wynick D, Steiner RA . Neuroendocrine profiles in
galanin-overexpressing and knockout mice. _Neuroendocrinology_ 2003; 77: 354–366. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Yun R, Dourmashkin JT, Hill JO, Gayles EC, Fried SK, Leibowitz SF .
PVN galanin increases fat storage and promotes obesity by causing muscle to utilize carbohydrate more than fat. _Peptides_ 2005, in press. * Nagase H, Nakajima A, Sekihara H, York DA, Bray
GA . Regulation of feeding behavior, gastric emptying, and sympathetic nerve activity to interscapular brown adipose tissue by galanin and enterostatin: the involvement of vagal-central
nervous system interactions. _J Gastroenterol_ 2002; 37: 118–127. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Menendez JA, Atrens DM, Leibowitz SF . Metabolic effects of galanin injections into
the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. _Peptides_ 1992; 13: 323–327. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hoffer LJ, Taveroff A, Hamadeh MJ . Dietary protein restriction alters
glucose but not protein metabolism in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. _Metabolism_ 1998; 47: 1145–1151. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Usami M, Seino Y, Seino S, Takemura
J, Nakahara H, Ikeda M et al. Effects of high protein diet on insulin and glucagon secretion in normal rats. _J Nutr_ 1982; 112: 681–685. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Farnsworth
E, Luscombe ND, Noakes M, Wittert G, Argyiou E, Clifton PM . Effect of a high-protein, energy-restricted diet on body composition, glycemic control, and lipid concentrations in overweight
and obese hyperinsulinemic men and women. _Am J Clin Nutr_ 2003; 78: 31–39. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We are grateful to Ms Olga Karatayev,
Kate Sepiashvili and Patricia Pamy for their help in the preparation of this manuscript. This research was supported by a USPHS grant, MH43422. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS *
The Rockefeller University, New York, NY, USA J Alexander, G Q Chang, J T Dourmashkin & S F Leibowitz Authors * J Alexander View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * G Q Chang View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * J T Dourmashkin View author publications You can also search for
this author inPubMed Google Scholar * S F Leibowitz View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to S F Leibowitz.
RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Alexander, J., Chang, G., Dourmashkin, J. _et al._ Distinct phenotypes of obesity-prone AKR/J, DBA2J and
C57BL/6J mice compared to control strains. _Int J Obes_ 30, 50–59 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803110 Download citation * Received: 30 November 2004 * Revised: 29 June 2005 *
Accepted: 31 July 2005 * Published: 11 October 2005 * Issue Date: 01 January 2006 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803110 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with
will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt
content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS * inbred mice * obesity-prone * galanin * fat * triglycerides







