
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:
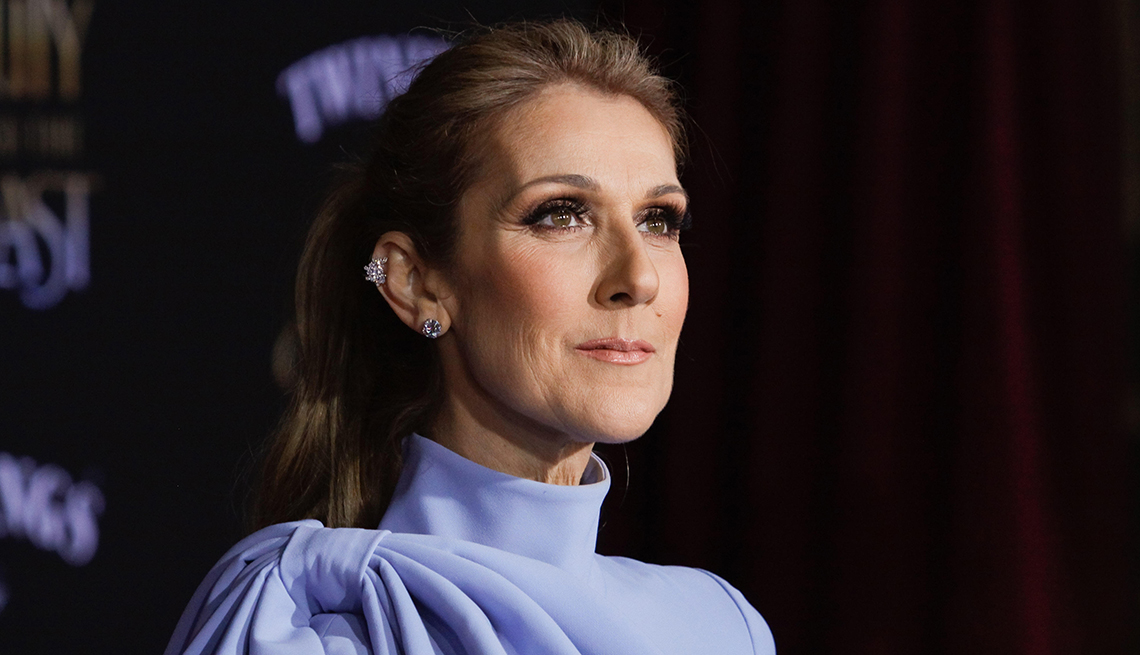
It’s been about a year and a half since famed singer Celine Dion revealed that she had been diagnosed with a rare neurological disorder known as stiff-person syndrome. Now the Grammy
Award–winning artist is sharing more about her struggles with the disease and the effect it’s had on her life and her music. “It’s been very difficult, very painful,” Dion, 56, told NBC’s
Hoda Kotb in a June 11 interview ahead of the release of her forthcoming documentary, _I Am: Celine Dion_. Still, Dion says she has plans to one day return to the stage — “even if I have to
crawl, even if I have to talk with my hands,” she told Kotb. WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF STIFF-PERSON SYNDROME? In December 2022, Dion opened up about her diagnosis in an emotional video
posted on Instagram, where the singer explained that she’d been battling health issues for a while, including severe and persistent muscle spasms that interfered with her performing.
“Unfortunately, the spasms affect every aspect of my daily life, sometimes causing difficulties when I walk and not allowing me to use my vocal cords to sing the way I’m used to,” Dion said
in the video. Muscle spasms are a common symptom of stiff-person syndrome, which also has features of an autoimmune disease and is estimated to affect fewer than 5,000 people in the U.S.,
according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH). “The body, for some reason, starts to fight itself in an autoimmune type of way, where it will attack the nerves in the muscles, causing
[them] to be more sensitive and overactive and stiff,” explains Desimir Mijatovic, M.D., a pain specialist with the Cleveland Clinic. The trunk and the abdominal muscles are typically the
first to stiffen, according to the Cleveland Clinic. The muscles in the limbs, even the face, can also be affected. Depending on the areas of the body that are impacted, “it can become
difficult to move around,” Mijatovic says, “so this can cause a lot of problems for people in their daily lives.” Stimuli like noise, stress and touch can trigger the stiff muscles to spasm.
(These spasms can occur for no reason, too.) Some people experience spasms so severe that the force generated can fracture a bone or cause them to fall, the NIH says.






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(749x0:751x2)/oscars-kerry-condon-022123-1-545faf1615f2481c8afb27a553cf44d9.jpg)
